The electric field in a region is described as a vector quantity E; the same field can also be described as a scalar quantity V at each point of space. This scalar quantity is defined as electric potential.
Consider when a test charge q is moved by an electric field from point a to b, while all the other charges remain fixed. If the electric potential energy changes by Ub – Ua due to this displacement, we say that the potential difference between the point a and b as
Vb-Va=(Ub-Ua)/q
The SI unit of potential difference is one volt (1V) in honour of the Italian scientist and electrical experimenter Alessandro Volta, which equals 1 joule per coulomb:
1V = 1 volt = 1 J/C = 1 joule/ coulomb
An instrument that measures the difference of potential between two points is known as a voltmeter.
Relation between potential difference and work done
Now, suppose the test charge is moved in an electric field without changing its kinetic energy. The total work done on the charge should be zero from the work-energy theorem.
If Wext is the work done by the external agent and Wel is the work done by the electric field as the charge moves,
We have,
W(total)=0
Or, Wext+Wel=0
Or, Wext= -Wel
Or, Wext= -U
Where ΔU is the change in electrical potential energy.
Using this equation and the equation that we found out for the potential difference, we can write,
Va-Vb=Wext/q
In other words, the potential of a concerning b equals the work that must be done to move a unit charge slowly from a to b against the electric force.
Since potential energy is a scalar quantity, the potential difference will also be a scalar quantity. Thus, if V1 is the potential at a given point due to the charge q1, and similarly V2 is the potential at the same point due to charge q2, the potential due to both the charges will be V1 + V2.
Electric potential difference from an electric field
We know that the force F on a test charge q can be written as F = qE, where E is the electric field. So from the equation of work done by the electric force as the test charge moves from A to B, we have,

The value of Va – Vb is independent of the path taken from a to b, just as the value of Wa-b is independent of the path. To interpret the above equation, remember that E is the electric force per unit charge on a test charge. If the line integral is positive, the electric field does positive work on a positive test charge as it moves from a to b. In this case, the electric potential decreases as the test charge moves, so the potential energy per unit charge decreases as well; hence Vb is less than Va, and Va-Vb is positive.
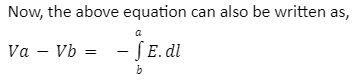
This equation has a negative sign compared to the previous equation, and the limits are reversed; hence both the equations are equivalent.
But the above equation has a different interpretation. To move a unit charge against the electric force, we must apply an external force per unit charge equal to -E, equal and opposite to the electric force per unit charge E.
Both the above equations show that the unit of potential difference is equal to the unit of the electric field multiplied by the unit distance. Hence, the unit of the electric field can be expressed as volts per metre.
Differential form: The above equation can be written as,
dV= -Edlcos
Or, -dV/dl=Ecos
We see that -dV/dl gives the component of the electric field in the direction of displacement dl.
If we move a distance dl in the direction of the field, ɸ is zero and, -dV/dl = E is maximum. Thus, the electric field is along the direction in which the potential decreases at the maximum rate.
If a small displacement dl is perpendicular to the electric field, then ɸ = 90o and, dV = -E.dl = 0. The electric potential does not change in a direction perpendicular to the electric field.
Equipotential surfaces
If a surface is drawn in such a way that the electric potential is the same at all the points of the surface, it is called an equipotential surface.
The components of the electric field parallel to an equipotential surface are zero, as the potential does not change in this direction. Hence, the electric field is perpendicular to the equipotential surface.
For example, for a point charge, the electric field is radial, and the equipotential surfaces are concentric spheres with the centres at the charge.
Conclusion
In the above article, we have learned about what is an electric potential difference.
Followed by its formulation and its relation with the work done. Then we saw a relationship between the electric field and the potential difference. We derived integral as well as differential forms of potential. Lastly, we saw what are equipotential surfaces with the help of an example.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





