Introduction
All gaseous atomic particles have a movement comprising random speed and direction. The average velocity of gaseous particles can be procured by taking the square root of the average velocities, i.e., the root mean square velocities of the gas particles. The root means square velocity has two considerations:
- Molecular weight
- Temperature.
Moreover, velocity is defined as a vector quantity that indicates the rate of change of position regarding time or a speed with a directional component.
The Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gaseous Molecules
The kinetic molecular theory of gases is used to portray two key ideas:
- The connection between the average kinetic energy of the particles in a sample of gas and the temperature.
- An actual model depends on a few basic assumptions.
- The distance between the particles is very less or zero.
- The particles are in steady movement.
- The average kinetic energy of an assortment of gas particles corresponds to the outright temperature of the gas.
- The particles go through flexible impacts with the dividers (there is no net energy shortfall).
- The particles do not draw in each other (there are no ‘intermolecular’ forces).
Derivation of Relationship from the Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases
A relationship from the kinetic molecular theory of gases can be derived as:
PV=nRT

The Relationship Between Temperature and Kinetic Energy
The active hypothesis of gases is that the average kinetic energy (Ek) for the particles in a gas test is relative to the temperature.
First, the average Ek is essentially the ‘average’ since not every particle will have indistinguishable energies. Some will be below the norm, and some will be higher than the average.
Second, Ek corresponds to the absolute temperature.
Thus, the actual relationship is given as:
Ek=3/2RT
where,
Ek=Average Kinetic Energy of gas
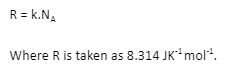
R=Universal Gas Constant
T=Temperature in Kelvin
Now, to derive the proportionality between the average kinetic energy and temperature, we use:
where,
Ek = Average kinetic energy of the gas
k = Boltzmann’s constant, which is utilised if singular molecule energy is being looked at
T = Temperature in kelvin
As we proceed to the next part of the derivation, we hold on to the energy of one mole of the same sample. Thus, R is utilised along with the Avogadro’s number to convert molecules to moles. Then,
The Relationship of Kinetic Theory of Gases with the Root Mean Square Velocity
Since we presently know how to relate the temperature and the kinetic energy of the gas, we can now relate temperature to the gas-particle velocity. Note that since these are appropriations, the primary values, be it Ek or velocity, that we are consistently discussing are averages in this case. Thus, as we know,

Conclusion
As per the kinetic molecular theory of gases, the gaseous particles are in a condition of steady arbitrary movement. Individual particles move at various velocities, continually impacting and taking a different path. We use velocity to portray the gaseous particle movement, considering both speed and the direction. Albeit the velocity of gaseous particles is continually changing, the circulation of velocities does not change. We cannot measure the velocity of every individual molecule; hence, we generally reason as far as the average behaviour of the gaseous particles is concerned.
By figuring out the velocities and taking the square root, we ‘defeat’ the directional part of the velocity while procuring the particles’ average velocity. Since the value prohibits the particles’ direction, we presently allude to the value as the average speed. The root means square velocity is the proportion of the speed of particles in a gas, characterised as the square root of the average velocity squared of the atoms in a gas.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out