The elements of groups 3-12 are placed in the periodic table, in the D-Block segment, where the D-Orbitals eventually fill throughout each of the four long periods.
In the central section of the periodic table, the D-Block is flanked by the s- and p-blocks. The elements of the D-Block are given the term ‘transition’ because of their position between s- and p-Block elements. When the D-orbitals of the penultimate energy level in their atoms absorb electrons, the transition metals three rows, 3d, 4d, and 5d, are produced. 6d’s sixth row is still incomplete.
General Properties of D-Block Elements
D-Block elements contain metallic properties like high tensile strength, ductility, ductility, high thermal and electrical conductivity, and metallic lustre. Except for Zn, Cd, Hg and Mn, they all have one or more conventional metal structures at room temperature.
With the exception of Zn, Cd and Hg, transition metals (D block elements) are very hard and not volatile. They possess extremely high melting and boiling points.
The high melting temperatures of these metals are responsible for the involvement of more (n-1)d electrons in addition to ns electrons in the interatomic metallic bonding.
Atomic and Ionic Size Variation in D-Block Elements
In general, as the atomic number increases, the radius of ions with the same charge in a series decreases. This is because each time the nuclear charge increases by one, a new electron enters a D-orbital. It is important to remember that the electronic shielding effect of D-Block elements is not very strong; therefore, the net electrostatic attraction between the nuclear charge and the outermost electrons increases with decreasing ionic radius.
The atomic radii of a given series follow the same pattern. Within a series, however, the fluctuation is fairly minimal.
Formation of Complex Compounds
Metal ions bind to a multitude of anions or neutral molecules in complex compounds, resulting in complex species with distinct characteristics.
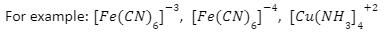
Transition metals form a large number of complex compounds. The availability of D orbitals for bond formation is due to the smaller size, high ionic charge, and availability of empty D orbitals of metal ions.
Magnetic Properties
When a magnetic field is applied to a substance, the most common magnetic behaviours are diamagnetism and paramagnetism.
The applied field repels diamagnetic substances while it attracts paramagnetic substances. Ferromagnetic substances are those that are strongly attracted to one other. In fact, ferromagnetism is a type of paramagnetism at its most extreme. Many transition metal ions have paramagnetic properties.
The presence of unpaired electrons leads to paramagnetism, where each electron has a magnetic moment related to spin angular momentum and orbital angular momentum. The contribution of orbital angular momentum is effectively quenched in compounds of the first series of transition metals and therefore has no effect. Number of unpaired electrons determines magnetic moment, which is calculated using the ‘spin-only’ formula:
Mathematically written as: =n(n+2)
Here, n represents the number of unpaired electrons, and m represents the magnetic moment in Bohr magneton units (BM).
The magnetic moment increases as the number of unpaired electrons rises. As a result, the observed magnetic moment can be used to estimate the number of unpaired electrons in an atom, molecule, or ion.
Conclusion
The D-Block, which comprises Groups 3-12, occupies the majority of the middle section of the periodic table. These elements’ inner D-Orbitals are gradually filled. The 4F and 5F orbitals are gradually filled in the elements of the F-Block, which is at the bottom of the periodic table.
Transition metals can be found in a wide range of complex compounds. The smaller size of metal ions, high ionic charge, and availability of empty D orbitals all contribute to the use of D orbitals for bond formation.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





