The SN1 reaction is a nucleophilic substitution process in which the rate-determining step occurs in a single molecular step. It is a form of organic substitution reaction in the classical sense. The abbreviation SN1 refers to substitution nucleophilic unimolecular. The rate equation (which indicates that the SN1 reaction is reliant on the electrophile but not on the nucleophile) holds true in instances where the amount of the nucleophile is significantly more than the amount of the carbocation intermediate in question.
What is the SN1 Reaction and how does it work?
The production of a carbocation intermediate is required for this reaction to occur. In most cases, it occurs in the reactions of tertiary or secondary alkyl halides with secondary or tertiary alcohols when the circumstances are extremely acidic or extremely basic, respectively. In inorganic chemistry, the SN1 reaction is referred to as the dissociative mechanism because of its dissociation nature. A few instances of nucleophilic substitution reactions of the SN1 type are shown in the following section.
SN1 Reaction is a chemical reaction that occurs in the body.
The Influence of Solvent
A solvent that facilitates the development of the carbocation intermediate will speed up the rate-determining step of the SN1 reaction, which is the rate-determining step of the reaction.
Solvents that are both polar and protic in nature are ideal for this type of reaction.
When it comes to stabilizing ionic intermediates, the polar nature of the solvent is beneficial, but the protic nature of the solvent is beneficial when it comes to solvating the departing group.
Water and alcohols are examples of solvents that have been utilised in SN1 reactions. These solvents also have the ability to act as nucleophiles.
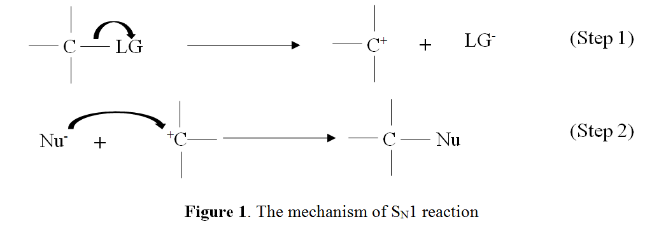
Mechanism of the SN1 Reaction
The following steps can be used to understand the mechanism of the SN1 reaction, which is illustrated by the hydrolysis of tertiary butyl bromide as an example.
Step-1
- The carbon-bromine bond is a polar covalent bond in the first step. When this connection is severed, the leaving group can be removed from the molecule (bromide ion).
- It is made when the bromide ion departs from the tertiary butyl bromide that a carbocation intermediate is produced.
- As previously stated, this is the phase in the SN1 mechanism that determines the rate of the process.
- Remember that the breakdown of the carbon-bromine bond is an exothermic reaction.
Step-2
- A step-by-step breakdown of the SN1 reaction mechanism.
- As part of the SN1 reaction mechanism’s second step, the nucleophile attacks the carbocation and causes it to dissociate.
- Because water is used as a solvent, the formation of an oxonium ion intermediate occurs.
- The neutral nature of the solvent necessitates the addition of a third step in which deprotonation takes place.
Step-3
- In the preceding step, the positive charge on the carbocation was transferred to the oxygen atom of the molecule.
- The water solvent now works as a base, deprotonating the oxonium ion, resulting in the formation of the necessary alcohol as well as a hydronium ion, which is the product.
- The second and third steps of this reaction are quick.
Conclusion
The sp² hybridized carbon intermediate created in step 1 of the SN1 reaction mechanism.. Its molecular geometry is trigonal planar, which allows for two alternative locations of nucleophilic attack on the molecule, one on the left and one on the right.SN1 reactions are significant because they define a mechanism of organic reactivity, or chemical reactivity, as far as we know. In terms of the rate-determining step, they describe a bond-breaking process, as opposed to SN2 reactions, which are bond-making processes.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




