Introduction
A homologous series is a collection of molecules with comparable chemical characteristics and functional groups that differ by CH2 from one another. In organic molecules with the same general formula, carbon chains of various lengths have been discovered. A series of organic compounds is formed by organic compounds that differ from one another by a repeating unit and have the same general formula. The most fundamental homologous series in organic chemistry is formed of alkanes

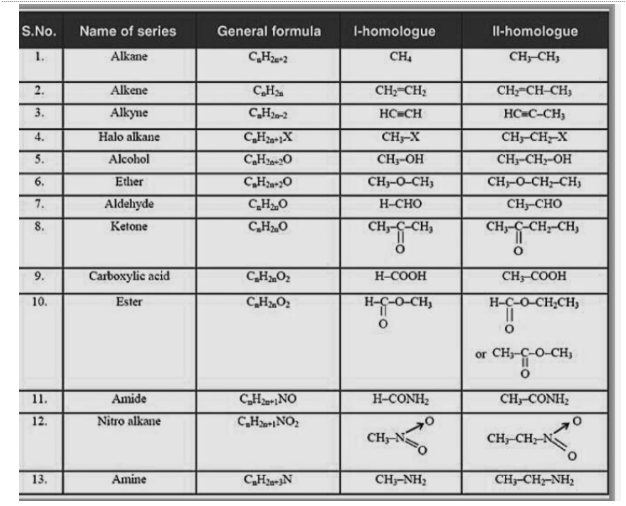
Homologous series examples
Each subsequent member differs from the previous by one CH2 unit. CH4 and C2H6 have a -CH2 unit difference, and C2H6 and C3H8 have a -CH2 unit difference as well. CH4, C2H6, and C3H8 are all homologous as a result. Alkenes with ethene as the first member and C3H6, C4H8, and C5H10 as the subsequent members show the same effect. They differ from one another by a –CH2 unit. Alkenes have the formula CnH2n.
The functional groups are the same for all members of this series. They have identical physical qualities that increase in mass in a fixed gradation. The characteristics of CH3OH, C2H5OH, and C3H7OH are similar and vary gradually as the molecular mass of subsequent members of the series increases. This is because the number of bonds increases as the molecular mass of the molecule increases. As a result, attributes reliant on the mass and total number of bonds in a compound, such as melting and boiling temperatures, solubility, and other properties, change gradually as the molecular masses of the compounds increase. Members of a homologous series have the same chemical features because they all have the same functional groups.
This series has allowed scientists and engineers to dig deeper into a variety of chemical compounds.Based on data from other members of the same homologous series, they can predict the properties of organic compounds belonging to that series. Organic compound research has been simplified.
Significance of homologous series
- Homologous series is a property of carbon compounds in which the number of carbon and hydrogen atoms in hydrocarbons varies according to a single parameter.
- Homologous series aid in the determination of the structure of each consecutive member of the series, as well as the prediction of the properties of those members.
Conclusion
Because the functional group of the molecule does not vary, homologues have comparable chemical properties. Keep in mind that the functional group is just the part of the molecule that is reactive or can change in chemical processes. Because each molecule in a homologous series has the same functional group, the homologues have identical reactivities.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





