During a redox reaction, an oxidising agent is a reactant that removes electrons from other reactants, which is known as oxidation. Typically, the oxidising agent absorbs these electrons for itself, resulting in the reduction of the oxidising agent and the gain of electrons. As a result, an oxidising substance serves as an electron acceptor. Another way to think about an oxidising agent is as a species that is capable of transferring electronegative atoms (particularly oxygen) to a substrate.
Oxidising agents are also referred to as Oxidants or oxidisers.
Oxidising substances include hydrogen peroxide, ozone, oxygen, potassium nitrate, and nitric acid, to name a few. Each and every one of the halogens is an oxidising agent (e.g., chlorine, bromine, fluorine).
During a chemical process, an oxidising agent acquires electrons and is reduced, whereas a reducing agent loses electrons and is oxidised during the same reaction.
Because an oxidizer has the potential to contribute to combustion, it may be classed as a potentially hazardous substance. When it comes to oxidizers, the hazard symbol is a circle with flames on top of it.
Factors Affect the Oxidising Power of an Oxidising Agent
oxidising agents are typically found in their most extreme oxidation states, and as a result, they have a significant potential to gain electrons and undergo reduction when exposed to oxygen. It is generally agreed that oxidizers are ions, atoms, and molecules that have a strong affinity for the electrons they contain. The oxidising power increases in direct proportion to the strength of the electron affinity.
Elemental fluorine is often considered to be the most powerful elemental oxidising agent available. This may be owing to the fact that fluorine is the most electronegative element in the contemporary periodic table, and as a result, it has the largest attractive force on electrons of all of the elements in the table. Because of diatomic fluorine’s oxidising strength, it may cause metals such as asbestos and quartz (as well as molecules like water) to burst into flames when they are exposed to it at high enough concentrations.
Among the other types of elemental oxidising agents are diatomic oxygen (O2), diatomic chlorine (Cl2), and ozone, to name a few examples (O3). This group of oxidizers contains the elemental forms of the second and third most electronegative elements (oxygen and chlorine, respectively), which makes them excellent electron acceptors.
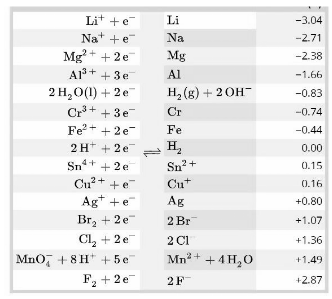
In a redox process, the standard electrode potential of a half-reaction offers information on the oxidising power of the chemical substance.
Examples of Oxidising Agents
Halogens
The Halogens are a set of seventeen elements in the periodic table that are collectively referred to as the Halogens. According to some, they have a significant ability to gain electrons, which can be explained by the fact that their electronegativities are higher than those of other elements in the same group. Essentially, this means that they have the ability to attract electrons to their respective nuclei with relative ease. Iodine, bromine, chlorine, and fluorine are just a few of the halogens that are effective oxidising agents. As previously noted, fluorine is considered to be the most powerful elemental oxidising agent since it has the highest electronegativity.
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element that has the atomic number 8 and is represented by the symbol ‘O’ on a periodic table. A non-metal with excellent oxidising properties, it belongs to the chalcogen group of the periodic table and is a highly reactive non-metal with excellent oxidising properties. The strong oxidising power of oxygen causes metals to react with oxygen in the atmosphere, resulting in the formation of metal oxides as a result. The presence of oxygen has been seen in the majority of combustion processes.
Hydrogen Peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is a chemical compound with the molecular formula H2O2. According to the human eye, it appears to be a colourless liquid with a viscosity that is higher than that of water. Hydrogen peroxide is the most basic chemical, consisting of a peroxide functional group linked to an oxygen-oxygen single bond and an oxygen atom. It can be used as a weak oxidising agent, disinfectant, and bleaching agent, among other things.
There are numerous more oxidising agents that are routinely utilised in industrial settings as well as in everyday human life. Household bleach (NaClO3), potassium nitrate (KNO3), and sulphuric acid are all examples of oxidising agents (H2SO4).
Applications of Oxidising Agents
Various commercial and industrial applications for oxidising agents can be found. Several of these uses are listed in the next section.
Fabrics are being bleached.
Water purification is a process.
The application of an oxidising agent is required for the combustion of fuel.
Batteries are used for energy storage.
Rubber has been vulcanised (increasing the strength and the elasticity of rubber).
Many biological functions, such as metabolism and photosynthesis, rely on oxidising agents for their proper functioning.
Conclusion
The oxidation number of an atom before and after the reaction can be used to identify the oxidising agent, and this information can be obtained from the oxidation number of an atom before and after the process. It is the loss of electrons by the material that is responsible for the increase in oxidation number as it moves towards the product side of the reaction. The substance received electrons and was reduced, resulting in a reduction in the oxidation number of the molecule as it moved towards the product side of the equation. Because it gains electrons, the material that is reduced in a reaction is referred to as the oxidising agent. Because it has lost electrons, the material that has been oxidised in a process is known as the reducing agent.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





