Isomers of a compound can be defined as molecules having the same chemical formula but different spatial orientation or structural arrangements.
Let’s take the example of a simple organic molecule – pentane (C5H12).
H3C – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – CH3 (straight chain)
H3C – CH (CH3)- CH2 – CH3(branched chain in which one methyl group is attached to second carbon from the left)
H3C – C(CH3)2 – CH3 (there is a carbon atom to which four methyl groups are attached)
All the above are isomers of pentane having the same chemical formula but different structures.
Isomerism can be of two types—structural isomerism and stereoisomerism. In the former, the chemical formula is the same, but the linkages of molecules and atoms may be different, as seen in the pentane example.
In stereoisomerism, however, there is a difference only in the spatial arrangement. Stereoisomerism may further be divided into geometrical and optical isomerism.
Geometrical Isomerism in coordination compounds notes
More than one kind of ligand must be attached to the metal, i.e., the compound must be heteroleptic.
Square Planar Compounds of the form AB2C2:
They exist in cis and trans forms. Trans is when the same ligand is opposite to each other.
Trans form Cis form
The first structure is trans, and the second is cis.
Let’s take the example of [Pt(NH3)2Cl2]
Cis form Trans form
The first compound is cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II). Two chloride ions are adjacent to each other and two amine molecules are adjacent to each other as well.
The second compound is trans-diamminedichloroplatinum(II). The two amine and chloride molecules are placed opposite to each other, respectively.
Octahedral Compounds of the form AB2C4:
They exist in cis and trans forms depending on the position of B. If B is opposite to each other, we get trans-isomer; else, we get cis-isomer.
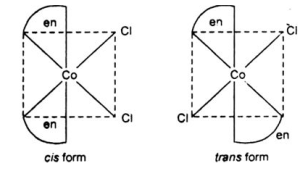
Compound [Co(NH3)4Cl2]+ is an octahedral compound that exists in the cis and trans forms. The first figure represents the cis-isomer, and the second one shows the trans-isomer of the compound.
Octahedral Compounds of the form AB3C3:
They exist in fac and mer forms. Fac form is when a ligand is present at the adjacent vertices of the octahedral. In the mer form, one pair of ligands of the same type would be opposite to each other, as in the left figure. Ligands are said to be positioned around the meridian of the polyhedron, as in the right figure.
Mer isomer Fac isomer
[Co(NH3)3(NO2)3] exists in fac and mer form as follows:
The left one is mer and the right one is fac.
Optical Isomerism in coordination compounds notes
Optical isomers of coordination compounds are the non-superimposable mirror images. It is observed most commonly in those octahedral compounds that have bidentate ligands coordinated to the centre metal ion. For example: [Co(en)3]3+
The left isomer is dextro (it rotates the plane of polarised light in the right direction), and the right isomer is laevo (it rotates the plane of polarised light in the left direction).
Structural Isomerism in coordination compounds
It can be further classified into the following types:
Linkage Isomerism
Coordination Isomerism
Ionisation Isomerism
Solvate isomerism
Linkage Isomerism in coordination compounds
This type of isomerism exists in complexes that have an ambidentate ligand. The ligand can coordinate with the metal ion through two donor sites. An example of ambidentate ligand is thiocyanate (SCN-), which can coordinate via nitrogen atom or sulphur atom (NCS-).
Coordination Isomerism in coordination compounds
It exists in compounds having two coordination spheres – one cationic and one anionic. Ligands can be exchanged between the two entities. An example is [Co(NH3)6][Cr(CN)6]. In this, the coordination sphere with Co is cationic and the other one is anionic. However, once the ligands are exchanged, we get [Cr(NH3)6][Co(CN)6].
Ionisation Isomerism in coordination compounds
It happens when the ion outside the coordination sphere replaces a ligand directly bound to the metal centre. [Co(NH3)5(SO4)]Br has bromide as the counter ion. However, Br- can replace sulphate inside the coordination sphere to give [Co(NH3)5Br]SO4.
Solvate Isomerism in coordination compounds
It is a type of ionisation isomerism in which the solvent acts as a ligand. For example, in [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3, one chloride counter anion can replace one of the aqua ligands and become [Cr(H2O)5Cl]Cl.H2O
Conclusion
Isomerism in coordination compounds can be of two types – structural isomerism and stereoisomerism. Stereoisomerism is when the isomers are different in terms of spatial arrangement. It can again be of two types – geometrical and optical. Geometrical isomers can exist in cis and trans forms or in the fac and mer forms. Structural isomerism can be classified into four types – linkage isomerism, coordination isomerism, ionisation isomerism, and solvate isomerism.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out