Introduction
It is important to purify organic compounds, however, it is a very critical procedure. The purification of any organic compound depends on its solubility and the impurities that it contains. Generally, purification is done to remove impurities of a compound. Some of the general purification methods are;
- distillation
- crystallisation
- sublimation
- Differential extraction
- chromatography
The general principle behind the procedure involves the shaking of organic compounds in a separating funnel, from which after some time the two different layers formed are extracted. The aqueous layer is separated by opening the tap at the bottom and again a small amount of aqueous solution is added into the organic solvent. The steps are repeated several times until the entire amount of organic compound is extracted. The organic layers obtained from all steps are taken in a distillation flask followed by distillation off of the organic solvent leaving the organic compound behind in the distillation flask. However, the efficiency of this process depends on the number of times the extraction steps are followed. The larger the amount of solvent, the greater the amount of material extracted. This method applies to non-volatile compounds like benzoic acid extracted from water using benzene.
We will study the various steps and procedures involved in Differential extraction in the upcoming section.
Body
Differential extraction in chemistry
It is also known as differential lysis. It is a method employed to separate any organic component from an aqueous solution. The principle behind the separation is the different solubilities of compounds present in an aqueous solution. It should be noted that the organic solvent used must be immiscible with an aqueous solution so that it can easily form layers and could be separated by a separating funnel easily.
It has been widely used in DNA profiling techniques and various forensic techniques.
Differential extraction method
This method is used for immiscible liquids like oil and water. The immiscible liquid is taken in a separating funnel and left undisturbed for a while. After some time they separate according to their gravity. The heavier one settles at the bottom and the lighter one is left on top. Then collection is done.
The purification can also be achieved by the separation of liquids depending on their solubilities. For example, phenol can be extracted using Sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
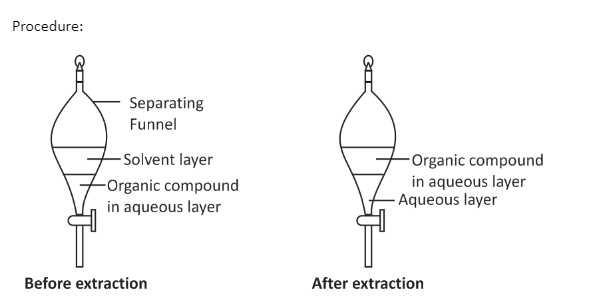
- Shaking- The aqueous solution containing the immiscible liquids/organic substances is shaken with a suitable specific organic solvent that is immiscible in water but can easily dissolve the organic substance that is supposed to be separated.
- Layers formation- after shaking two different layers are formed i.e. the aqueous layer and the solvent layer. The aqueous layer contains the organic compound.
- Separating funnel- the layer containing organic substance is separated by a separating funnel leaving behind the impurities in the aqueous layer.
- Distillation- Finally the organic substance is removed by distillation to obtain the organic compound/substance.
Differential extraction chemistry
Differential extraction technique allows the selective lysis of DNA and isolation of DNA from epithelial and sperm cells mostly in cases of sexual assault to determine DNA profiles of the victim.
- By staining and light microscopy, the presence of a sperm cell in a rectal/vaginal sample is identified, then the subject’s epithelial cells are lysed by phenol/chloroform DNA extraction and DNA is extracted.
- The sperm cell’s DNA precipitates attached with protamines(rather than histones) held with disulfide bonds and the epithelial DNA is removed and saved.
- a chemical called DDT (dithiothreitol) is used to disrupt the sulphur bonds in protamines and release DNA.
- Once the detachment of DNA to protamines occurs, it is prone to standard Extraction methods of DNA.
- This results in the separation of two different DNA fractions from one sample i.e. one fraction of the victim and one fraction of the perpetrator.
However, this method is quite difficult to carry out as it involves a large amount of labour and requires a huge amount of time.
Workflow of Differential extraction method:
The differential extraction technique helps in the selective physical isolation of male fractions. The various steps are described as follows:-
- Lysis of epithelial cells: the epithelial cells are firstly lysed by the help of the addition of SDS and proteinase K. (The sperm cells are resistant to lysis by SDS and Proteinase K).
- Centrifugation:- after the lysis of epithelial cells, centrifugation is done to pellet any intact sperm cells.
- Separation:- the supernatant that contains the DNA from male and female epithelial cells are removed to a separate tube.
- Lysis of sperm cells:- The isolated sperm cells are lysed by the addition of DDT, SDS and proteinase K. The DDT breaks the disulphide bonds present in sperm nuclear membranes, hence releasing the sperm cell DNA.
- The DNA in the sperm cell fraction and the epithelial cell fraction is then isolated by organic methods and non-organic methods.
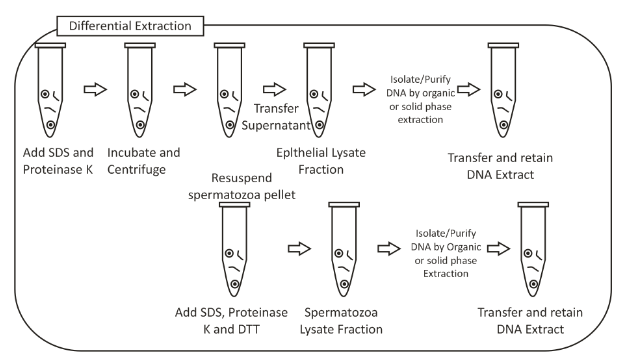
The above image depicts the workflow of the Differential extraction method.
The method simplifies the interpretation of DNA profiling results by increasing the chances of obtaining a clear male DNA profile from sperm fraction. Recently a new method of multistep nucleic acid extraction was introduced to provide high-quality DNA Lysates. It is suitable for DNA extraction procedures by Differential extraction for forensic samples like epithelial cells, saliva or sperm cells.
Conclusion
This method is used to recover the organic compounds from aqueous solutions. It is simply done by shaking the compound in a separating funnel with a specific solvent which is capable of dissolving the organic compound but is immiscible in the water. Some of the examples are; ether, chloroform, benzene, carbon tetrachloride and Sodium hydroxide. After shaking the separating funnel (containing the organic compound and solvent) the funnel is left undisturbed for some time until the organic solvent and water forms different layers. The lower aqueous layer is further run oit/collected out by opening the tap of the funnel. Again the aqueous solution is poured into the funnel and mixed with a small quantity of organic solvent. The process is repeated several times until the organic compound is extracted. The efficiency of this process depends upon the number of times the extraction is repeated. This method is generally applied to non-volatile compounds such as benzoic acid which can be extracted from its water solution with the help of benzene.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





