The Schiff test is a chemical method for determining whether or not an analyte contains aldehydes. This is accomplished by mixing a little amount of Schiff reagent with the analyte (which is the product formed in certain dye formulation reactions such as the reaction between sodium bisulfite and fuchsin). Schiff’s reagent, Schiff test, Schiff reagent formula, Schiff reagent test, Schiff reagent preparation, Rosaline structure, and Schiff’s test for aldehydes are all covered in this article.
About Schiff’s Test
The Schiff test is a rather generic chemical test for the identification of numerous organic aldehydes that have also found utility in the staining of biological tissues. It was invented by Hugo Schiff in early organic chemistry. The Schiff reagent is the reaction product of a dye formulation like fuchsin and sodium bisulfite; dye alternatives like pararosaniline (which lacks an aromatic methyl group) and new fuchsin (which is uniformly mono-methylated ortho to the dye’s amine functionalities) do not have comparable detection chemistry.
When the unknown material is given to the decolourized Schiff reagent as a qualitative test for aldehydes, a characteristic magenta colour develops when aldehyde is present. Various biological tissue staining procedures, such as Feulgen stain and periodic acid-Schiff stain, use Schiff-type chemicals. The termini of saccharides in human skin also contain aldehyde functional groups, hence it is discoloured.
Composition of Schiff’s Test
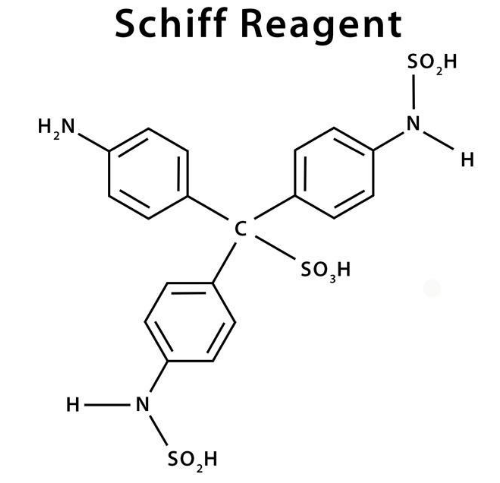
The chemical formula of the reagent is C19H21N3S2O7.4H2O
The reagent is composed of :
Water (H2O) >98%
- Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) <1%
- Sodium Metabisulfite <1%
- Basic Fuchsin Hydrochloride <1%
The solution is shaken at regular intervals before being decoloured with charcoal. After that, the mixture is filtered. To ensure the production of a totally colourless solution, fresh activated charcoal must be utilized. If the solution is not colourless, it is filtered again.
Preparation of Reagent
The following are the specific steps in the preparation process:
- 5g basic fuchsin, dissolved in 900ml boiling water
- Cool the solution until it reaches a temperature of roughly 50°C
- Slowly pour 100ml of 1M HCl into the diluted fuchsin solution
- Reduce the temperature of the solution to 25°C once more
- 10g K2S2O5 should be added to the cooled solution
- Shake the aforementioned solution for 3 minutes before putting it in a dark area to incubate for 24 hours
- Add 5g fine activated charcoal to the reaction mixture after it has been incubated and rested
- Filter the solution after 3 minutes of shaking
- Refiltration and retreatment are required if a crystal clear solution cannot be obtained
- In a foil-covered vial, keep the prepared solution at 4°C
- If the Schiff reagent is not stored properly, it will precipitate a white crystalline material
- As a result, fresh batches must be prepared every 2-3 weeks to ensure accurate findings
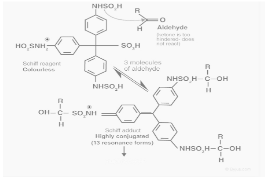
Schiff Test Mechanism
The bisulfite and para-rosaniline react to form a decolourized adduct with a sulfonated central carbon. Now, the aromatic ring’s free and uncharged amine groups combine with the aldehyde group to generate an aldimine. Because the aldimine group is a strong electrophile, it conducts a second reaction with the bisulfite ion. Finally, a bisulfite adduct of purple or magenta colour forms.
Conclusion
The result of several dye formulation processes, such as the reaction between sodium bisulfite and fuchsine, is Schiff reagent. It’s used to see if there’s any aldehyde in an analyte. It can help distinguish between aldehydes and ketones. Sodium bisulfate decolorizes fuschsine or rosaniline hydrochloride, a magenta-coloured dye having the molecular formula C19H21N3S2O7.4H2O .
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





