The Electromagnetic spectrum is the range of spectrums of electromagnetic waves. So, we have to review electromagnetic waves. Electromagnetic waves are produced when an oscillating share is taken. Both electric and magnetic fields are taken into consideration while studying electromagnetic waves.
The electric field is produced by stationary charges. The electric field is directed along the direction of the force exerted on a positive test charge. Positive charges accelerate in the electric field direction, and negative charges accelerate in the direction opposite to the direction of the electric field.
The Magnetic field is produced by moving charged particles. Because of moving
charges, a force is exerted on the other moving charges. The force on these charges is always perpendicular to the velocity and magnetic field direction.
Electromagnetic waves are produced when an oscillating charge is taken. This oscillating charge produces an oscillating electric field, which, in turn, produces an oscillating magnetic field. As both electric field and magnetic field are perpendiculars, they form an electromagnetic wave travelling perpendicular to both electric and magnetic fields.
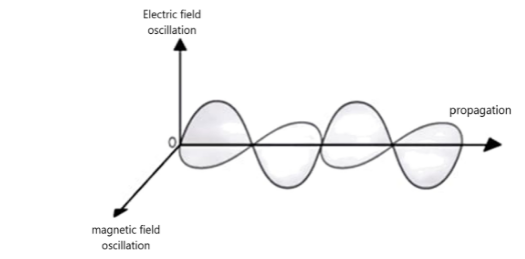
Graphical representation of the electromagnetic wave
A plane electromagnetic wave propagates along the z-direction. The electric field Ex is along the x-axis and varies sinusoidally with z at a given time. The magnetic field By is along the y-axis and again varies sinusoidally with z. The electric and magnetic fields Ex and By are perpendicular to each other, and the direction z of propagation.
James Clerk Maxwell predicted the existence of electromagnetic radiation, while Heinrich Hertz tested a successful experiment to prove the existence of electromagnetic waves conclusively.
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The distribution of the electromagnetic waves according to the wavelengths of frequency into distinct groups having widely differing properties is called the electromagnetic spectrum.
The main parts of the electromagnetic waves are
- Radio waves
- Microwaves
- Infrared waves
- Visible rays
- Ultraviolet waves
- X-rays
- Gamma rays
The various regions of the electromagnetic spectrum do not have any sharp boundaries. They collide with each other in experimental results. So, the classification is roughly how the waves are detected or produced.
Electromagnetic Spectrum
We briefly describe these different types of electromagnetic waves with their significance.
Radio waves
Radio waves have the longest wavelength and lowest frequency compared to all EM waves, discovered by Marconi in 1895. It ranges within the frequency range of 500 kHz to 1000 MHz. The wavelength lies in the range of 1 mm to several hundred meters.
After discovering radio waves, they were mostly used for radio broadcasting. Radio waves are also used in the communication industry for cellular links as they are efficient in interpreting through rigid material.
As radio waves can travel large distances and penetrate rigid materials, this property is utilised for communication with the help of communication satellites. The radio wave containing information is transmitted by sending waves to the radio wave Detectors on satellites which receive and transmit signals to the station.
Microwaves
Microwaves are produced by oscillating currents in special vacuum tubes like Klystrons, Magnetrons, and Gun diodes. Microwaves are electromagnetic waves having wavelength next smaller to radio waves. Their frequency lies between 109Hz to 1012Hz. Due to their shorter wavelengths, they can travel like a beam in a signal.
They have properties of reflection, refraction, diffraction, and polarisation. The primary use of the microwave is in the field of radar. If you open any website to see a meteorological forecast of the weather, you should be thankful for microwaves.
In the field of molecular physics, microwaves are commonly used for the analysis of fine details of molecular and atomic structures. Also, there are many areas in Biomedical remote sensing where microwave radiation is used.
Infrared waves
The infrared waves are sometimes referred to as heat waves or thermal radiations, producing a heating effect. These radiations lie close to the low-temperature or long-wavelength of the visible spectrum. Hot bodies and molecules produce them. It ranges within the frequency range of 1011Hz to 5 X 1014Hz. William Herschel discovered infrared waves in 1800.
The main significance of Infrared waves is to maintain the average temperature of the earth’s greenhouse gases. These greenhouse gases capture waves in the atmosphere to raise their temperature and parallelly the atmosphere.
Most remote controls operate by infrared pulses. With electronic devices like TV remotes, DVD players, projectors, etc. Infrared is often used to send signals through fibre optic cables to transmit audio to sound systems and high-speed internet connections.
Visible rays
It’s part of the spectrum that is detected by human eyes. Its wavelength ranges from about 700 nm to 400 nm. Our eyes are sensitive to this range of wavelengths. Different animals are sensitive to different ranges of wavelengths. For example, snakes can detect infrared waves.
Detected by stimulating nerve endings of the human retina. Can cause a chemical reaction.
Ultraviolet rays
These waves can be detected just beyond the violet end of the solar spectrum. Wavelengths range from about 400 nm (4×10-7 m) – to 0.6 nm (6×10-10 m). The source of the ultraviolet waves is High voltage gas discharge tubes, arcs of iron and mercury and the sun.
Ultraviolet waves can cause many chemical reactions. For example, the tanning of the human skin. Ionized atoms in the atmosphere, resulting in the ionosphere.
X-rays
X-rays were used in the photoelectric experiments to bombard the electrons, which were the historic success to determine the particle nature of the electrons. Beyond the UV region of the electromagnetic spectrum lies the X-ray region. It covers wavelengths from about 10-8 m (10 nm) to 10-13 (10-4 nm).
Because of the property of reflection and diffraction of X-rays by crystals, they are used in the study of crystals structure. X-rays are also used in radiotherapy to cure untraceable skin diseases and malignant growths.
Gamma rays
Discovered by Henry Becquerel in 1896, gamma rays are electromagnetic radiations of the highest frequency range and lowest wavelength range. Radioactive nuclei and nuclear reactions are sources of gamma rays. The wavelength ranges from 10-14 m to 10 -10 m and frequency ranges from 1018Hz to 1022Hz. These are the most penetrating electromagnetic waves.
In the field of nuclear reaction, gamma rays are used to initiate some nuclear reactions. To preserve foodstuff for a long time, gamma rays are used because gamma rays can kill microorganisms.
Conclusion
Electromagnetic Waves, which is commonly known as EM Waves, consists of 2 perpendicular sinusoidal Electric and magnetic field vectors which are also perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave. The orderly distribution of the electromagnetic waves by their wavelength or frequency into distinct groups having widely differing properties is called the electromagnetic spectrum. The various regions of the electromagnetic spectrums do not have sharply defined boundaries, and they overlap.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





