One of the major branches of Chemistry is organic chemistry, which mainly revolves around structures, properties, and reactions of organic compounds with covalent bonds and carbon atoms.
Hydrocarbons are organic compounds that compose two different kinds of atoms, hydrogen and carbon. These compounds are generally colourless and possess a weak odour. Ancient chemists describe hydrocarbons as either aromatic or aliphatic. There are several ways through which we can prepare hydrocarbons.
What are Hydrocarbons?
As mentioned earlier, hydrocarbons are organic compounds made up of essential atoms called hydrogen and carbons. Generally, these are colourless gases with nearly no odour.
Based on their types, hydrocarbons may possess simple or complex structures. In everyday life, hydrocarbons play a significant role, and their study provides a deep insight into the properties and preparation of its functional groups.
We can divide hydrocarbons into six categories. These include Saturated hydrocarbons, Unsaturated hydrocarbons, Cycloalkanes, Aromatic hydrocarbons, Aliphatic hydrocarbons, and Alicyclic hydrocarbons.
What are Alkanes?
We can describe alkanes as organic compounds that possess single-bonded hydrogen and carbon units. CnH2n+2 is the formula of Alkanes.
We can further divide alkanes into three major groups: cycloalkanes, branched alkanes, and chain alkanes.
List of Alkanes | Molecular Formula |
Methane | (CH4) |
Ethane | (C2H6) |
Propane | (C3H8 |
Butane | (C4H10) |
Pentane | (C5H12) |
Hexane | (C6H14) |
Heptane | (C7H16) |
Octane | (C8H18) |
Nonane | (C9H20) |
Decane | (C10H22) |
Preparation of Alkanes
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons. Their carbon atoms bind closely to different sets of carbon atoms with sigma bonds only.
In alkanes, the first four members, starting from C1 to C4, are gases, and from C5 to C17, they are liquids. In contrast, those that have 18 and more than that are solids.
They do not hold any colour or odour and are prepared in several industries using different techniques.
Preparation of Alkanes from the unsaturated hydrocarbon
Let us look at the different methods to prepare alkanes:-
From Alkenes and Alkynes
We use a process called hydrogenation to prepare alkanes from alkene and alkyne. Dihydrogen gas is mixed with alkynes and alkenes to a catalyst, like palladium and nickel, to form alkanes.
In the presence of nickel, the reaction occurs at an increased temperature. Whereas, in the case of palladium, the reaction occurs at room temperature.
Preparation of Alkanes from Alkyl Halides
There are two ways to prepare alkanes through alkyl halides. They are as follows:
All alkanes, excluding fluorides, are prepared from the alkyl halide through dilute hydrochloric acid and zinc reduction.
CH3Cl + H2 (Zn,H+)→ CH4 +HCl
Another method to prepare alkanes through alkyl halides is called the Wurtz reaction. When we treat alkyl halides with sodium metal in the dry ether, alkane production is higher. With even carbon numbers, the reaction can achieve higher alkanes.
Here is the chemical equation for the same:
CH3-Br + 2Na + BrCH3 → CH3-CH3 + 2NaBr.
Preparation of Alkanes from Carboxylic Acids
We can prepare alkanes from carboxylic acid in two ways as follows:
We have to remove carbon dioxide from carboxylic acid to prepare alkanes. This process is called decarboxylation. The produced alkane has less amount of carbon atoms that are present in the carboxylic acid.
Here is the chemical equation for the same:
Kolbe’s electrolytic method uses the electrolysis of potassium salts of sodium carboxylic acid to produce alkane. This reaction takes its name after Rudolf Schmitt and Hermann Kolbe.
Here is the chemical equation for the same:
2CH3COO–Na+ + 2H2O → CH3 –Ch3 + 2CO2 + H2 + 2NaOH.
Sodium acetate
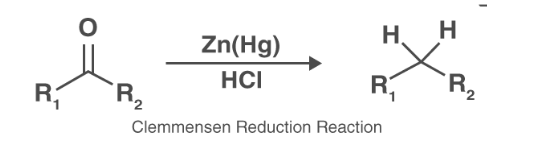
Clemmensen’s Reduction
Clemmensen’s reduction is the reaction used to reduce ketones or aldehydes to the alkanes using zinc amalgam and hydrochloric acid. This reaction’s name originated from Erik Christian Clemmensen, a Danish chemist.
Conclusion
Hydrocarbons are organic compounds made up of essential atoms called hydrogen and carbons. On the other hand, alkanes are organic compounds that possess single-bonded hydrogen and carbon compounds and have the chemical formula CnH2n+2. Further, we can divide alkanes and cycloalkanes, branched alkanes, and chain alkanes. Here, we discussed the preparation of hydrocarbons – alkanes.
We can prepare alkanes from alkene and alkyne through hydrogenation. There are two ways to prepare alkanes through alkyl halides. Firstly, through reduction with dilute hydrochloric acid and zinc. Another one is called the Wurtz reaction. We also discussed the preparation of alkanes from carboxylic acids and briefly explained Clemmensen’s Reduction.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





