Greenhouse gases are naturally present in the Earth’s atmosphere in less than 1%. Their role is significant in supporting life on Earth as they maintain the hospital temperature for survival. Without greenhouse gases, the Earth’s average temperature would fall from 14 degrees Celsius to a freezing minus 18 degrees Celsius! However, today anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions lead to rising Earth’s temperature and warming it to an above-normal level. It occurs due to the increased amount of greenhouse gases in the Earth’s atmosphere (Troposphere) that prevents the solar radiation from falling onto it to escape via infrared radiation.
This phenomenon is Global Warming which is already wreaking havoc on the natural greenhouse effect balance. In this study material notes on the Greenhouse effect, we shall discuss everything about the greenhouse effect.
Greenhouse Gases
Almost 75% of the Solar radiation that falls on the Earth’s surface gets absorbed by greenhouse gases and water vapours and warms it up. It is responsible for maintaining the Earth’s average temperature hospitable at 15 degrees Celsius for living organisms. However, if the greenhouse gases amount cross more than a suitable degree, it causes unnatural heating of the Earth, known as Global Warming.
- Greenhouse gases are all those gases that absorb the sun’s infrared radiations as heat and prevent them from escaping back to space and contributing to the Earth’s warming.
- It includes Carbon dioxide, Ozone, Methane, chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), NO, etc.
Natural Greenhouse Effect
The natural greenhouse effect is the trapping of heat by the atmospheric gases analogous to a glass-covered greenhouse used to grow vegetables in cold climates. The blanket of air functions as glass and traps the sun’s heat to maintain the Earth’s constant temperature.
Functioning of a GreenHouse
- As the sun’s radiations pass through the transparent glass, they get absorbed by the soil and plants.
- The warmed soil and plants emit infrared radiations that get partly reflected or reabsorbed as infrared radiations can’t pass through the glass.
- The following continuous mechanism helps the heat to remain trapped in the greenhouse and maintain the temperature.
Global Warming & Greenhouse Effect
- Greenhouse gases like Carbon oxide are pervious to around 90% of the solar radiation but impervious to infrared or heat radiation.
- Thus, when the greenhouse exceeds their delicate proportion in the atmosphere, they start to entrap more heat and disturb the natural greenhouse effect balance.
- Out of all the greenhouse gases, Carbon dioxide is the prime contributor to global warming.
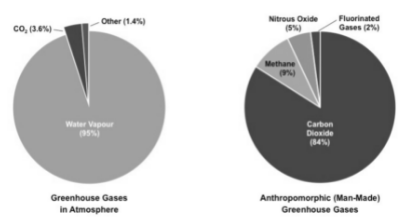
Contribution of Greenhouse Gases
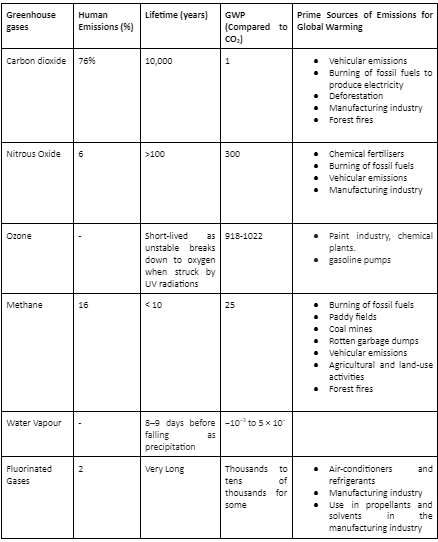
- Not all greenhouse gases contribute equally to the greenhouse effect. The contribution of greenhouse gases depends on their concentration, lifetime, and global warming potential (GWP).
- GWP refers to the amount of energy a gas absorbs, usually over 100 years w.r.t emissions of one ton of CO2.
- Water vapours contribute the most to the greenhouse effect, followed by Carbon dioxide while the least by Ozone. However, Methane has more GWP than CO2, more capacity to absorb heat and re-radiate as infrared. But since Carbon dioxide is much more than Methane in the Earth’s atmosphere, its effect is much more prevalent.
Ways to Reduce Enhanced GreenHouse Effect
- Minimise burning of fossil fuels
- Reduce dependence on automobiles
- More use of renewable sources of energy
- Energy-saving electronic devices
- Afforestation
Do Greenhouse gases remain in the atmosphere?
No, such gases are usually removed from the atmosphere periodically. Carbon dioxide also gets absorbed in the ocean to maintain the equilibrium of the atmospheric and oceanic concentrations. It also is absorbed by other carbon sinks like plants, soil, etc.
Though, the synthetic greenhouse gases that arise anthropogenically can get destroyed only by sunlight above the troposphere and include gases like Ozone.
Effects of Global Warming
- Melting of polar ice caps and glaciers leading to flooding
- The rise in oceanic water level
- Frequent and intense weather changes and events like droughts, hurricanes, etc.
- Alter natural habitat and ecosystems
- High global temperatures contribute to widespread incidences of infectious diseases like Yellow fever, Malaria, Dengue, etc.
- It results in ocean acidification due to the dissolution of Carbon dioxide in the water
- Destroying aquatic life due to the warming of water bodies
4-Ways to Reduce Enhanced GreenHouse Effect
- Minimise burning of fossil fuels
- Reduce dependence on automobiles
- More use of renewable sources of energy
- Energy-saving electronic devices
Conclusion
The solar radiations fall on the Earth’s surface and get reemitted as infrared radiations. These infrared radiations are a type of short-wave radiation that gets absorbed by the greenhouse gases present in the atmosphere.
Carbon dioxide is the major contributor to the greenhouse effect and thus global warming. The prime sources of greenhouse gases emissions include Transportation, Manufacturing & Industrial sectors, Electricity generation, Forest fires, etc.
We can reduce global warming by focussing on sustainable development with the switch to renewable resources, etc.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





