A molecule that has the tendency to react with other molecules containing a donatable pair of electrons is an electrophile. A molecule that contains a donatable pair of electrons or lone pair that can be easily shared with electrophile is a nucleophile. A type of reaction in which an electrophile and nucleophile react together and get added to a double or triple bond is called an electrophilic addition reaction.
A wide variety of useful products are obtained by undergoing electrophilic reactions. Electrophilic addition reactions are observed in compounds containing Pi bonds, so the reaction involves the removal of a Pi bond and the creation of another Sigma bond to it.
Addition Reaction
When two or more molecules combine to form an adduct or addition, the result is an addition reaction. It is a common organic chemistry reaction. The scope of this reaction is limited to molecules that have unsaturation. So in order to proceed with an addition reaction, there must be a double or triple bond present.
An electrophilic addition reaction is a type of addition reaction in which molecules that have an unsaturation, like a double or triple bond, undergo an addition reaction with the formation of an intermediate electrophile. Hence, it is called electrophilic addition. It is also called the reverse of elimination reaction.
Meaning of Electrophilic Addition
An electrophilic addition reaction has a wide application in organic chemistry. A chemical compound or an organic compound having a double or triple bond—containing a Pi bond—undergoes this reaction. The bond that is present in the double or triple bond is broken, and in turn, a new sigma bond is formed.
Steps Involved
The steps for electrophilic addition reactions involve the formation of a carbocation intermediate. A molecule that has an electron-rich centre or unsaturation is first attacked by an electrophile H+ from HBr. Then, a bond is formed with the carbon and the electrophile. Later, this results in the formation of a carbocation formation of the covalent bond between the carbon and the electrophile. The reaction that occurs this way is shown below:-
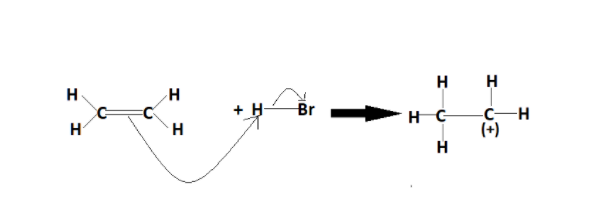
In the first step, a carbocation is formed, which reacts with another electron-rich species to form another sigma bond or covalent. The breaking of the pi bond involves the formation of two sigma bonds.
The electrophilic addition reaction is a reaction that consists of two steps. The second step, which is the addition of nucleophile or electron-rich species or nucleus loving species, is just the same as the SN1 reaction. The figure below shows the reaction taking place over here :-
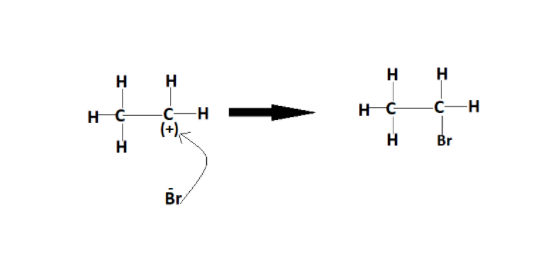
Thus, the electrophilic addition results in the formation of saturated compounds.
Conclusion
The reactions which involve the use of electrophiles or work on the basis of electrophiles are electrophilic addition reactions. As the reaction does not take place without an electrophile or electron-loving species, the name electrophilic reaction is given to this type of addition. There are a wide variety of useful organic compounds that can be synthesised easily with the help of this reaction. There are two steps involved in this type of reaction—the first step is the attack of the electrophile, and the second step is the attack of a nucleophile or nucleus-loving species since a carbocation intermediate is formed.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





