Maltose are a type of carbohydrate. Carbohydrates are one of the nutrients that our bodies require to function correctly and are one of the body’s main sources of energy. Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen are the most common elements found in them. Maltose is created by joining two glucose units. Glucose is made up of six carbon atoms, six oxygen atoms, and twelve hydrogen atoms.
Structure and Formula of Maltose
Maltose chemical formula can be written as- C12H22O11
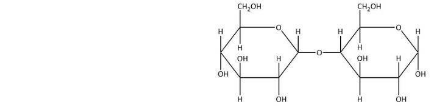
Maltose represents a type of carbohydrate, it comprises Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen. Generally a maltose is formed by combining two glucose units together via O-glycosidic bond. The 1st carbon or the alpha carbon(C1) is attached to the second glucose molecule at the fourth carbon(C2) atom. The link is referred to as ‘α’ since the glycosidic bond of the anomeric carbon (C1) atom lies at the opposite plane of the CH2OH unit of the same ring.
If this glycosidic bond of anomeric carbon is present in the same plane to CH2OH unit then it would refer to as β(1,4) and the resulting compound is known as cellobiose. The 1st Carbon or the anomeric carbon (C1) of the second glucose molecule which cannot be involved in glycosidic bond and represents α- or β-anomer depending upon the bond direction of hydroxyl group with respect to CH2OH unit of same ring thereby resulting in the formation of α-maltose or β-maltose.
During this formation, one molecule of Oxygen and two molecules of Hydrogen is lost as water. Due to the presence of two glucose molecules maltose is also referred to as disaccharide. Maltose is formed with the help of an enzyme diastase by hydrolysing starch.
Hence, the effective atomic number of this compound is 36, which is equal to the atomic number of krypton(36).
Properties of Maltose
It is a reducing sugar due to the presence of a free aldehydic group at one of its carbon atoms.
It is found in white powder or crystal form.
Maltose on reaction with sulphuric acid forms carbon-dioxide, water and sulphur dioxide.
C12H22O11 + 24H2SO4 → 12CO2 + 35H2O + 24SO2
Maltose upon hydrolysis forms ethanol and carbon-dioxide.
C12H22O11 + H2O → 4C2H5OH + 4CO2
Hydrolysis of maltose with maltase enzyme also converts maltose into glucose.
C12H22O11 + H2O → 2C12H22O11
Maltose can be detected with the help of Woehik test or Fearon’s test.
The melting point of maltose is found to be 160-165 °C.
Solubility of maltose is 1.080 g/mL (at 20 °C).
The density is 1.54 g.cm-3 and molar mass is 342.297 g.mol-1.
Uses of Maltose
Maltose can be used as a source of low-cost sugar in the form of corn syrup.
It can be used in making beer and in the malting process of barley this malting process helps in adding sweet flavour to barley.
Because of maltose’s caramel-like taste it can be used in bakeries, soft drinks, infants food, alcoholic drinks, sweets and can also be used in sugar free products.
Amylase an enzyme helps in production of maltose during germination of seeds by hydrolysing starch to a disaccharide.
Partially starch is transformed into maltose with the help of amylase at the time of digestion. The maltase secreted by the intestines helps in conversion of maltose into glucose. This glucose can be used by the body or it can be stored in the liver in the form of glycogen.
Difference between Maltose, Sucrose and Lactose
Maltose, Sucrose and Lactose all of these are disaccharides of glucose but all three of them differ in their structure:
A maltose is formed by two molecules of glucose.
A sucrose is formed by a combination of a fructose and a glucose molecule.
Whereas a lactose is formed by a galactose and a glucose molecule.
Conclusion
Maltose is a component of malt which is obtained by softening the grain in water. It can be found in varieties of partially hydrolyzed starch products such as corn syrup, maltodextrin and acid thinned starch. Maltose can be broken down in humans by various maltase enzymes and giving two molecules of glucose which can be further broken down to produce energy or it can also be stored in the form of glycogen. Lack of an isomer of maltose namely sucrase-isomaltase in humans results in sucrose intolerance. With the help of this article you will be able to get a clear concept of maltose structure, its properties, uses and also its difference from sucrose, lactose and cellobiose.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





