The atomic number of an element is defined as the total number of electrons or protons in an atom. Effective atomic number is defined as the total number of electrons around the metal (its own electrons + the electrons donated by the ligands). It is abbreviated as EAN or Zeff, and effective atomic number rule importance in coordination chemistry is unparalleled. It is also referred to as the Sidgwick rule as Nevil V. Sidgwick coined it. He concluded that the metal in coordination compounds, by virtue of their own electrons and ligand electrons, have 18 electrons, which means they have a noble gas-like character.
Effective Atomic Number Rule Importance
Effective atomic number essentially means the total number of electrons that the metal effectively has. Metal in a coordination compound has its own electrons and those donated by the ligand. The effective atomic number is associated with an atom’s effective nuclear charge.
In [Ni(CO)4], Sidgwick observed that nickel has the same number of electrons as a noble gas. This is why it is also called the ‘inert gas rule’ as the stability associated with such 18-electrons compounds is very high, similar to the stability of inert gas. Nickel has 28 protons in its nucleus. However, due to screening by inner-shell electrons, an electron does not experience the electrostatic force of 28 protons but a lower number of protons.
Effective atomic number rule states that a compound is thermodynamically stable when it has 18 valence electrons or electrons equal to 36, 54, or a noble gas configuration. So, this rule gives information about the stability of the complex.
Effective Atomic Number rule:
Effective Atomic Number = atomic number of a metal + (Number of ligands x electrons donated by each ligand) – positive charge on the metal.

Hence, the effective atomic number of this compound is 36, which is equal to the atomic number of krypton(36).
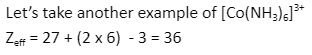
Important Concepts Related to the EAN Rule
The atomic number of the metal must be known to calculate the effective atomic number. It should be known how many electrons are donated by one ligand.
Electrons donated by the most commonly found ligands are:
Ligand | Electrons donated |
Ammonia | 2 |
Water | 2 |
Carbonyl | 2 |
Nitrosyl | 2 |
Chloride | 1 |
Fluoride | 1 |
Oxide | 2 |
Cyanide | 1 |
Isocyanide | 1 |
Thiocyanide | 1 |
Isothiocyanide | 1 |
Acetate | 1 |
Nitride | 3 |
Nitrate | 1 |
Nitrite | 1 |
Iodide | 1 |
𝜼5-Cyclopentadienyl | 5 |
An anionic ligand donation to the metal is equivalent to the charge on the ligand. For example, the contribution of all halides is considered one, which is equal to the charge on them.
A neutral ligand’s donation to the metal is equivalent to 2.
Difference between 18-electron rule and effective atomic number rule
Although the two rules are used interchangeably, there are specific differences between them. The 18-electron rule states that the compound should have 18 electrons in its valence shell to be stable. However, the effective atomic number rule says that the metal should have a total number of electrons equal to the electrons of noble gas in its period (36, 54, or 86). It is concerned with the total number of electrons, as opposed to the 18-electron rule concerned with valence electrons.
Let’s take the example of [Fe(CO)5]
As per the 18-electron rule, we would have to calculate using the following formula:
Valence electrons of the metal + contribution by the ligand – positive charge on the coordination sphere + negative charge on the coordination sphere
So, for [Fe(CO)5], it would be 8 + 5×2 = 18. 8 is the number of valence electrons in iron.
Conclusion
Effective atomic number rule importance is that it gives valuable information about the stability of the complex. It is believed that every compound wants to have an effective atomic number equal to the atomic number of noble gases in its period. It is when the compound has the most stability. To calculate it, we must know the atomic number of the metal, the contribution of the ligands, and the charge on the metal centre. The contribution of anionic ligands is equal to the charge on them, and for neutral ligands, it is two. For ligands showing multiple hapticity, it can vary depending on how many ligand atoms are bound to the metal at a time.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




