Chlorine is a dense greenish-yellow gas with an unpleasant odour (The smell is similar to ammonia or bleach). Its name comes from the Greek word “Chloros”, meaning greenish-yellow. Chlorine can become quite toxic in high concentrations and was used in World War I as poison gas.
Pure Chlorine is a yellow-green gas at room temperature and atmospheric pressure, two and a half times heavier than the air. Chlorine is a strong oxidation agent as it is quickly reduced.
On its own, Chlorine is not combustible. However, many of its reactions become exothermic and produce heat when reacting with different elements. Chlorine has the highest electron affinity and third highest electronegativity, only behind oxygen and fluorine. Chlorine, being extremely reactive, is found in Earth’s crust in the form of ionic chloride compounds, including such as NaCl (table salt) and KCl (sylvite).
Chlorine molecules are diatomic in nature, occurring as Cl2 and combine with almost all the elements, except for the lighter noble gases, to give chlorides.
The simplest chlorine compound is Hydrogen Chloride, both in gas and liquid medium as Hydrochloric Acid.
Chlorine reacts with different elements and forms binary chlorides. Chlorination of metals with Cl2 usually leads to a higher oxidation state.
However, Chlorides can be made by reaction of an element or its oxide, hydroxide, or carbonate with hydrochloric acid.
Similarly, Chlorine forms compounds such as PolyChlorine Compounds, Chlorine Fluorides, Chlorine Oxides, Chlorine oxoacids and oxyanions and Organochlorine compounds.
Reactions with Chlorine
Let’s begin with the simplest of reactions.
-
Reactions of Chlorine with air
However, Chlorine, Cl2 is not reactive towards Oxygen, O2, or Nitrogen N2.
Although chlorine usually possesses -1 oxidation state, it can have oxidation states of +1, +3, +4, or +7 in some specific compounds, such as in the case of Oxoacids with the alkali metals.
|
Oxidation State |
+1 |
+3 |
+5 |
+7 |
|
Compound |
NaClO |
NaClO2 |
NaClO3 |
NaClO4 |
Chlorine does, in fact, reacts with the deadly carbon monoxide, CO, forming COCl2
Cl2 (g) + CO(g) → COCl2
-
Reaction of Chlorine with Water
Chlorine, Cl2, reacts with water, H2O, to produce Hypochlorite, OCl-
Cl2 (g) + H2O (l) ⇌ OCl– (aq) + 2 H+(aq) + Cl–(aq)
Usually, reactions of chlorine with water are for disinfection purposes. Chlorine is ever so slightly soluble in water, with its maximum solubility occurring at 49° F. After that, its solubility decreases until 212° F. At temperatures below that range, it forms crystalline hydrates (usually Cl2 ) and becomes insoluble. Between that range, it usually forms hypochlorous acid (HOCl). This is the primary reaction used for water/wastewater disinfection and bleaching.
Cl2 + H2O ➝ HOCl +HCl
At the boiling temperature of the water, chlorine decomposes water
2 Cl2 + 2 H2O ➝ 4 HCl +O2
-
Reactions of Chlorine with Bases
Here, OH- acts as a base.
Chlorine, Cl2, reacts with hot aqueous alkali, forming chlorate, ClO3–
33 Cl2(g) + 6OH- (aq) → ClO3 – (aq) +5 Cl– (aq) +3H2O (l)
-
Reaction of Chlorine with Halogen
Remember, Chlorine is a halogen. In this reaction, a halogen reacts with a halogen.
Chlorine, like many of the other halogens, can form interhalogen compounds (examples include BrCl, ICI, ICl2). The heavier elements in one of these compounds act as the central atom. For Chlorine, this occurs when it is bonded to fluorine in ClF, ClF3, and ClF5

-
Reactions of chlorine with hydrogen
Hydrogen reacts with Cl2 forming hydrogen chloride, HCl. The reaction is slow at room temperature and increases in speed as the temperature increases. You could say that the speed of the reaction is directly proportional to temperature. Under the right conditions, the reaction can be explosive.
H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) → 2 HCl (g)
HCl can also be produced by reacting Chlorine with compounds containing Hydrogen, such as Hydrogen sulphide.
-
Reaction of chlorine with metals/metal ions
Chlorine reacts with most metals and forms metal chlorides, with most of these compounds being soluble in water. Examples of insoluble compounds include AgCland PbCl2. Gaseous or liquid chlorine usually does not have an effect on metals such as iron, copper, platinum, silver, and steel at temperatures below 230°F. At high temperatures, however, it reacts rapidly with many metals, especially if the metal is in a form with a high surface area (such as when powdered or made into wires).
Chlorine can oxidise iron

-
Reaction of chloride with phosphorus
Phosphorus reacts with excess Cl2 forming phosphorus chloride
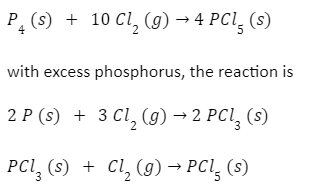
-
Reaction of Chlorine with sulphur
Sulphur reacts with excess chlorine forming sulphur(I)chloride or sulphur(II)chloride

Conclusion
Chlorine is a halogen that forms reactions with water, Hydrogen, halogen, metals, metal ions, phosphorus, sulphur. The products obtained in the reaction with Chlorine have many uses.
One might wonder what the use of knowing these reactions is? Many reactions to Chlorine are found in our daily life. For e.g., Chlorine, Cl2 reacts with sodium hydroxide NaOH to form sodium chlorate, a common household bleach, in a disproportionation reaction. Chlorine reacts with sodium to form sodium chloride, which is common table salt. Similarly, Chlorinating water prevents millions of deaths by killing harmful pathogens.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





