INTRODUCTION
The smallest gathering of atoms that has the overall symmetry of a crystal, and the whole lattice is actually developed by repetition in three dimensions is named a unit. Crystalline solids display a daily and repeating pattern of constituent particles.
Unit Cell Types
- Primitive Unit Cells
Primitive Unit Cells are formed when the constituent particles possess just the corner places.
- Unit Cells that are centred
A Centred Unit Cell is one in which the constituent particles occupy places other than those at the corners. There are three different kinds of centred unit cells:
- Body Centred Unit Cell
When a constituent particle is located at the body’s centre, it is called a body-centred unit cell.
- Face Centred Unit Cell
A Face Centred Unit Cell is one in which the constituent particle is located in the centre of each face.
- End Centred
An End Centred Unit cell is one in which the constituent particle is located in the middle of two opposed faces.
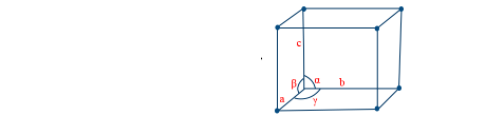
Let a = length of edge of a unit cell
r = radius of atom (point) rank of unit cell
z = Number of atoms in the unit cell
d = density of unit cell
NA = Avogadro’s number
M = Molecular mass of unit cell
Primitive Cubic Units
You may be aware that the component particles of a primitive unit cell, whether they be atoms or molecules or ions, can only be located in the corners of the unit cell. As previously mentioned, a Consequently Number of atoms in unit cell in the corner of a unit cell contributes one-eighth of itself to the total amount of matter in that unit cell. A cube now has eight corners, which is an improvement.
Consequently, in a primitive unit cell, there are eight particles at each of the cubic structure’s eight corners, for a total of sixteen particles. Because of this, the total contribution may be calculated in the following manner:
1/8 (contribution of corner atoms) × 8 (number of corners) = 1
Base Centre unit cell
Let’s now turn our attention to what the number of atoms in bcc arrangement is? In a body-centered unit cell, there are eight atoms in each of the four corners and one atom in the center of the cell. It is now possible to distinguish between particles in the center and those on the margins regarding their contributions. The periphery contributes one-eighth of a particular unit cell’s total capacity. The center unit cell is not shared by any other unit cells in the lattice. The total number of atoms in a body-centered unit cell is therefore determined as follows when we calculate the total number of atoms:
(1/8 × 8) + (1 × 1) = 2
Face Centered Unit Cells
Face-centered unit cell particles are now present throughout the edges and faces of the cubic structure, forming a face-centered unit with cell particles. The atoms in the eight corners each contribute one-eighth of the total amount of energy in the unit cell. When there is a lattice, two unit cells share the atoms at the face of the structure equally. Consequently, their contribution is just a half-atom in size, at most. Note that a cubic cell has six faces, which is important to remember. Thus, the total number of atoms in a face-centered unit cell is
(1/8 × 8) + (1/2 × 6) = 4
HCP Unit Cell Volume
A unit cell is the most minor representation of a crystal that can be made. The hexagonal closest packed (HCP) crystal structure has a coordination number of 12 and a unit cell density of 6 atoms, making it the densest crystal structure known. The face-centered cubic (FCC) structure has a coordination number of 12 and a unit cell size of 4 atoms, making it an asymmetric structure.
NUMBER OF PARTICLES PER UNIT CELL IN A CUBIC CRYSTAL SYSTEM CALCULATION:
1. Calculation of the contribution of each atom at each lattice location
- A corner atom is shared by eight unit cells. Hence Essential its contribution is = 1x(1/8)=1/8.
- Because an atom on the face is shared by two unit cells, its contribution equals =1x(1/2)=1/2.
- An atom at the center of a unit cell is not shared by any other unit cell, its contribution is=1
- An atom on edge is shared by four unit cells, its contribution is =1x(1/4)=1/4
2. Counting the number of atoms in a unit cell
- Simple [basic] unit cell: It only has eight atoms present in the corners, each of which contributes 1/8, therefore 8 x 1/8 = 1 atom.
- Body centering unit cell (BCC):
- – 1/8 x 8 = 1 atom = 1. 8 atom on corner
- 1 atom in the middle = 1 x 1 = 1
- So the total number of atoms is 1 + 1 = 2 atoms.
3. In a face-centered unit cell (FCC):
- Atomic contribution at the corner = 1/8 x 8 = 1
- Atomic contribution at faces = 1/3 x 6 = 3
- So the total number of atoms is 3 + 1 = 4.
Conclusion
We have learned that the unit cell is the basic building block of crystalline solids.Consider a binary substitutional alloy to understand better the importance of the lattice and other crystalline defects to a self-consistent thermodynamic depiction of the crystal.
The unit cell can take on a number of shapes depending on the angels among cell edges & their corresponding edges.It is the fundamental building block with a unique atomic configuration.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





