A coordination entity is an arrangement consisting of a metal ion that acts as a centre, to which neutral or anionic ligands are covalently bonded. A coordination entity is enclosed inside square brackets. It may be charged or neutral, depending upon the complex. The metal inside the coordination entity has a fixed coordination number (which Werner referred to as the secondary valency of the metal). It wants to satisfy its coordination number and it does so by combining it with ligands. Coordination entity is the essence of a coordination complex.
Important Terms Pertaining to Coordination Entity
Centralion
Each coordination entity has a central metal ion, which occupies a central position and binds the other atoms or groups of atoms (ligands) to itself.
For example, in K4[Fe(CN)6]4- the central ion is Fe2+. The oxidation state of the metal can be calculated by taking into consideration the charge of ligands and that of the coordination sphere. In this case, charge on the sphere = -4. Charge of 1 cyanide ion = -1, so that of six cyanide ions = -6. Now, the charge on iron has to be +2 for the overall coordination sphere to have a charge of -4.
Ligands
They are the Lewis bases that bind with the ligand and donate their electron density into their vacant orbitals. The atom in the ligand which is directly bound to the central atom is known as donor atom. For example, in K4[Fe(CN)6]4- the ligand is CN– ion, but the donor atom is carbon. In [Co(NH3)6]Cl3 the ligand is NH3 molecule and the donor atom is nitrogen.
Ligands can be anionic or neutral. Common examples of anionic ligands are – fluoride, chloride, cyanide, thiocyanide, acetate, oxalate, oxide, iodide, bromide, sulphate, carbonate, etc. Examples of neutral ligands are carbonyl, nitrosyl, ammonia, water, etc.
Ligands can also be classified on the basis of their denticity, which is defined as the number of donor atoms present in the ligand. Based on their denticity, there are following kinds of ligands:
- Unidentate Ligand: If a ligand has only one donor site/group, it is called unidentate. They are also known as ‘one-toothed’ for they attack (or bite) the metal only at only one place. Examples are Cl-, NH3, etc. They donate one lone pair of electrons to the metal.
- Multidentate Ligand: If a ligand has more than one donor site/group, it is called multidentate. It can further be divided into the following types based on the number of donor sites:
- Bidentate Ligand: They have two donor sites, and both of them can participate in the bond formation simultaneously. Ethylenediamine is an example of a bidentate in which there are two nitrogen atoms that can donate electrons simultaneously to the metal centre.
- Tridentate and tetradentate ligands: They have three and four donor sites respectively. Diethylenetriamine is a tridentate ligand having three nitrogens that can donate electrons. Triethylenetetrammine is a tetradentate ligand having four nitrogens.
- Hexadentate: There are six donor sites. Example: EDTA
- Polydentate Ligand: When a ligand can exhibit multiple denticities, it is called polydentate. EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetate) is an example that can donate a different number of electron pairs, ranging from one to six. It can bind with the metal centre via two nitrogens or via four acetate group’s oxygens.
The actual denticity depends on external factors like pH.
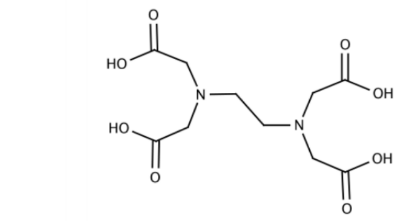
- Ambidentate: A ligand that has more than one donor site but only one of them can be involved in bonding at one time. For example: SCN– is ambidentate because it can donate from both sulphur and nitrogen centres. NO2– is ambidentate as it can donate from both oxygen and nitrogen centres.
Geometry of the Compound
The geometry of the coordination compound is decided by the geometry of its coordination entity only. The most common geometries are tetrahedral, square planar, and octahedral. Their geometry is explained by valence bond theory.
Let’s take the example of [Fe(CN)6]4-
Fe2+ has an electronic configuration of d6, meaning electrons in one d-orbital are paired and in the rest of them are unpaired. However, cyanide is a strong field ligand, so it pairs up all the electrons in the d-orbitals of iron.
As a result, two d-orbitals become vacant. The compound’s net hybridisation becomes d2sp3 meaning that it has an octahedral geometry.
Let’s take the example of [ZnCl4]2-
Zn2+ has an electronic configuration of d10, meaning that there is no vacant d-orbital. The compound exists in the hybridisation of sp3, forming a tetrahedral compound.
Compounds with a coordination number of 4 form tetrahedral or square planar compounds. Tetrahedral is formed in case of sp3 hybridisation, which is observed in the presence of weak field ligands like iodide, chloride, bromide, etc.
Square planar is formed in case of dsp2 hybridisation, which is observed in the presence of strong field ligands which cause unpaired electrons in the d-orbitals to pair up. Examples are cyanide, carbonyl, etc.
Conclusion
Hopefully, you are clear with the concepts of introduction to coordination entities. Its study is important as the colour of coordination compounds is decided by the coordination entity only. The optical and magnetic properties are also decided by the coordination entity. Let’s move on to coordination entity frequently asked questions.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





