Acids and bases are the first thing that is taught to a budding chemist. The use of acids is imperative and infinite. The correct use of acids is required when working in a laboratory as without it, not many chemical reactions can happen.
One of the most often used acids is Sulphuric acid. Widely known as the king of all acids, sulphuric acid is used in a lot of chemical reactions and industrial processes. Therefore sulphuric acid preparation is of prime importance due to the high amount of usage in laboratory work as well as industrial production like in the paper industry, textile industry etc.
What is sulphuric acid?
Sulphuric acid or the oil of vitriol, is a very corrosive and hazardous acid. It is formed by the trifecta of sulphur, water and oxygen. The combination of these three elements is in the ratio 2:1:4 and the chemical formula of sulphuric acid is H2SO4.
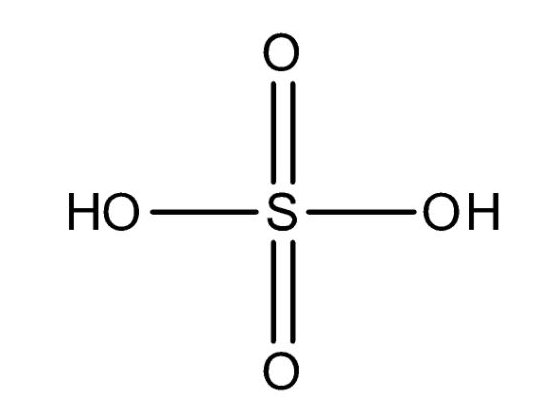
Pure sulphuric acid is impossible to find on earth since sulphuric acid has a very high affinity towards water vapour and gets dissolved in it. The structure of sulphuric acid contains a central sulphur atom that is surrounded by two oxygen atoms and two hydroxyl groups (OH).
Structure of Sulphuric Acid
The central sulphur atom forms double bonds with each of the two oxygen atoms and has a single bond with the two oxygens in the hydroxyl group. Sulphur forms six bonds and has a formal charge of zero. The two single oxygen atoms are double bonded, have two lone pairs of electrons each and a formal charge of zero. The hydroxyl groups have a formal charge of zero and the oxygens in the hydroxyl group have two lone pairs of electrons each.
Sulphuric acid is colourless and odourless acid. It is known for its dehydrating properties and is used as a dehydrating agent often . It is viscous in nature and miscible with water. The mixing of sulphuric acid with water generates a huge amount of heat. Sulphuric acid is always added to water and not the other way around, as the vice versa releases a tremendous amount of heat causing the mixture to boil and splatter drops of sulphuric acid.
Contact Process of manufacturing Sulphuric acid
The production of sulphuric acid is the backbone of many industries. Sulphuric acid preparation is so important that a country’s industrial strength can be guessed by the amount of sulphuric acid that it produces.
The best method in present times to produce high concentrations of sulphuric acid is the contact process. Contact process is a four stage process. The process is started by the formation of sulphur dioxide and ends at the formation of sulphuric acid by dissolving oleum in water. The most important of these processes is the second process that involves conversion of sulphur dioxide to sulphur trioxide that is then used to produce oleum.
Sulphur Dioxide formation
Sulphur dioxide is formed at the industry levels in two ways. Either by heating pure sulphur in the presence of oxygen or by roasting the metal sulphides to obtain sulphur dioxide. We shall see both these processes;
Burning Sulphur in air
The burning of any substance in air in the presence of oxygen, also referred to as combustion, leads to the formation of oxides of that substance. Similarly burning sulphur in the presence of oxygen results in sulphur getting oxidised to form sulphur dioxide. The reaction can be given as
S + O2 + Heat → SO2
Roasting of metal sulphides
Roasting involves heating metal sulphide ores in excess air. This causes the sulphur that is present in them to form oxides and get released in the gas form.
The reaction for roasting zinc sulphide (a sulphide ore of zinc) can be given as
2ZnS + 3O2 → 2ZnO + 3SO2
2. Generation of Sulphur trioxide from Sulphur Dioxide
At the second stage, sulphur dioxide is made to react with excess oxygen to yield sulphur trioxide. But the formation of sulphur trioxide is a very sensitive process to temperature and pressure. The reaction is given as
2SO2 + O2 2SO3
The above reaction is exothermic with the heat enthalpy of the reaction being
ΔH = –196 kJ/mol
According to Le Chattelier’s principle, a low temperature shall favour the formation of sulphur trioxide but a very low temperature will also mean that the rate of the reaction will be too slow to produce economical results. Therefore a compromise temperature of 450 degrees celsius is used in the reactor towers.
Again a high pressure shall favour the formation of more sulphur trioxide, yet the reaction is carried out at 1-2 atm pressure. This is because the increase in the rate of the reaction is not economical when compared to the overheads of increasing the pressure.
Vanadium Pentoxide is the catalyst that is used to push the equilibrium to the right side.
3. Formation of Oleum
Now that sulphur trioxide is formed, it is dissolved in sulphuric acid to form oleum. The direct addition of sulphur trioxide to water also yields sulphuric acid but the result is extremely exothermic. Therefore the direct addition of sulphur trioxide to water yields acid vapours and not liquid sulphuric acid.
On the other hand, oleum can be easily dissolved in water to form highly concentrated sulphuric acid. The reaction is not exothermic compared to directly dissolving sulphur trioxide in water and also allows greater control over the concentration of acid that is formed.
The reaction is given as
SO3 + H2SO4 → H2S2O7
4. Dissolving Oleum in Water
Oleum is then dissolved in water to yield sulphuric acid. The reaction is then given as
H2S2O7 + H2O → 2H2SO4
Conclusion
Sulphuric acid or the oil of vitriol, is a very corrosive and hazardous acid. It is formed by the trifecta of sulphur, water and oxygen. The combination of these three elements is in the ratio 2:1:4 and the chemical formula of sulphuric acid is H2SO4.
The best method in present times to produce high concentrations of sulphuric acid is the contact process. Contact process is a four stage process. The process is started by the formation of sulphur dioxide and ends at the formation of sulphuric acid by dissolving oleum in water.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





