In chemistry, Calgon’s process can be defined as a process to create complex anions by ionising them. Calgon’s process is used to soften water by eliminating calcium and magnesium ions from hard water.
Softening of Water
What is Hardness of Water?
Water with high dissolved mineral salt content of metals such as calcium, iron or magnesium is known as hard water, whereas water free of such dissolved mineral salt content is called soft water. Calcium (Ca²+) and magnesium (Mg2+) ions are very common in hard water. If there is a concentration of various cations, the water becomes hard. Cations (metal ions) with a charge more than 1+, such as 2+, are known as multivalent cations. Ca²+ and Mg²+ are cations found in water. These ions enter a water supply leaching through aquifer minerals (such as limestones).
Calcite and gypsum are two common minerals that have calcium. Whereas dolomite is a typical magnesium mineral with calcium minerals present in it. Rainwater and other types of water can be called soft water due to the presence of fewer ions. Hard water is found in groundwater or wells. Surface water (lakes, rivers, and streams) is generally soft and has a low hardness level. Hard water is not harmful for health as such, but it leads to many damages. Water hardness may be a severe problem as it may affect everything from the production of suds in bathing and washing to the costly breakdowns of boilers, cooling towers, and other water-handling equipment.
Here is the equilibrium reaction that tells the dissolving/formation of calcium carbonate scales:
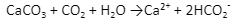
Excess of calcium and magnesium ions from hard water can be easily removed by processes such as the ion exchange process.
Water Softening process
According to Calgon’s process, water softening is a method of removing hardness from water. If the water has dissolved minerals in excess, then regular tap water also becomes hard water. The presence of high calcium and magnesium levels makes the water slimy. It becomes difficult to dissolve soaps and detergents in hard water. It can also clog pipes and cause hard water stains in bathtubs and sinks.
Water softening can help remove calcium, magnesium, and iron ions from water. These ions make it harder for elements containing other positively charged ions to dissolve in hard water. There are various methods of water softening that help to remove excess minerals from water.
Removal of hardness of water through various processes:
There are several methods to remove the hardness present in water. Some of them are:
- Chemical process of boiling hard water
- Adding slaked lime (Clark’s Process)
- Adding washing soda
- Calgon process
- Ion exchange process
- Ion exchange resins
1. Washing soda process: When chlorides and sulphates of calcium and magnesium are found in hard water, precipitates of insoluble calcium and magnesium carbonates should be filtered off. This is done by treating hard water using a specific amount of washing soda.

2. Calgon’s method: Sodium hexametaphosphate (Na⁶P⁶O¹⁸) commercial, known as Calgon, can decrease the hardness of water. The reaction is as follows:-
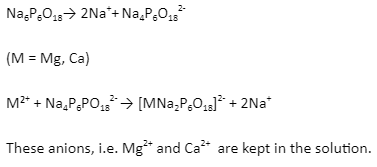
3. Ion exchange: Ion exchange is a water treatment process that involves exchanging one or more unwanted ionic contaminants with less valued ions. Both the contaminant and the mineral that is present must be exchanged and dissolved. Moreover, it should have the same electrical charge type (positive or negative).
This process aims to reduce calcium and magnesium concentration. The ion exchange method is also useful for eliminating hazardous metals from water.
4. Synthetic resins method: The synthetic resins method is a process for removing water’s persistent hardness. In this Ion exchange process, resin (RSO3H) is converted to RNA by treating them with NaCl. After this, RNA exchanges Na+ ions with Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions, thus softening the water.
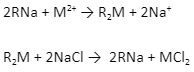
5. Adding slaked lime: One of the most common methods of water softening is chemical precipitation. Lime (calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2) and soda ash (sodium carbonate, Na2CO3) are used as chemicals in this process. Lime can remove carbonate hardness-causing compounds. If the hardness still persists, it is reduced by using soda ash.
Hardness-causing minerals can produce insoluble precipitates when added to lime and soda ash. Calcium carbonate is formed due to the presence of calcium (CaCO3). Whereas magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2) forms the precipitate of magnesium. These precipitates are removed using traditional coagulation or flocculation, sedimentation and filtration techniques.
Conclusion
Hard water contains calcium and magnesium salts due to the presence of bicarbonates, chlorides and sulphates. Ferrous ions oxidise and leave a reddish-brown stain on washed fabrics and enamelled surfaces. It is, therefore, important to remove the hardness of water to prevent damages. In this article, we have studied various methods of removing water hardness, including the Calgon process.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out



