In 1913, Niels Bohr proposed the atomic Hydrogen hypothesis. It is a positively charged nucleus made up of protons and neutrons that is surrounded by a negatively charged electron cloud, according to him. In the model, electrons are arranged in atomic shells around the nucleus. Electrostatic interactions between the positive nucleus and the negative surrounds hold the atom together.
Hydrogen Energy Levels
The structure of hydrogen energy levels is described using the Bohr’s model. The maximum energy is the ionisation energy of 13.598eV, and the quantity of energy in each level is reported in eV.
Hydrogen Spectrum
- A spectrum is produced by electrons moving between these different energy levels. The Balmer equation is used to describe the four different Hydrogen wavelengths that exist in the visible light spectrum. The wavelengths are 656, 484, 434, and 410 nm, respectively.
- As an electron in an excited state goes down to the energy level n=2, photons are emitted. For all energy level transitions, the Rydberg formula (below) generalises the Balmer series. The Rydberg formula with a nf of 2 is used to generate the Balmer lines.
- The Rydberg formula describes the various transition energies that occur between energy levels.
- A photon is emitted when an electron goes from a higher to a lower energy level. Depending on the initial and final energy levels of the transition, the hydrogen atom can emit different wavelengths of light. It emits a photon with an energy equal to the square of the energy levels of the final (nf) and initial (ni).
Bohr’s Radius
If ‘e,”m,’ and ‘v’ are the charge, mass, and velocity of the electron, respectively, ‘r’ is the radius of the orbit, and Z is the atomic number, the equation for the radii of the permitted orbits ,
r = n2 xr1
Where, ‘n’ is the principal quantum number, and r1 is the least allowed radius for a hydrogen atom, known as Bohr’s radius having a value of 0.53 Å.
- The nonclassical assumption that electrons travel in specified circular orbits around the nucleus underpins Bohr’s hydrogen model. An integer, the quantum number n, is used to designate the orbits. By emitting or absorbing energy, electrons can jump from one orbit to the next.
- The following energies for an electron in the shell were computed using Bohr’s model:

- The hydrogen spectrum was explained by Bohr in terms of electrons absorbing and emitting photons to alter energy levels, where the photon energy is measured in eV, are as
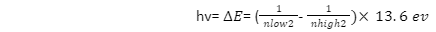
Note
- For systems with more than one electron, Bohr’s model fails.
Bohr Model for heavier atoms
- The nucleus of heavier atoms has more protons than the nucleus of hydrogen atoms. To cancel out the positive charge of all of these protons, more electrons were needed. Each electron orbit, according to Bohr, could only hold a certain amount of electrons. Once the level was filled, additional electrons would be bumped up to the next level.
- For heavier atoms, the Bohr model explained electron shells. The model explained some of the atomic properties of heavier atoms, which had never been reproduced before.
- The shell hypothesis, for example, explained why, although having more protons and electrons, atoms become smaller as they move across a period (row) of the periodic table.
Refinements and Improvements to the Bohr Model
- The Sommerfeld model, sometimes known as the Bohr-Sommerfeld model, was the most notable improvement to the Bohr model. In this model, electrons orbit the nucleus in elliptical orbits rather than circular orbits. The Sommerfeld model does a better job of explaining atomic spectral effects including spectral line splitting’s Stark effect. The magnetic quantum number, on the other hand, was not accommodated by the model.
Limitations of Bohr’s Model
- The Bohr Model was a significant step forward towards atomic theory development. It does, however, have some drawbacks.
- It goes against Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle. The Bohr Model assumes that electrons have a defined radius and orbit, which Heisenberg says is impossible.
- The size of the Bohr Model is extremely constrained. When dealing with larger atoms, poor spectral predictions are produced.
- It is unable to estimate spectral line relative intensities.
- It doesn’t account for the Zeeman Effect, which occurs when a spectral line splits into many components in the presence of a magnetic field.
- The fact that accelerating electrons do not emit electromagnetic radiation is disregarded by the Bohr’s Model.
Conclusion
In 1913, Niels Bohr proposed the atomic Hydrogen hypothesis. It’s a positively charged nucleus made up of protons and neutrons that’s surrounded by a negatively charged electron cloud, according to him. In the model, electrons are arranged in atomic shells around the nucleus. Electrostatic interactions between the positive nucleus and the negative surrounds hold the atom together. The structure of hydrogen energy levels is described using the Bohr model. Each shell corresponds to the energy levels shown. The maximum energy is the ionisation energy of 13.598eV, and the quantity of energy in each level is reported in eV.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





