In coordination chemistry, ligands are molecules or ions that act as Lewis bases and donate their electron density to the vacant hybrid orbitals of the metal. They form coordinate covalent bonds with the metal. Ligands can be classified into various types based on their denticity, charge, and field strength. They are so important that they also determine the magnetic properties, geometry, and colour of coordination compounds. The word ‘ligand’ comes from Latin, which means ‘to bind’. It binds with the metal centre and forms coordination compounds.
Ligands Meaning
Ligands, as specified above, donate electron density to the metal ion. Going by this very definition, it is obvious that the ligand must have either a lone pair of electrons or a negative charge. Based on this, ligands can be of two types – neutral and anionic.
Anionic ligands are the ones that have a negative charge on them. There can either be molecular ions or atomic ions.
Examples of atomic anions are halide ions, oxide, and nitride.
Molecular anions are composed of more than one type of element.
Examples are hydroxide, cyanide, thiocyanide, nitrate, sulphate, acetate, etc.
Knowing the charge and name of some of the most important anionic ligands is important.
Name of the anion | Symbol | Charge |
Hydride | H– | -1 |
Chloride | Cl– | -1 |
Fluoride | F– | -1 |
Bromide | Br– | -1 |
Iodide | I– | -1 |
Oxide | O2- | -2 |
Sulphide | S2- | -2 |
Nitride | N3- | -3 |
Cyanide | CN– | -1 |
Isocyanide | NC– | -1 |
Sulphate | SO42- | -2 |
Thiosulphate | S2O32- | -2 |
nitrite | NO2– | -1 |
nitrate | NO3– | -1 |
thiocyanate | SCN– | -1 |
Isothiocyanate | NCS– | -1 |
Oxalate | C2O42- | -2 |
Acetate | CH3COO– | -1 |
Neutral ligands have a lone pair of electrons that they can donate to the metal. The most common examples are as follows:
- Water (H2O)
- Ammonia (NH3)
- Carbonyl (CO)
- Nitrosyl (NO)
- Methylamine (CH3NH2)
- Triphenylphosphine (PPh3)
Denticity
One of the most important concepts associated with ligands is that of denticity. Denticity is defined as the number of donor sites present in the ligand. Let’s take the example of halides. They are anions of group 17 elements. One halide ion can bind in only one way with any metal.
Now let’s compare it with the cyanide ion (CN-). There are two donor sites – C and N. The ligand can bind with the metal through either.
Now, let’s take the example of oxalate ion (C2O42-). There are two oxygen ions that can simultaneously bind with the metal and form a coordination complex.
Ligands can be classified based on their denticity:
Unidentate Ligand: If a ligand has only one donor site/group, it is called unidentate. Examples are Cl-, NH3, etc.
Multidentate Ligand: It is called multidentate if a ligand has more than one donor site/group. Multidentate ligands show a chelate effect. It can further be divided into the following types based on the number of donor sites:
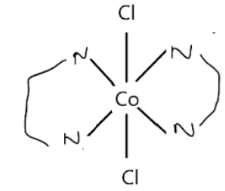
Bidentate Ligand: They have two donor sites, and both of them can participate in the bond formation simultaneously. Ethylenediamine is an example of a bidentate in which two nitrogen atoms can donate electrons simultaneously to the metal centre.
Tridentate and tetradentate ligands have three and four donor sites, respectively. Diethylenetriamine is a tridentate ligand having three nitrogens that can donate electrons. Triethylenetetrammine is a tetradentate ligand having four nitrogens.
Hexadentate: There are six donor sites. Example: EDTA
Polydentate Ligand: When a ligand can exhibit multiple denticities depending on the external conditions, it is called polydentate. EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetate) is an example that can donate a different number of electron pairs, ranging from one to six. It can bind with the metal centre via two nitrogens or four acetate groups’ oxygens.
Ambidentate: A ligand that has more than one donor site but only one of them can be involved in bonding at one time. For example, SCN is ambidentate because it can donate from sulphur and nitrogen centres. NO2- is ambidentate as it can donate from oxygen and nitrogen centres.
Hapticity
Hapticity of a ligand is defined as a binding ligand with the metal centre through a series of contiguous atoms. Multiple atoms can coordinate with the metal via pi-bonding interactions. Ligands that exhibit hapticity are cyclopentadienyl anion, benzene, etc. It is represented by the Greek symbol 𝞰. The number of atoms coordinated with the metal at a given type is written at the top right corner of this symbol.
For example, if only two atoms of benzene are coordinated with the metal, it would be called 𝞰2-benzene. If four atoms are coordinated, then 𝞰4-benzene.
Examples of such coordination compounds: ferrocene (iron is bonded with two cyclopentadienyl rings), nickelocene, etc.
Conclusion
Ligands are lewis bases that can bind with the central metal ion and donate their electron density to their vacant orbitals. They can be classified into various types based on their denticities. They can be unidentate, multidentate, ambidentate, or polydentate. Multidentate ligands show a chelate effect, which increases the stability of the coordination complex.
Hence, the effective atomic number of this compound is 36, which is equal to the atomic number of krypton(36).
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out