Acetanilide, P-Nitro Acetanilide, Aniline Yellow, and Iodoform are different organic compounds examples. They belong to different categories of organic compounds and thus have different physical and chemical properties. All of these compounds have varied usage in the commercial market and are highly useful compounds because of their properties.
The sections below will study the structure, chemical formula, preparation, properties, and uses of these organic compounds.
Let us start with Acetanilide.
![]()
![]() P- nitroacetanilide or Para nitroacetanilide is an organic compound that is a nitroacetanilide derivative.
P- nitroacetanilide or Para nitroacetanilide is an organic compound that is a nitroacetanilide derivative.
![]()
![]() Aniline Yellow or para amino azobenzene is an organic compound that is an aromatic amine. It is a derivative of azobenzene. It has the appearance of an orange powder and exists as a yellow dye.
Aniline Yellow or para amino azobenzene is an organic compound that is an aromatic amine. It is a derivative of azobenzene. It has the appearance of an orange powder and exists as a yellow dye.
![]()
![]() It can also be prepared from acetone and iodine in the presence of sodium hydroxide.
It can also be prepared from acetone and iodine in the presence of sodium hydroxide.
![]()
Acetanilide
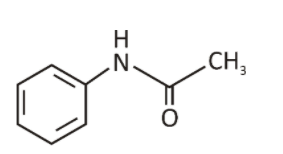
Acetanilide is a synthetic organic compound.
- IUPAC Name: N-Phenylacetamide
- Molecular Formula: C8H9NO
- Molar Mass: 135.17 g/mol
- Classification: Acetanilide is a member of the acetamides class. It is also known as Acetanil or N-phenylacetamide.
- Appearance: Acetanilide is an odorless solid. It has a solid leaf or flake-like appearance.
- Structure: It is an anilide that has one of the hydrogen atoms attached to the nitrogen substituted by a phenyl group.
- Preparation: When acetic anhydride reacts with aniline in the presence of Zn dust, you get Acetanilide. The chemical reaction is as follows:
Physical Properties
- Acetanilide is in the form of a white to gray solid.
- It is stable under most conditions.
- It is slightly soluble in water.
- It has a melting point of 114.3 degrees.
Uses
- Used in the manufacture of colored dyes for textiles.
- Used as a reagent in rubber production.
- As an inhibitor in hydrogen peroxide decomposition.
- Widely used in the pharmaceutical field as an analgesic and the synthesis of penicillin and sulfa drugs.
P-Nitro Acetanilide
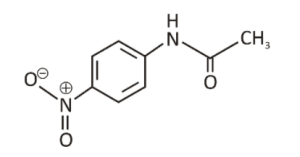 P- nitroacetanilide or Para nitroacetanilide is an organic compound that is a nitroacetanilide derivative.
P- nitroacetanilide or Para nitroacetanilide is an organic compound that is a nitroacetanilide derivative.
- IUPAC Name: N-(4-nitrophenyl) acetamide
- Molecular Formula: C8H8N2O3
- Molar Mass: 180.16 g/mol
- Classification: P- nitroacetanilide belongs to the class of nitro derivative of Acetanilide. It is also known as Para nitroacetanilide or 4-Nitroacetanilide.
- Appearance: Whitish green or brown solid.
- Structure: It is an anilide that has one of the hydrogen atoms attached to the nitrogen and is substituted by a phenyl group.
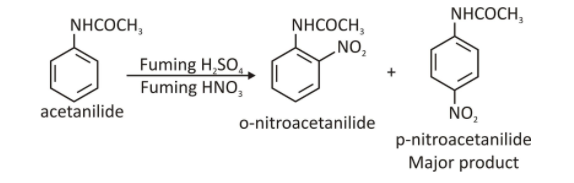
- Preparation: When acetanilide is nitrated, p-nitroacetanilide is prepared. Acetanilide is treated with a special nitrating mixture of nitric acid and sulphuric acid. The resulting products are p-nitroacetanilide and o-nitroacetanilide. P-nitroacetanilide can be isolated through crystallization as o-nitroacetanilide is soluble in alcohol.
The chemical reaction is as follows:
Physical Properties
- P-nitroacetanilide is a colorless to white crystalline solid.
- It is a stable compound and combustible.
- It is soluble in water and alcohol but insoluble in cold water.
- It has a melting point of 215 degrees C.
Uses
- P-nitroacetanilide is used in the pharmaceutical industry for preparing paracetamol and phenacetin.
- It is also used as a pesticide and in rubber chemicals.
- It is commonly used as an intermediate for dyes.
Aniline Yellow
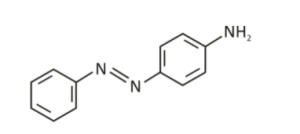 Aniline Yellow or para amino azobenzene is an organic compound that is an aromatic amine. It is a derivative of azobenzene. It has the appearance of an orange powder and exists as a yellow dye.
Aniline Yellow or para amino azobenzene is an organic compound that is an aromatic amine. It is a derivative of azobenzene. It has the appearance of an orange powder and exists as a yellow dye.
- IUPAC Name: (E)-4-(phenyldiazenyl)aniline
- Molecular Formula: C12H11N3
- Molar Mass: 197.24 g/mol
- Classification: Azobenzene derivative
- Appearance: Solid powder with orange needle-shaped crystals.
- Structure: It consists of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, and this aniline is the simplest aromatic amine.
- Preparation: Aniline yellow is prepared by a coupling reaction between benzene diazonium chloride and phenylamine or aniline in an acidic medium
Physical Properties
- Aniline Yellow or para amino azobenzene has the odor of rotten fish like most volatile amines.
- It readily burns with a smoky flame.
- It is a stable compound under normal temperature and pressure.
- It is slightly water-soluble.
- It has a melting point of 123 to 126 degrees C.
Uses
- Aniline Yellow or para amino azobenzene is a significant industrial chemical.
- It is a starting material for fine chemical synthesis.
- It is used in the manufacture of polyurethane and other industrial chemicals.
- It is also popularly used in dyeing and as an intermediate product in the manufacture of Acid Yellow and other diazo dyes.
Iodoform

Iodoform is an organic iodine compound.
- IUPAC Name: Triiodomethane
- Molecular Formula: CHI3
- Molar Mass: 393.73 g/mol
- Classification: Iodoform belongs to the organic halogen compound family.
- Appearance: A pale yellow, crystalline, solid, or powder
- Structure: An iodoform molecule follows tetrahedral molecular geometry.
- Preparation: Iodoform is prepared from ethanol and acetone in several steps in the lab.
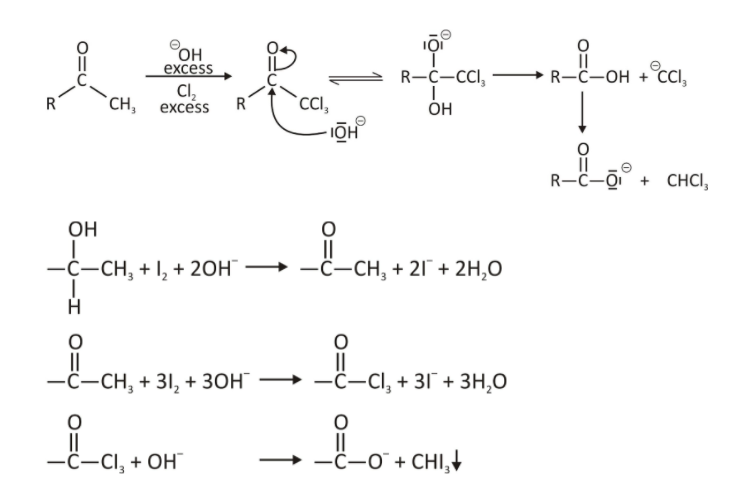 It can also be prepared from acetone and iodine in the presence of sodium hydroxide.
It can also be prepared from acetone and iodine in the presence of sodium hydroxide.

Physical Properties
- Iodoform has a distinct pungent odor.
- It has a sweetish taste like chloroform.
- It is insoluble in water but soluble in ether or ethanol.
- It has a melting point of 121 degrees C.
Uses
- Iodoform can be used as a disinfectant.
- It is also used for antiseptic dressing of wounds or sores.
- It was previously used for sterilizing the instruments that are used for surgery.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





