When ninhydrin (a chemical molecule having the formula C9H6O4 and the IUPAC name 2,2-dihydroxybenzene-1,3-dione) is added to a test solution of the analyte, the result is known as the ninhydrin concentration. It is believed that the development of a deep blue colour in the analyte is due to the presence of ammonia, primary or secondary amines, or amino acids.
Test for Ninhydrin
The amino group of the analyte results in the formation of a molecule that is comparable to diketohydrin. The colour of this combination is a deep blue that is sometimes referred to as Ruhemann’s purple.
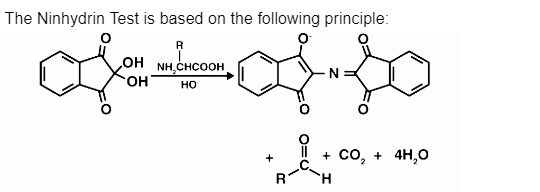
The amino group of a free amino acid is subjected to a chemical reaction with ninhydrin, which has the property of acting as an oxidising agent. When exposed to ninhydrin, the amino acid undergoes oxidative deamination, resulting in the release of CO2, NH3, and an aldehyde, as well as the formation of hydrindantin and other byproducts of the reaction (which is a reduced form of ninhydrin).
As a result of this reaction, the ammonia reacts with yet another ninhydrin molecule, resulting in the formation of diketohydrin (also known as Ruhemann’s complex). The vivid blue colour is due to the presence of this compound.. Because proline is an amino acid, a yellow coloured compound is generated when the analyte contains Amino-acids, such as proline. When asparagine is employed, the resultant complex has a brown colour to it.
The Ninhydrin Test is based on the following principles:
- A deep purple or blue colour, known as Ruhemann’s purple, is produced when two molecules of the compound ninhydrin (2,2- dihydroxyindane-1,3-dione) react with a free alpha-amino acid. The reason for this reaction is unknown.
- When used in this reaction, the oxidising agent ninhydrin causes the deamination and decarboxylation of the amino acids to occur at a high temperature, causing the process to proceed.
- This reaction is followed by condensation between the reduced ninhydrin molecules, the released ammonia, and the second molecule of ninhydrin, which is a product of the first reaction.
- It takes the entire reaction time to build the complex of diketohydrin, which has a rich purple colour at the conclusion of it.
- This test produces an iminium salt, which is yellow-orange in colour, when amino acids such as proline and hydroxyproline are tested.
- The same is true for proteins that include a free amind group, such as the amino acid asparagine, which react with the ninhydrin reagent to generate an orange coloured result.
- The intensity of the complex that has formed is related to the concentration of amino acids in the forming solution.
- Furthermore, the type of amino acid present has an effect on how bright the colour appears.
Procedure for the Ninhydrin Test
- A 2 percent solution of ninhydrin must first be made by dissolving 0.2 grams of the drug in 10ml of either ethanol or acetone. After that, the solution can be used.
- It is necessary to make a 1 percent solution of the amino acid (analyte) in distilled water at this point. It is necessary to add a few drops of the 2 percent ninhydrin solution to this solution in order to make it work.
- It is necessary to place the test tube in a warm water bath for approximately 5 minutes.
Conclusion
Therefore it can be concluded, presence of amino acids, the development of a deep blue/violet colour shows their presence.
Interpretation of the Ninhydrin Test Results
Ammonia, primary/secondary amines, and amino acids all produce a deep purple colour when exposed to light.
A yellow colour is created from the amino acids hydroxyproline and proline.
When asparagine is used, a brown colour is produced.
It is assumed that the analyte does not include amino acids, amines, or ammonia if no colour change is detected.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





