The human body is a single structure which consists of billions of smaller structures. The smallest structure of the human body is referred to as a cell. An average adult has around 30-40 trillions of cells. These cells constitute various elements. Approximately 99% of the mass of an average human body consists of mainly 11 chemical elements out of 92 naturally occurring elements on earth, which are found in larger quantities. Any amount equal to or less than 0.01% or is referred to as a trace element. The eleven most important elements present in the human body are hydrogen, carbon, Nitrogen, Oxygen, sodium, magnesium, Phosphorus, Sulphur, chlorine, potassium and Calcium.
Elements in the Human Body
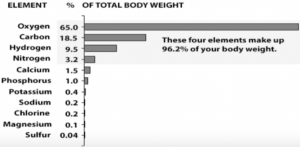
The top four elements found in the human body are oxygen, hydrogen, carbon and nitrogen. Most of the body mass of an individual comprises oxygen. The second most important element present in the human body is carbon.
Oxygen
- The atomic number of oxygen is 8 and it comprises 65% of body weight.
- It is the most abundant element present in the human body.
- It is mainly present in the form of water (bound to hydrogen).
- It can be seen in all the four of the major classes of organic molecules: protein, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids.
- Function: Oxygen functions as a key element in the aerobic cellular respiration. It is used up by the mitochondria inside the cells to produce energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Carbon
- The atomic number of carbon is 6 and it comprises 18% of a human body weight.
- It is considered as the second most abundant element present in the human body; it also serves as the basis of organic chemistry.
- Function: The chains of carbon help in building up carbohydrates, fats, nucleic acids and proteins.
Hydrogen
- The atomic number of hydrogen is one and it comprises 10% of a human body weight.
- Most of the hydrogen present in the human body is bound with oxygen and present in the form of water.
- Function: It is an important element in organic molecules. And perform important functions in the form of water.
Nitrogen
- The atomic number of nitrogen is 7 and it comprises 3% of a human body weight.
- Human beings obtain nitrogen from food.
- Function: Nitrogen plays an important role as being an essential component of the nucleic acids DNA and RNA.
Calcium
- The atomic number of calcium is 20 and it comprises 1.4% of a human body weight.
- Function: Calcium is an important element which is present in the bones and teeth of a human body. It acts as a structural material of bones and is also essential for protein regulation and muscle contraction.
Phosphorus
- Atomic number of phosphorus is 15 and comprises 1% of body weight.
- Phosphorus is present in the ATP which is the energy carrier molecule in the cells.
- Function: Phosphorus is found in our bones and teeth. It serves as an important electrolyte and is used to transmit nerve impulses and regulate heartbeat.
Potassium
- The atomic number of Potassium is 19 and comprises 0.25% of body weight.
- Function: It is an important electrolyte. Potassium helps in the regulation of heartbeat and is also used in nerve conduction. Potassium plays an important role in the functioning of cells in the body.
Sulphur
- The atomic number of sulphur is 16 and comprises 0.25% of body weight.
- It is mainly present in several amino acids which are used in the formation of proteins in the body.
- Function: They mainly help in the formation of proteins and help them to perform their functions.
Sodium
- The atomic number of sodium is 11 and comprises 0.15% of body weight.
- It is an important cation in the human body.
- Functions: Sodium plays an important role in the muscle function and impulse transmission from the nerve cells.
Chlorine
- The atomic number of chlorine is 17 and comprises 0.15% of body weight.
- Function: It is a negatively charged ion which mainly plays an important role in maintaining the fluid balance in the body. It also helps in the formation of teeth and bones. It also helps in the proper functioning of the liver and helps in the elimination of organic waste from the body.
Magnesium
- The atomic number of magnesium is 12 and it comprises 0.005% of human body weight.
- Functions: Magnesium helps in binding of ATP and nucleotides. It also acts as an important cofactor in many enzymatic reactions.
Conclusion
We can study the composition of the human body in several ways. Most of the human body is made up of water. Apart from water there are certain different elements that comprise the human body. Approximately 99% of the mass of the human body mainly consists of 11 chemical elements out of 92 naturally occurring elements on the earth. Different elements play different roles in the human body. Oxygen functions as a key element in the aerobic cellular respiration. The chains of carbon help in building up carbohydrates, fats, nucleic acids and proteins. Hydrogen is an important element in organic molecules. And perform important functions in the form of water. Nitrogen plays an important role as being an essential component of the nucleic acids DNA and RNA. Calcium acts as a structural material of bones and is also essential for protein regulation and muscle contraction. Phosphorus is found in our bones and teeth. It serves as an important electrolyte and is used to transmit nerve impulses and regulate heartbeat. Potassium helps in the regulation of heartbeat and is also used in nerve conduction. Sulphur mainly helps in the formation of proteins and helps them to perform their functions. Sodium plays an important role in the muscle function and impulse transmission from the nerve cells. Chlorine plays an important role in maintaining the fluid balance in the body. It also helps in the formation of teeth and bones. Magnesium helps in binding of ATP and nucleotides.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





