Hydrogen halides are a type of diatomic, inorganic compounds which function as Arrhenius acids. The hydrogen halides can be represented by formula HX where X represents any of the halogens (Chlorine, Fluorine, Bromine, Iodine and Astatine). At Standard Temperatures and Pressure all hydrogen halides exist as gases. The hydrogen halides are also known as hydrohalic acids. The diatomic molecules of hydrogen halides do not have the tendency to ionize in the gas phase. This helps the chemist to distinguish hydrogen chlorides from hydrochloric acid. Hydrogen Chloride at room temperature occurs in the form of a gas and reacts with water to give acids. Due to the formation of acids the diatomic molecules are reformed with difficulty via distillation. Hydrogen Chloride acts as a primary component of gastric acid, whenever it is present in the form of hydrochloric acid. Majority of hydrogen halides occur in sea water as halide ions.
Synthesis of Hydrogen Halides
Reaction of hydrogen with chlorine and fluorine leads to the production of hydrogen fluoride and hydrogen chloride respectively. These gases are formed upon reaction of halide salts with sulphuric acid. Hydrogen bromide can be prepared upon reaction of hydrogen with bromine in the presence of a platinum catalyst at high temperatures. Whereas, hydrogen iodide is synthesized by reaction of iodine with hydrogen sulphide or hydrazine. Hydrogen iodide is found to be the least stable hydrogen halide.
Properties of Hydrogen Halides
General properties
Alongwith the decreasing bond dissociation enthalpy from fluorine to iodine the thermal stability of halides also decreases in the same trend. This can be seen in an example of hydrogen iodide which decomposes at 40°C whereas hydrogen chloride and hydrogen fluoride are stable at these temperatures.
Again at room temperatures halides of hydrogen are present in gaseous form whereas hydrogen fluorides at this temperature can be readily liquefied. The hydrogen halide gases are found to be colourless, whereas with moist air they give white fumes because of the production of droplets of hydrohalic acid. Hydrogen Fluoride (HF) is an exception for having high melting and boiling points; this is due to the presence of strong hydrogen bonds. This property is not seen in any other hydrogen halide.
Boiling points of hydrogen halides
Hydrogen fluorides possess highest boiling points followed by hydrogen iodide, hydrogen bromide and at last hydrogen chloride which have the lowest boiling point. The high boiling points of HF is because of hydrogen bond formation which is absent in other three halides, since their electronegativities are not large enough to form a dipole. Due to an increase in halogens size the boiling point increases from HCl to HI. This shows that Van der Waals force of attraction is stronger down the group, and requires high amounts of energy to overcome the intermolecular forces. Thus, higher the energy higher is the boiling points of hydrogen halides. The boiling point strengths can be written as follows:
HF>HI>HBr>HCl
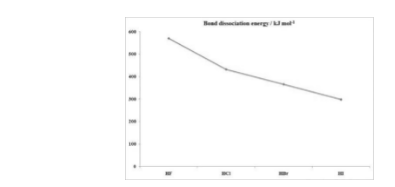
Acidic strength of hydrogen halides
According to Bronsted Lowry’s definition hydrogen chloride refers to an acid as it is able to transfer protons to other different species. HCl, HBr, and HI all the three are strong acids whereas HF is a weak acid the acidic strength of the above compounds increases with a decrease in pKa values this can be as follows: HF (pKa = 3.1) < HCl (pKa = -6.0) < HBr (pKa = -9.0) < HI (pKa = -9.5).
The reason for hydrogen fluorides being a weak acid as the trend of ionic size increases down the group. Since fluorine is present at the top of the halogen series, this shows that the F– ions is the smallest halide and the electrons are arranged around the nucleus leading to a shorter H-F bond. Thus, these types of shorter bonds are relatively more stable and difficult to break. Following fluorine, trends down the chlorine changes. Since chlorine is a larger atom with more electrons the H-Cl bonds are longer and weaker. When water is present the electrostatic attractions among water’s partially negative oxygen and partially positive hydrogen are stronger enough to break the H-Cl bond and dissociate the ions in solutions. For HBr and HI the same reason is only accepted. Due to larger Br– and I– ions, the H-Br and H-I bonds are weaker and dissociate in solutions. The trend can be written as follows: HF<HCl<HBr<HI
Reactions
Hydrogen halides upon dissociation with an exothermic material such as water gives different types of acids. These acids are stronger and reflect their tendency to ionize in aqueous solution producing hydronium ions (H3O+). Homoconjugation is the main reason for the complicated acidic strength of hydrofluoric acid.
Hydrogen halides react with ammonia to form ammonium halide
HCl + NH3 → NH4Cl
Conclusion
In hydrogen halides the boiling points and melting points of hydrogen fluoride is greater than others due to electronegativity. Thus, HF is able to form hydrogen bonds. We hope that this article was able to clear all your doubts regarding hydrogen halides, its synthesis, properties (both acidic and boiling) and reactions. We have also discussed a few questions for a better understanding.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





