By the process of induction, friction and conduction a neutral object loses or gains its valence electron and gets charged. The surrounding space of the charge gets modified and converted to an electric field which is the basic source of electrostatic force. The electric field is a vector field. In this electric field the presence of another charge is modified by the electric field and an attraction or repulsion force is created and the direction of the force also depends on the charge participle whether it is positive or negative. So before understanding the force due to the electric field we have to know about the some basic properties of charge, electrostatic force and electric field.
Charge
Charge is the property of matter due to which it produces and experiences both electric and magnetic effects. As mass is responsible for Gravitational force,Similarly Charge is responsible for electric force.Fundamentally there are two types of charge one is positive charge and another is negative charge. If a body loses electrons it becomes +ve, If a body gains electrons it becomes -ve. A charge particle can create an electric field. When a charge particle comes in a electric field it experience force,
Electrostatic force
The force experienced by a charge particle due to another charge particle or due to an electric field called electrostatic force. It can be attractive or repulsive depending upon the nature of charges and electric field. The force of attraction and repulsion was given by the Coulomb;s law of electrostatics.
Coulomb’s Law of Electrostatic
Coulomb’s Law of Electrostatic states that “ The force of interaction between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of charges and inversely proportional to square of distance between them. And the force acts along the line joining the centre of two charges.”
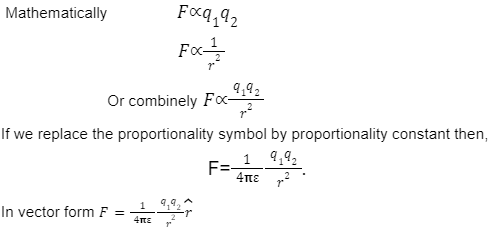
Where, F is the electrostatic force.
q1,q2= magnitude of two charges.
r=Separation between q1and q2
r= Unit vector directed along the line joining the centre of two charges.”
Now let us discuss the electric field.
Electric field
When an electric charge is kept in space or in some medium it develops a force field around it, which is called electric field.
We can also define the magnitude of the electric field at a point due to a charge q as the force experienced by a unit positive charge at that point due to charge q.

- it’s direction is the direction along which the test charge will move when it is allowed freely
- If the source charge is +ve electric field away from it.
- If the source charge is -ve electric field is towards it.
Force due to electric field
Electric field gives the information about electrostatic force to electric charge. Electric field consists of a number of electric field vectors each point in space around the point charge.
Consider a point charge q that creates an electric field around it. To measure the electrostatic force in that electric field place a test charge q0 in that electric field. If the

As we write in vector form that, if the test charge is a positive charge then direction of force Fand the direction of electric field E are the same. In case of negative charge the directions are opposite.
Here we consider a test charge whose magnitude is very small such that it does not affect the electric field. If we take a large value then there may be some error in measurement of force.

Conclusion
In all electrical instruments the force due to the electric field is used as a fundamental principle. In order to calculate drift velocity, relaxation time in current we use the formula F=Eq0.
It is the fundamental relation which is useful to derive the expression for electric
field at any point due to the charged body. This study material contains notes on electric charge electric field and the force experienced by the charged particle due to the electric field.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out