During the race in finding out the right model that could represent the atomic structure, many scientists came and the second amongst them was a physicist from New-Zealand named Ernest Rutherford.
Rutherford again did his studies with respect to the Thomson model and for that he couldn’t agree much, so he decided to do his own experiments and research to give out the results for how the atomic structure basically exists in nature.
Geiger-Marsden Experiment
Aim: To investigate the structure of atom
Requirements: A microscope, a thin piece of gold foil, 360 degree phosphorescent screen of zinc sulphide, and radioactive Alpha source.
Procedure:
- Place the thin sheet of gold foil in between the 360 degrees.
- Phosphorescent zinc sulphide screen and the Alpha source.
- Point the Alpha particles being created by the radioactive element, at the piece of gold foil.
- Let the Alpha particles be emitted by the Alpha source as probes to hit the 100nm thick gold foil.
- Observe with the help often microscope the different parts of the screen and look for little flashes of light.
- Note down the different angles at which the beam of Alpha particles reflect.
Observation:
You might notice three different types of observations:-
- First of all you will see some of the Alpha particles that surpass the 100nm thick gold sheet as it is and hit the phosphorescent screen.
- This kind of Alpha particles will be in large amounts.
- The second observation will be that some of the Alpha particles reflect from the gold sheet forming acute angles.
- This will be fewer in amount.
- The last but not the least observation will be that few Alpha particles will hit the gold foil and reflect back forming an obtuse angle, and some of them will form about 180 degree as well.
Result:
- From the above monitoring it was concluded that the particles that went across the foil remarked that the Atom was mostly empty.
- But the particles that deflected in small amount which is making an acute angle designated that, they were positive charges in the atom which were not uniformly distributed and same did large reflection point at, that the positive charges were present inside the atom but in a very small amount( in a condensed manner).
- By this he pointed that high Central charge was present into a very minute volume in comparison to the rest of the atom and through this he gave the knowledge about the nucleus, pointing it as a central charge which is tiny in size and heavy.
Structure of Atomic Model proposed by Rutherford
The cation particles and most of the mass of an atom were focused in an extraordinarily minute volume. He referred to this location of the atom as a sort of central charge in a big way.
The Rutherford model proposed that the negatively charged species definitely surround the kind of central charge of an atom, which for the most part is fairly significant. He also claimed that the electrons surrounding the nucleus revolve around it.
Electrons being negatively charged and the centre of the atom being a mass of positive charge, are held together by using a sturdy electrostatic force of attraction, which for the most part is quite important in order to explain how electrons and the central charge acquire a sustainable balance.
Limitations
- Rutherford’s proposal of orbits in which the negatively charged electrons revolve around the central charge, was not found to be in accordance with the theory of Maxwell.
- Also couldn’t define the positioning of electrons in the atom.
Conclusion
A physicist from New-Zealand named Rutherford again experimented on the atomic structure when he was not able to make accordance with Thomson Atomic Model, gave his own Model was proved to be the base for research on the structure of model but it faced some limitations that were late overcome by different scientists like the stability and positioning of electrons in the respective atom.
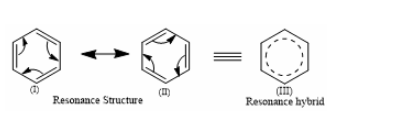
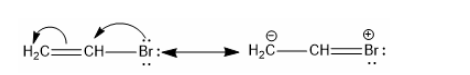
Three C-C single bonds with a bond length of 1.54 A and three C=C double bonds with a bond length of 1.34A are found in the aforementioned structures (I) and (II). However, it was discovered that all six carbon and carbon bonds are identical, and a 1.39 A intermediate C-C and C+C bond was discovered. The poor reactivity of halogen in vinyl bromide can be explained further by the phenomena of resonance.
Resonance energy is the difference between the real molecule and the more stable canonical form.
Application of resonance effect
The high utility of resonance theory and its worth comes from the fact that it maintains the simple and unsophisticated form of structural representation.
Stability of carbocation
The carbocation that conjugates a positive charge with a double bond tends to be more stable. The allylic carbocation is more stable than the comparable alkyl cation because of the resonance structure. The resonance structures are formed when the negative electrons of the conjugated double bonds are delocalised, which increases their stability. The stability will be great if the resonating structure is great.
Carbanion of stability
The availability of double bonds or an aromatic ring will enhance the anion’s stability around the negatively charged atom because of resonance.
A point to be noted: the bigger the resonance structure, the more stable it will be.
Due to resonance, the negative charge on benzyl carbanion disperses over additional carbon atoms, making it more stable than ethyl carbanion.
Stability of free radicals
Due to depolarisation of the unpaired electrons across the system, simple alkyl radicals are less stable allylic and benzylic forms of free radicals.
Mesomeric effect vs resonance effect
- Resonance effect can be defined as the process in which two or more structures can be written for the real structure of a molecule, but none of them fully explains all characteristics of molecules. Substituents or functional groups in a chemical molecule cause the mesomeric effect, denoted by the letter M.
- Delocalisation of electrons in a system is known as resonance whereas the mesomeric effect is known as the resonance effect. It is a long-term impact that is reliable on the substituents or functional groups in a chemical compound.
- The +R (electron releasing) group is equal to the +M effect, while the –R (electron attracting) group is equal to the –M effect.
Principle of resonance
- The most fundamental resonance is the one that is generated with the least charge.
- The resonance of a full octet is more substantial than that of a partial octet. The most essential forms are those in which positive charges operate on the least electronegative atom.
- The resonance structure with the greatest covalent bond is the most significant.
Resonance effect vs inductive effect
- An inductive effect occurs when the polarisation of one link is caused by another link. On the other hand, the resonance effect occurs when two or more structures may be described for molecules, but none can describe all the characteristics of a molecule on their own.
- The difference in electronegativity between two atoms in a bond affects the inductive effect directly, whereas the number of resonant structures affects the stability.
Occurrence of resonance
- A pi bond conjugated with the other pi bond
- A pi bond conjugated with a negative charge
- A pi bond with a positive charge conjugated to it
- A negative charge conjugated with the lone pair or a positive charge conjugated with a lone pair
- A pi bond conjugated with a lone pair or a free radical
Conclusion
In chemistry, resonance is an intramolecular electrical phenomenon in which the location of a pi bond(s) or a nonbonding electron changes (also called a sigma bond). In this procedure, however, the location of an atom is changed by modifying the pi electrons’ position or the non-bonding electrons’ position.
Resonance is a property of organic compounds. In organic chemistry, the delocalised electrons inside a specific compound when a single Lewis structure does not express the bond are referred to as resonance. To portray delocalised electrons in an ion or molecule, several structures known as resonance can be used.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





