Introduction
Sodium is an important compound in basic chemistry and even in daily life. Present in many day-to-day products used for cleaning and other household purposes, it belongs to the alkali metal group with a position in group 1 of the periodic table. Sodium marks itself as the most abundant element on Earth and covers almost 2.8 per cent of its crust. Sodium is associated with many other elements – sodium chloride, sodium hydrogen carbonate, sodium hydroxide, etc. It combines with another element because it has a highly reactive nature when in a free state.
About Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate
In daily routine, baking soda is a very familiar product – this compound has the chemical name sodium hydrogen carbonate or sodium bicarbonate. This is a very important sodium compound and has the chemical representation NaHCO3. This compound is highly usable as bread soda or cooking soda. It is an alkali metal bicarbonate and contains sodium compounds as positive (+ve) ions and hydrogen and carbon as negative (-ve) ions. It is a solid compound in a free state with a salty appearance and taste.
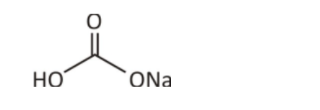
This is the structural representation of sodium hydrogen bicarbonate. In this diagram, sodium, hydrogen and carbon form a combination in the presence of oxygen. Hence, oxygen is associated with each element, which eventually provides sodium hydrogen carbonate color – a salty white texture with a similar taste.
Structure of Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate
The structure of the sodium hydrogen carbonate has a complex structure with minimal elements have the involvement in the formation of this compound. Here is the chemical formula and representation:
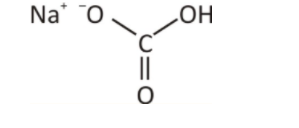
The above diagram is the chemical formula of sodium hydrogen carbonate. Here, a bond between sodium, hydrogen and oxygen is the ionic bond. The charge of all the elements is different, but the final element has a positive charge. The hydrogen and oxygen have a negative charge, whereas sodium comprises the positive charge.
The use of sodium hydrogen carbonate is very common in industrial uses, especially in the food industry. The oxidation state of sodium in the formation of this compound is with the positive charge and +1. The mass of the molecule collectively here is almost 84.007g/mol.
Properties of Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate
Several properties of the compound combine the elements like sodium, hydrogen, and carbon. Due to the highly reactive nature of sodium, sometimes it needs an external interference to neutralize the outcome. The combination of sodium hydrogen carbonate and tartaric acid neutralizes the reactive property of sodium. It avoids the decomposition process, which occurs when it undergoes heating procedures.
The element has various physical and chemical properties, which prove its variation in different reactive positions.
Physical Properties
- The physical properties of sodium hydrogen carbonate occur in the element without changing it into any other element. In simple terms, the observation allows our senses to feel the property is the physical property of any chemical compound.
- Sodium is a highly reactive metal that belongs to the alkali metal family.
- The colors of sodium hydrogen carbonate are slightly silver-white with a salty appearance.
- This element occurs in the crystal-solid state, but it is present in the form of fine powder in a usable state.
- The compound is very easily soluble in water but not soluble in ethanol.
- It has a slight alkaline salty taste and sometimes the washing powder texture and taste.
Chemical Properties
Chemically the sodium hydrogen carbonate undergoes many processes and changes. These procedures affect in many ways and may change the reactive properties of the compound.
- Hydrolysis: When the compound undergoes the hydrolysis process, it forms an alkaline solution. As sodium hydrogen carbonate has alkali properties after the process, there is a noticeable variation in the physical and chemical reactive properties.
2NaHCO3 + H2O ↔ NaOH + H2CO3
This is the formula representation of the compound formation after the hydrolysis. Sodium hydrogen carbonate color changes and turns yellow with methyl orange. The solution is completely aqueous in all states. The color is transparent, which performs the reaction with Phenolphthalein. The state of the solution after the hydrolysis process is comparatively weaker than the original state.
- Dissociation: When falling in the dissociation process in water, sodium hydrogen carbonate makes the elements of the compound change in charge. The sodium ions come into a positive state and form Na+ while the other elements get the negative charge to form HCO3–.
NaHCO3(s) → Na+(aq) + HCO3–(aq)
- Reaction with metal salts: When the sodium hydrogen carbonate reacts with the metal salts, it converts to form the normal carbonates. As the compound is alkali in nature and has metallic properties thus when it reacts to metallic salts. For example, if the zinc undergoes the reaction with the compound, the expression of reactivity is –
ZnSO4 + 2NaHCO3 → ZnCO3 + Na2SO4 + H2O + CO2
- Thermal decomposition: This is one of the most reactive procedures of sodium hydrogen carbonate. While this reaction occurs when the heating process happens, the carbon dioxide present in the elements gets into the evolution mode. This means the carbon dioxide present in the compound forms carbonate elements with the evolution of carbon dioxide. The expression on this process is –
2NaHCO3 → Na2CO3 + H2O + CO2
- Reaction with acids: As the compound consists of salts like texture and properties, it forms salt and water when it reacts with the acids; the reaction evolutes the carbon dioxide gas present in it. The use of sodium hydrogen carbonate is frequent in food products because it contains a stable state in the dry air while it becomes decomposable in the air, which has moisture. When it reacts with the hydrogen chloride, it forms sodium chloride as natural salt and water in the presence of carbon dioxide. The expression is –
NaHCO3 + HCl → NaCl + H2O + CO2
Similarly, it forms into sodium acetate, water, and carbon dioxide when it reacts with acetic acids. The expression is –
NaHCO3 + CH3COOH → CH3COONa + H2O + CO2 (g)
In the above reaction, the common factor is that the carbonate in both elements forms an acidic nature and decomposes into carbon dioxide and water.
Sodium hydrogen carbonate, also called sodium bicarbonate, is a simple compound acting differently with different elements. It is a highly usable element for food and medical activities. The simple powder-like element falls in the alkali family. It is also a necessary option that is effective for the use of disinfectant and other cleaning options. Medically it has the use in chemotherapy and dental procedures. Due to its reactive nature, sometimes sodium hydrogen carbonate and tartaric acid form a balance in moisture to get the perfect reaction. It is a useful product with complete chemical balance and a reactive nature in a positive way.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





