When it comes to oxoacids, these are the compounds that contain oxygen, hydrogen and any other element. The inclusion of sulphur in the oxygen and hydrogen combination yields the oxoacids of sulphur that are known with the names of their salts. There are multiple such compounds with different chemical structures. Let us go deep in detail about these oxoacids.
About Oxoacids of Sulphur
Oxoacids or oxyacids or ternary acids are the acids that contain oxygen. So, any acid having oxygen, hydrogen, and any other element are termed the oxoacids of the specific element. When it comes to sulphur oxoacids, it contains oxygen, hydrogen, and sulphur. Out of all the multiple oxoacids of the popular sulphur element, some of them are widely used like sulphuric acid.
The electronegativity and number of oxygen atoms of the central atom of the oxoacids determine its acidity. Some of the common types of organic acids include carboxylic acids and sulphur oxoacids. Thus, the main requirements of all oxoacids of sulphur include:
- Presence of oxygen atom
- Presence of at least one hydrogen atom bonded to oxygen
- Presence of at least one other element
- Should be able to form ions by the loss of one or more protons in an aqueous solution
Let us now have a detailed look at the multiple oxoacids of sulphur and its associated structure, and other properties.
Structure of multiple oxoacids of sulphur
The details of oxoacids of sulphur, their structure and properties are:
- Sulphuric acid
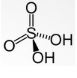
Its chemical formula is H2SO4 and has a +6 oxidation number. The related anions are sulphates and bisulphates. It’s S-O bond length is 157.4 pm and O-H bond length is 97 pm. It has a tetrahedral geometry as the bond angle of O=S=O is greater than that of HO-S-OH. It is a commonly used chemical in multiple commercial and industrial applications.
- Polysulphuric acid
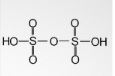
Its chemical formula is H2SO4. nSO3 and has a +6 oxidation number. The related anions are disulphates. It is also called oleum and is prepared by reacting sulphuric acid with excess sulphur trioxide.
- Peroxymonosulphuric acid
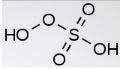
Its chemical formula is H2SO5 and has a +6 oxidation number. The related anions are peroxomonosulfate. The sulphur central atom has tetrahedral geometry and is indicated by HO-O-S(O)2-OH.
- Peroxydisulfuric acid
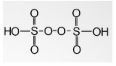
Its chemical formula is H2S2O8 and has a +6 oxidation number. The related anions are peroxydisulfates. It is written as HO3SOOSO3H and is called Marshall’s acid due to its inventor Professor Hugh Marshall. These are widely used as oxidizing agents in multiple industries.
- Dithionic acid
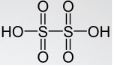
Its chemical formula is H2S2O6 and has a +5 oxidation number. The related anions are dithionate. Its shape is like ethane but two SO3 groups adopt eclipsed conformation. S-S bond length is 2.15 A and that of S-O is 1.43 A.
- Thiosulfuric acid
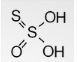
Its chemical formula is H2S2O3 and has a +4 oxidation number for the central number and 0 for the terminal sulphur. The related anions are thiosulphates.
- Disulfurous acid
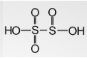
Its chemical formula is H2S2O5 and has a +5 oxidation number for the sulphur atom bonded to 3 oxygen atoms and a +3 for the other sulphur atoms. The related anions are metabisulphites.
- Sulphurous acid
Its chemical formula is H2SO3 and has a +4 oxidation number. The related anions are bisulfites, sulphites, etc. Its molecule is found in a gaseous phase alone. In this, one atom of sulphur bonds with two hydroxyl groups and one oxygen atom forms a pie bond with the same sulphur atom. It is widely used as reducing agents and disinfectants.
- Dithionous acid
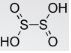
Its chemical formula is H2S2O4 and has a +3 oxidation number. The related anions are dithionites. Its stable structure is HOS(=O)-S(=O)OH and is due to the existence of intermolecular hydrogen bonds.
- Sulfoxylic acid
Its chemical formula is H2SO2 and has a +2 oxidation number. The related anions are sulfoxylates. It has two hydroxy groups attached to the sulphur atom. It is also detected in the gas phase strictly.
- Polythionic acid
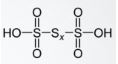
Its chemical formula is H2SXO6 and has 0 oxidation number for the bridging sulphur atom and a +5 for the terminal central sulphur atoms. The related anions are polythionates. It has a straight chain of sulphur atoms and these are found in the crater lakes.
- Thiosulphurous acid
Its chemical formula is H2S2O2 and has a -1 oxidation number for the exterior sulphur atom and a +3 for the central sulphur atom. The related anions are thiosulphites. It is a hypothetical compound with possible isomers are dihydroxydisulphane, a linear chain, and thiothionyl hydroxide, which is a tautomer.
- Dihydroxydisulphane
Its chemical formula is H2S2O2 and has a +1 oxidation number. All atoms are arranged in a chain and are one of the isomers of thiosulphurous acid. The other isomers include HS(=O)2SH and HOS(=O)SH, HOS(=S)OH, etc.
Conclusion:
Hope you’re all clear about the structure of oxoacids of sulphur. The different types of oxoacids make it easy to understand their structure and associated properties. It is easy to further know multiple properties like electronegativity, and acidity of the oxoacids after going through the structure.
We came to know about different types of bonds and their polarity of sulphur oxoacids. Hence, all major properties including physical and chemical properties can be justified from the structure details only. Unacademy brings the best details about oxoacids of sulphur, prepared by experienced chemistry tutors, from the point of view of IIT-JEE aspirants.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





