Molecular orbital theory- The molecular orbital theory or the MOT is a way of explaining the electronic structure of atoms and molecules using quantum mechanics. The basic principle of this theory is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a particular number of atomic orbitals merge to create the same number of molecular orbitals, although the electrons entangled may be redistributed among the orbitals. The MO theory is appropriate for simple diatomic molecules such as dihydrogen, dioxygen, and carbon monoxide. However, it becomes difficult while discussing polyatomic molecules, such as methane.
Homonuclear species- A homonuclear molecule is a molecule that contains only one element. It may have various numbers of atoms of the same element.
Diatomic species – A diatomic molecule is a molecule that has two molecules of the same or different elements.
Homonuclear diatomic species-A homonuclear diatomic molecule is a molecule that has two atoms of the same element—for example, H2, O2, and N2.
MO diagrams
In a Molecular orbital energy diagram, horizontal lines are in the centre, forked by constituent atomic orbital energy levels. The energy levels increase from the bottom to the top. A diatomic molecular orbital diagram helps us deduce the magnetic properties of the molecule, changes during ionization, bond order, and the number of bonds formed. Following are the MO diagrams of some homonuclear diatomic species.

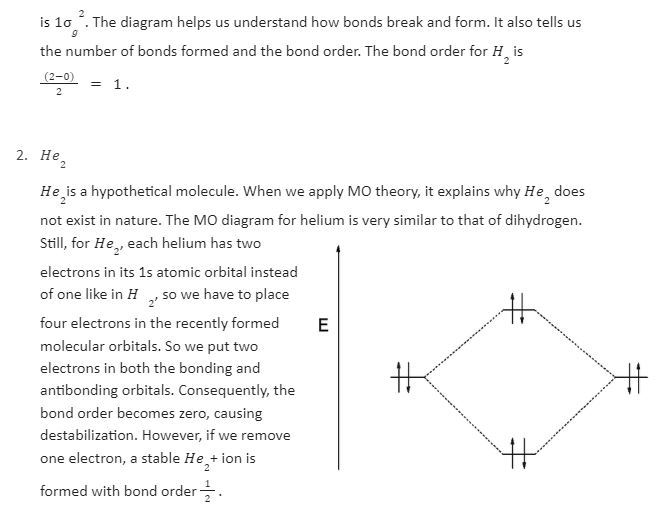
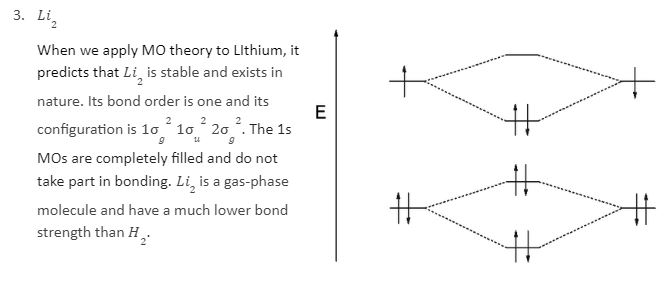
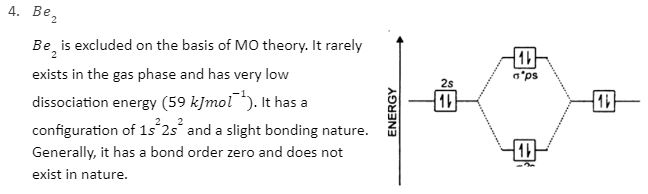

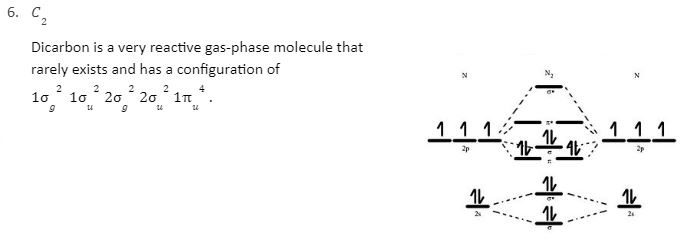
7. N2
Here, we can see the two molecular orbitals mix and repulse energy. It has a bond order of three and a configuration of 1σg2 1σu2 2σg2 2σu2 1u4 3σg2. The MO diagram explains the experimental photoelectron spectrum for nitrogen.


Conclusion
Molecular orbital energy diagrams help us understand the electronic configuration of elements using quantum mechanics.Molecular orbital is appropriate for simple diatomic molecules like hydrogen,lithium etc,but difficult for polyatomic molecules like ethane,methane etc.A horizontal baseline is present at the centre.Atomic orbitals above baseline have high energy whereas atomic orbitals below baseline have low energy.Molecular orbitals also help us evaluate several features of an element like magnetic nature,bond order etc.Molecular orbitals contain bonding and antibonding electrons.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





