At room temperature, diborane is a colourless gas with an unpleasant, sweet odour. It easily generates explosive combinations when mixed with air. At room temperature, diborane will spontaneously ignite in moist air. Diborane is employed as a reducing agent, a rubber vulcaniser, a catalyst for hydrocarbon polymerisation, a flame-speed accelerator and a doping agent in rocket propellants. It’s also used in electronics to give pure crystal electrical characteristics.
Water decomposes diborane releasing hydrogen gas, a volatile gas and boric acid, an uncontrolled substance. Its vapours are heavier than air. After long-term exposure to low levels or short-term exposure to high concentrations, inhalation of these vapours can have adverse health effects. It’s also used in electronic materials.
All about Diborane
Preparation of diborane
We can prepare diborane by the action of metal hydride with boron. This process is used for industrial production. To obtain diborane in small quantities by the reaction of iodine with sodium borohydride, diglyme is needed.
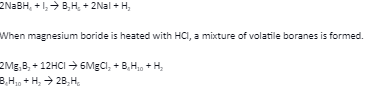
Properties
Boranes are diamagnetic compounds that are colourless in nature and have low thermal stability. Diborane is a sweet-smelling gas that is highly poisonous at room temperature. It’s also highly reactive. It generates higher boranes at higher temperatures, releasing hydrogen.
Diborane reacts with water and alkali to give boric acid and metaborates.
Hydroboration
At room temperature, diborane combines with alkenes and alkynes in an ether solvent. Hydroboration is a reaction that is commonly employed in synthetic organic chemistry, particularly for anti-Markovnikov’s addition.
Action of air
Pure diborane does not react with air or oxygen at room temperature, but in the impure form, it gives B2O3 along with a large amount of heat.

Structure of Diborane
Two bridging hydrogens connect two BH2 units in diborane. Therefore, it has 8 B-H bonds in it. On the other hand, Diborane only has 12 valence electrons, which are insufficient to create regular covalent bonds. The normal covalent bonds make up the four-terminal B-H bonds (two centre – two-electron bond or 2c-2e bond). The bridging bonds will require the remaining four electrons. Two electrons are used in each of the two three-centred B-H-B bonds. As a result, these are three-centre-two-electron bonds (3c-2e). The boron in diborane is sp3 hybridised.
Three of the four sp3 hybridised orbitals contain a single electron, and the fourth orbital is empty. Each boron has two half-filled hybridised orbitals that overlap with the two hydrogens to produce four-terminal 2c-2e bonds, leaving one empty and one half-filled hybridised orbital. The B-H-B bond is formed by overlapping one boron’s half-filled hybridised orbital, the vacant hybridised orbital of the other boron, and the half-filled 1s orbital of hydrogen.
Bonding
Diborane has a D2h structure with four terminal hydrogen atoms and two bridging hydrogen atoms. According to the molecular orbital theory model, the links between boron and the terminal hydrogen atoms are standard 2centre-2electron covalent bonds. However, in contrast to hydrocarbon compounds, the relationship between the boron atoms and the bridging hydrogen atoms is different.
Each boron has one valence electron left for further bonding after attaching to the terminal hydrogen atoms with two electrons. Each of the bridging hydrogen atoms contributes one electron. As a result, four electrons hold the B2H2 ring together, which is an example of 3centre-2electron bonding. This form of bond is sometimes called a ‘Banana Bond’.
Bonding
Diborane and its derivatives are important organic synthesis reagents for hydroboration, which involves adding alkenes across B-H bonds to produce trialkyl boranes. Diborane is utilised as a reducing agent with a reactivity similar to lithium aluminium hydride. The molecule quickly converts carboxylic acids to alcohols, whereas ketones only react slowly with acid as starting materials.
Uses of Diborane
- Diborane is utilised as a propellant with a high energy density.
- In organic chemistry, it is used as a reducing agent.
- It is used in welding torches.
Conclusion
One of the most typical reaction patterns is the formation of adducts with Lewis bases. Such initial adducts frequently develop swiftly to produce other products. Borane-tetrahydrofuran, for example, degrades to borate esters, which are commonly used as a diborane replacement. Its dimethyl sulphide adduct is an important chemical reagent. Ammonia diborane is coupled with ammonia borane to produce diammoniate of diborane, or DADB, depending on the conditions.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





