Metal halides are formed when metals and halogens combine. Some are ionic, like sodium chloride, whereas others are covalently bonded. Although a few metal halides are isolated molecules, such as uranium hexafluoride, the majority adopt polymeric forma, such as palladium chloride. Many metals salts and ionic liquids have been reported to cleave alkyl aryl ethers. These reagents are dealkylated via SN² reaction of the anion liberating phenol. Metals seldom promote the reaction by coordination to the ether oxygen, and ionic liquid provides a medium or way which accelerates SN² reactions. Oxophilic metals like Li, Zn, and Mg are the most prevalent, and Iodide is the most reactive anion. Microwave heating and ionic liquids have been reported to facilitate this type of ether cleavage reaction.
What are Halides?
To generate a fluoride, chloride, bromide, iodide or astatide chemical, a halide is a binary compound in which one component is a halogen atom, and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative than the halogen. Halides make up many salts; with the halogens, all group 1 metals create halides which are white solids. A halide ion is a negatively charged halogen atom. Fluoride (F), chloride (Cl), bromide (Br), iodide (I), and astatide (At) are the halide anions. All ionic halide salts contain these ions.
Halides in organic chemistry
Halides are functional groups in organic chemistry. A halide is an organic compound that contains at least one halogen atom. Alkyl halides are organic compounds with an alkyl group R that is covalently bound to a halogen X.
Pseudohalides have the same charge and reactivity as halides; typical examples include azides NNN– isocyanate -NCO, Isocyanide, CN–, and others. The Carius halogen method is a chemical test for detecting halogen in chemical compounds. In the synthesis of cyclic alkanes, dihalides are frequently utilized.
Structure and Reactivity of Metal Halides
Metal halides with ‘’ionic’’ properties (mostly alkali and alkali earth) have extremely high melting and boiling point. They are highly soluble in water, and some of them are deliquescent; they have low solubility in an organic solvent. Some transition metals with low oxidation states, such as ferrous chloride, nickel chloride, and cupric chloride, have halides that dissolve quickly in water. Metal cations with a high oxidation state, such as ferric chloride, aluminum chloride, and titanium tetrachloride, are more likely to undergo hydrolysis.
The melting and boiling points of the discrete metals are quite low. Titanium tetrachloride, for example, melts at 25 degrees Celsius and boils at 135 degrees Celsius, making it a liquid at room temperature. They are usually water-insoluble; however, they are soluble in organic solvents.
Polymeric metal halides have higher melting and boiling temperatures than monomeric metal halides. Still, they have lower melting and boiling values than that of ionic metal halides, only in the presence of a ligand that produces distinct units that are soluble. Palladium chloride, for example, is insoluble in water but dissolves readily in a strong sodium chloride solution:

Palladium chloride is insolvent in most organic solvents, but it forms solvent monomeric units with acetonitrile and benzonitrile.
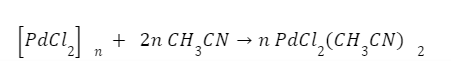
Applications of Metal Halides
The volatility of the tetrachloride and tetraiodide complexes of Ti(IV) is exploited in the purification of titanium by the Kroll and van Arkel-de-Boer processes. The metal halides act like Lewis acids. Although ferric and aluminum chlorides are catalysts for the Friedel-Crafts process, they are frequently used in stoichiometric amounts due to their low cost. Hydrosilylation requires the use of chloroplatinic acid (H2PtCl6) as a catalyst.
What is a metal halides lamp?
An electrical lamp is a metal halide lamp. The electrical breakdown of a gaseous combination of vaporized mercury and metal halides creates light. Metal halides coupled with bromine or iodine are employed for this purpose. These metal halides augment the light’s intensity and color perception.
Conclusion
Metal halides are formed when metals and halogens mix. The elements in the s and d blocks are metals. The elements in group 17 are known as halogens. Cations are generated when one or more electrons from a metal’s outermost electron shell are withdrawn. Halides are halogen anions. The outermost electron shell of halogens can accept electrons. As a response, an ionic bond can develop between these two elements. An ionic bond is a chemical bond in which a cation and an anion are attracted to each other via electrostatic attraction. Electrostatic attraction exists between metal cations and halide anions in this metal halide. Sodium chloride, for example, is an ionic metal halide compound.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




