Imines are organic compounds where nitrogen forms a double bond with the carbon atom of any group. If the nitrogen is attached to alkyl groups, it is termed a Schiff base. German chemist Albert Ladenburg coined the term imine in 1883. The general formula of imines is R2C=NR. Aldimine is an imine analogue of aldehyde. The formula is R-CH=N-R’. Similarly, ketimines are imine analogues of ketones. An important member of aldimines is the Schiff base which has all alkyl or aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom with no hydrogen atom attached. Imines can be synthesised from primary amines and aldehydes. There are various reactions in which imines take part. Imines can be converted into amines, aldehydes and ketones.
Imine synthesis
Imines can be synthesised from various compounds like primary amines, aldehydes, etc.
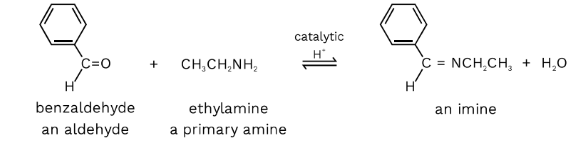
- The reaction of ketone, aldehydes with ammonia or primary amines produces an imine derivative commonly known as Schiff base. This is a condensation reaction where a molecule of water is eliminated. The reaction is acid-catalysed and reversible in nature. This reaction occurs at a regulated pH of 5. If the pH increases, OH will not be protonated in the intermediate step and removal of water will not take place. If the pH is low, then the imine conjugate will become non-nucleophilic, and the reaction will not proceed. This reaction is a nucleophilic addition reaction. An intermediate, which is hemiaminal, is formed. It then proceeds with the removal of water.

- Metal carbenoids with organic azides also form imines.
- Condensation of carbon acids with nitroso compounds form imines.
- Schmidt reaction is where alkenes and hydrazoic acid react to form imines.
- Hoesch reaction is where nitrile, hydrochloric acid and an arene reacts to form imines.
Imine conversion
Imines can be converted to aldehyde, ketones, etc., with different processes.
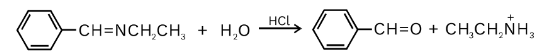
Hydrolysis: Imines react with water to form either aldehyde or ketones. The reaction takes place in the presence of an acid catalyst. Initially, in the presence of water, the imine nitrogen is protonated, which leads to the formation of an iminium ion. The ion then undergoes 1,2 addition of water. The formed compound then undergoes transfer of proton followed by 1,2 elimination of ammonia, which leads to the formation of an oxonium ion. This oxonium ion is deprotonated to form a ketone compound respectively.
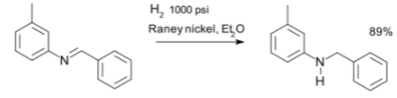
- Reductive amination: Imines can form amines with the process of reductive amination, like in the synthesis of m-tolyl benzyl amine. The commonly used reducing agent in this reaction is sodium borohydride (NaBH4). Sequential reductive amination results in the synthesis of tertiary amines. Intramolecular reductive amination results in the formation of cyclic amines in the presence of a catalyst NaBH3CN.
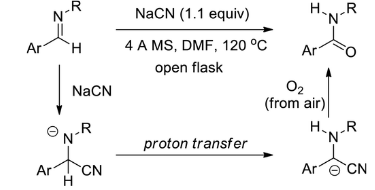
- Imines can be converted to amides from aromatic aldehydes in a metal-free aerobic oxidation in the presence of cyanide. Here, cyanide is added to the imine, followed by proton transfer from carbon to nitrogen in the imine. This leads to the formation of carbanions of alpha-amino nitriles that then undergo oxidation reactions to form amides.
Uses of imines
- Imines are used in the formation of dyes.
- Imines can also be used in the manufacturing of coordination polymers.
- Imines also have importance in biology as enzymes use imines in their reaction mechanisms. For example, the formation of an imine bond between the carbonyl group of 1 amino acid and the amine of the lysine.
- The formation of imine is also a very important reaction in the field of chemistry and biology.
Conclusion
Imines are organic compounds where nitrogen and carbon are covalently attached with a covalent double bond. The general formula of imines is R2C=NR. Imines can be further divided into primary and secondary imines. Imines derived from aldehyde are known as almidine, and imines derived from ketones are known as ketimines. Imines are commonly known as Schiff bases. They are generally used as catalysts, pigments and dyes, corrosion inhibitors, intermediates in organic reactions and also as polymer stabilisers. They are also known to have antimicrobial, antiviral and anticancer properties. They play an important role in reactions like decarboxylation, transamination, etc. Imines undergo hydrolysis reactions to form aldehyde and ketone. Imines undergo reductive amination to form amines and sequential reductive amination to form tertiary amines. It also undergoes intramolecular reductive amination to form cyclic amines.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





