The mole concept is a convenient way of expressing the amount of a substance in a given amount of space. Almost any measurement can be broken down into two parts: the numerical magnitude and the units in which the numerical magnitude has been expressed. The magnitude of 2 kilogrammes is represented by the number ‘2’, and the unit is represented by the number ‘kilogramme’, for example.
If we’re talking about particles at the atomic (or molecular) level, it’s well known that even one grain of a pure element contains a significant number of atoms. This is one of the most common applications of the mole concept. In particular, it focuses on the unit known as a ‘mole,’ which represents the total number of particles in a very large number of particles.
In mathematics, the number 6.02214076*1023 is referred to as the Avogadro constant, and it is frequently denoted by the symbol NA.’ Atoms, molecules, monatomic/polyatomic ions, and other elementary entities that can be represented in moles include atoms, molecules, and other elementary entities (such as electrons).
Taking carbon-12 (12C) as an example, one mole of pure carbon-12 (12C) will have an exact mass of 12 grammes and will contain 6.02214076*1023 (NA) atoms of 12C. This formula can be used to represent the number of moles of a substance present in a given pure sample of that substance:
n = N/NA is the number of times the letter n appears in a sentence.
Avogadro’s constant is defined as: n = number of moles of the substance (or elementary entity), N = number of elementary entities in the sample, and NA = Avogadro constant.
Mole is a term that was first used in 1896 by the German chemist Wilhelm Ostwald, who derived the term from the Latin word moles, which literally translates as a ‘heap’ or a ‘pile.’
The number of moles of a molecule may not always be the same as the number of moles of the elements that make up the molecule itself. For example, a mole of water contains a non-zero number of hydrogen atoms (H2O). Each water molecule, on the other hand, contains two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. As a result, one mole of H2O contains two moles of hydrogen and one mole of oxygen in equal proportions.
When we talk about an element’s atomic mass, we are talking about the mass of one atom of that element expressed in atomic mass units (amu). It allows you to account for the abundance of the various isotopes of the element and assign a weighted average value to the mass of one atom of an element.
According to the International Atomic Mass Units System, the atomic mass of carbon is 12.011 atomic mass units because carbon samples typically contain 98.89 percent of the carbon-12 isotope, 1.11 percent of the carbon-13 isotope, and trace amounts of carbon-14. The atomic masses of these isotopes, on the other hand, are different.
In comparison to carbon-12, carbon-13 has an atomic mass of 13 atomic mass units (amu), which is greater than 12 amu for carbon-12. When it comes to elements, the atomic mass of a given element is approximately equal to the sum of all the protons and neutrons present in the element’s nucleus. The molecular mass of an element is equal to the sum of the atomic masses of all of the elements that make up the element in question. It is also possible to express this quantity in terms of atomic mass units. Thus, the molecular mass of water is equal to the sum of the atomic masses of its constituents – hydrogen and oxygen – and is called the molecular weight of water. Hydrogen has an atomic mass of 1.00794 amu, while oxygen has an atomic mass of 15.9994 amu. Because water molecules contain two hydrogen atoms and only one oxygen atom, the molecular mass of H2O is 18.0154 amu, which is the same as the molecular mass of water.
Generally speaking, the molar mass of a substance is defined as the total mass contained in one mole of the substance. It is frequently expressed as a number of ‘grammes per mole’ (g/mol) units. The SI unit for this quantity, on the other hand, is kilogrammes per mole. It is possible to represent molar mass using the following formula:
The molar mass of a substance is equal to (the mass of the substance in grams) divided by 100. (Number of Moles)
The molar mass of water is approximately 18.015 g/mol, which corresponds to the mass of one hundred and fifteen water molecules (NA number).
![]()
It is possible to calculate the total number of atoms/molecules present in a sample by multiplying the number of moles present with the Avogadro constant. This formula can be expressed as follows:
Number of Atoms or Molecules = (Number of Moles)*(6.022*1023) = Number of Atoms or Molecules
The following equation describes the relationship between the atomic mass unit (amu) and the gramme:
The unit of one amu is one gramme divided by (6.022*1023), which equals 1.66*10-24 grammes.
As a result, the mass of one mole of an element will be equal to the atomic mass of that element expressed in grammes.
1 mole of H2 contains 6.022*1023 molecules, and each molecule of H2 contains two electrons. 1 mole of H2 is equal to 6.023*1023 molecules.
1 mole is equal to 6.023*1023 grams.
The total number of electrons contained in a mole of H2 is 12.046*1023, as a result.
Mole
6.02214076 * 1022 ‘elementary entities’ of the given substance is defined as a mole in the field of chemistry, and a mole is defined as the amount of a substance that contains exactly 6.02214076 * 1023 ‘elementary entities’ of the given substance.In mathematics, the number 6.02214076*1023 is referred to as the Avogadro constant, and it is frequently denoted by the symbol NA.’ Atoms, molecules, monatomic/polyatomic ions, and other elementary entities that can be represented in moles include atoms, molecules, and other elementary entities (such as electrons).
Taking carbon-12 (12C) as an example, one mole of pure carbon-12 (12C) will have an exact mass of 12 grammes and will contain 6.02214076*1023 (NA) atoms of 12C. This formula can be used to represent the number of moles of a substance present in a given pure sample of that substance:
n = N/NA is the number of times the letter n appears in a sentence.
Avogadro’s constant is defined as: n = number of moles of the substance (or elementary entity), N = number of elementary entities in the sample, and NA = Avogadro constant.
Mole is a term that was first used in 1896 by the German chemist Wilhelm Ostwald, who derived the term from the Latin word moles, which literally translates as a ‘heap’ or a ‘pile.’
The number of moles of a molecule may not always be the same as the number of moles of the elements that make up the molecule itself. For example, a mole of water contains a non-zero number of hydrogen atoms (H2O). Each water molecule, on the other hand, contains two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. As a result, one mole of H2O contains two moles of hydrogen and one mole of oxygen in equal proportions.
Quantities associated with the mole concept, as well as their formulae
Atomic and molecular masses are two different things.When we talk about an element’s atomic mass, we are talking about the mass of one atom of that element expressed in atomic mass units (amu). It allows you to account for the abundance of the various isotopes of the element and assign a weighted average value to the mass of one atom of an element.
According to the International Atomic Mass Units System, the atomic mass of carbon is 12.011 atomic mass units because carbon samples typically contain 98.89 percent of the carbon-12 isotope, 1.11 percent of the carbon-13 isotope, and trace amounts of carbon-14. The atomic masses of these isotopes, on the other hand, are different.
In comparison to carbon-12, carbon-13 has an atomic mass of 13 atomic mass units (amu), which is greater than 12 amu for carbon-12. When it comes to elements, the atomic mass of a given element is approximately equal to the sum of all the protons and neutrons present in the element’s nucleus. The molecular mass of an element is equal to the sum of the atomic masses of all of the elements that make up the element in question. It is also possible to express this quantity in terms of atomic mass units. Thus, the molecular mass of water is equal to the sum of the atomic masses of its constituents – hydrogen and oxygen – and is called the molecular weight of water. Hydrogen has an atomic mass of 1.00794 amu, while oxygen has an atomic mass of 15.9994 amu. Because water molecules contain two hydrogen atoms and only one oxygen atom, the molecular mass of H2O is 18.0154 amu, which is the same as the molecular mass of water.
Molar mass
Molar Mass is a term used to describe the amount of matter in a molar mass.Generally speaking, the molar mass of a substance is defined as the total mass contained in one mole of the substance. It is frequently expressed as a number of ‘grammes per mole’ (g/mol) units. The SI unit for this quantity, on the other hand, is kilogrammes per mole. It is possible to represent molar mass using the following formula:
The molar mass of a substance is equal to (the mass of the substance in grams) divided by 100. (Number of Moles)
The molar mass of water is approximately 18.015 g/mol, which corresponds to the mass of one hundred and fifteen water molecules (NA number).
Gram Atomic Mass and Gram Molecular Mass
A gram of an element’s atomic mass is equal to the mass of one mole of that element in grams. Similar to this, the gramme molecular mass of a compound is the mass of a single mole of that compound. As a result, the gramme atomic mass of hydrogen is approximately 1.007g, and the gramme molecular mass of water is approximately 18.015g per gramme of hydrogen.Formulae that are related
It is possible to calculate the number of moles present in a given sample of an element or compound by dividing the sample’s total mass by the molar mass of the element or compound in question, as described by the following formula: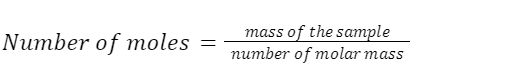
It is possible to calculate the total number of atoms/molecules present in a sample by multiplying the number of moles present with the Avogadro constant. This formula can be expressed as follows:
Number of Atoms or Molecules = (Number of Moles)*(6.022*1023) = Number of Atoms or Molecules
The following equation describes the relationship between the atomic mass unit (amu) and the gramme:
The unit of one amu is one gramme divided by (6.022*1023), which equals 1.66*10-24 grammes.
As a result, the mass of one mole of an element will be equal to the atomic mass of that element expressed in grammes.
The number of electrons contained within a molecule of hydrogen
Approximately how many electrons are contained in a mole of hydrogen molecule is1 mole of H2 contains 6.022*1023 molecules, and each molecule of H2 contains two electrons. 1 mole of H2 is equal to 6.023*1023 molecules.
1 mole is equal to 6.023*1023 grams.
The total number of electrons contained in a mole of H2 is 12.046*1023, as a result.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






