Entropy is one of the state functions used to measure the randomness of the thermodynamic system. Entropy is usually measured for a system and surroundings together to calculate the overall change in the Entropy.
∆S = Ssystem – S surroundings
Or
∆S = Sfinal – S initial
Or
∆S = S2-S1
Only the difference between the initial and final state entropy values can be calculated to measure the overall Entropy. Energy and Entropy are related but are different terms. Energy is usually conserved according to the law of conservation of energy. Energy cannot be created and cannot be destroyed but can be converted from one form to the other. Unlike energy, Entropy is not conserved, and there is no principle for the Entropy conservation.
Entropy is a physical property, and its value can change only if the state of the system changes; hence the change in Entropy is zero (∆S = 0) if there is no change in the state of the system.
Briefing the content
The Entropy of the system is a measure of disordered ness. The Entropy of the system increases with the increase in the randomness of the system. Entropy can be the least value for solids and the maximum value for gaseous particles.
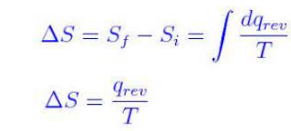

Zero entropy condition
The zero entropy condition is also called the absolute zero condition. This condition is observed in pure and perfectly crystalline solids at absolute zero temperature. This statement is from the third law of thermodynamics. Absolute zero temperature is the temperature of -273 degrees Celsius or 0 Kelvin where the particles cease to move or freeze with the least motion, then the system is said to be very much ordered, and Entropy is considered to be zero where the state of every particle can be known. But zero entropy condition is not possible because all the natural processes are spontaneous and move towards the increase in entropy direction. The least entropy condition can be attained in many solids where the particles just vibrate in their mean positions without showing movement.
Example: Perfectly crystalline solid at zero Kelvin
Minimum entropy condition: Entropy can take up a minimum value for a system if the system is more ordered and possesses less energy. The processes during which the decrease in Entropy is observed are freezing, condensation, and solidification. All these processes are non-spontaneous.
- Freezing: When a liquid freezes to solid ice in a refrigerator, the particles come close to each other and become more ordered, reducing the Entropy in the final state compared to the initial state. This is a non-spontaneous process carried out by supplying energy and does not take place on its own.
- Condensation: When the liquid is heated turns to vapour, and when it’s no longer supplied with energy, vapour starts cooling and turns to liquid droplets where the system is changing its state from less ordered to more ordered form. So, Entropy decreases.
- Solidification: When vapour particles of solid get cooled, which are formed by the heating of solid, then the Entropy of the system decreases. Compared to vapour form, particles in solid form are more ordered and less random, and so the Entropy is a lesser value.
Maximum entropy condition: Entropy can reach a maximum value in the processes which are spontaneous and naturally occurring on their own without any external assistance. The processes involve melting, vaporisation or evaporation, sublimation.
- Melting: Melting is the process of turning a solid into its liquid form. Example- When an ice cube placed outside the refrigerator starts melting, and within no time, the liquid is formed. Ice has particles or molecules in an ordered way that takes up the fixed shape and crystalline, but liquid particles are free to move and more random. This process increases the Entropy of the system and hence the spontaneous process.
- Evaporation: Vaporisation is the process of turning a liquid into its vapour form. Example- When water is boiled using heat energy, particles gain energy, move far apart from each other, and exist in continuous random motion. It increases the Entropy of the system.
- Sublimation: Sublimation is the process of heating a solid and turns to a vapour form directly without forming a liquid. In this process, the system is changing from solid form to vapour form, where we observe the randomness to be increasing and hence entropy increases.
Infinite Entropy
The Maximum Entropy of the universe can be reached S=10123kB or can reach a factor of a hundred quintillion greater than today’s existing Entropy. There is no such maximum limit for Entropy since its most unusable energy and the quality of energy.
Conclusion
Entropy of a system is a relative value which depends on various factors of matter in the system and surroundings. We cannot say that entropy has a limit. So, entropy can have any value according to the conditions.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





