Amines are derived from ammonia. Alkyl or aryl groups replace one or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia. The –NH2 group is known as the amino group. Amides have a nitrogen atom attached to the carbonyl group. Amides have similar chemical properties to that of amines. Amines are further divided into 3 categories; aliphatic amines, aromatic amines and heterocyclic amines. When an alkyl group is attached to the nitrogen it is Aliphatic amine. When an aryl group is attached to the nitrogen it is aromatic amine. When nitrogen of an amine is a part of a cyclic ring it is heterocyclic amine.
Classification
Amines can be classified into 3 categories on the basis of hydrogen atoms replaced in the ammonia molecule.
- Primary amine- 1 hydrogen molecule of ammonia molecule replaced by any functional group or aromatic ring.
H2NCH3
- Secondary amine- 2 hydrogen molecules of ammonia replaced by any functional group or aromatic ring.
CH3–H2N–CH3
- Tertiary amine- 3 hydrogen molecules of ammonia replaced by any functional group or aromatic ring.
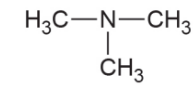
Aromatic Amine Basics
Aromatic amines are Aromatic hydrocarbons where one hydrogen molecule of the aromatic ring is replaced by an amino group.
Aromatic amines are also known as arylamines.
Examples- aniline, toluidines, phenylenediamine, etc.
Preparation of Aromatic amines
Aromatic amines can be prepared by reduction of Aromatic nitro compound.
Example- Nitrobenzene converted to aniline in presence of tin(Sn), concentrated HCl and NaOH.

Physical Properties
Aromatic amines are colourless liquids or solids with an unpleasant odour.
The melting and boiling points of aromatic amines are greater compared to aliphatic amines of the same molecular weight.
The melting and boiling point of aromatic amines also increases with increase in molecular weight of the compound.
They are completely soluble in organic solvents but insoluble in water. Exception- Aniline is more soluble in water than in an organic solvent.
Due to the presence of 2 electrons that bond directly with the benzene ring, aromatic amines do not participate in hydrogen bonding. This is also a reason for increased the boiling point of aromatic amines compared to aliphatic amines.
Chemical Properties
Aromatic amines are basic in nature due to the presence of two non-bonded electrons on the nitrogen atom.
Aromatic amines and acid form salt.
Aromatic amines denote electron pairs.
Reactions of Aromatic Amine

Diazonium salt of aromatic amines
- Diazonium salts are a group of organic compounds. The formula of diazonium salt is R-N2+X– Here R stands for an aryl group and X stands for halogens.
- Primary aromatic amines form arenediazonium salts.
Preparation of Diazonium salt
Reaction of Benzenamine with nitrous acid at 273-278K yields Benzenediazonium chloride. Diazotization is the conversion of primary aromatic amines into diazonium salts.
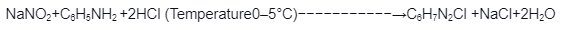
Characteristics of Diazonium salt
Benzenediazonium chloride, a colourless solid, is readily soluble in water but insoluble in organic solvents. It decomposes easily in a dry state.
Diazonium salts reactions either involve displacement of nitrogen or retention of the diazo group.
Uses of Aromatic amines
- Aromatic amines can be used in manufacturing of rubber and dyes as intermediates in Azo-dye manufacturing.
- It can also be used as pesticides due to its tumour causing properties.
- It can be used in manufacturing of drugs, dyes, resins etc.
- Often Azo dyes are used in the food industry. Like tartrazine, azorubine etc.
- Often used as acid base indicators like methyl orange.
Conclusion
Aromatic amines are amines where an aromatic ring is attached to the nitrogen of the Ammonia, hence they are aryl derivatives of ammonia. Aromatic amines are weak base when compared to ammonia due non availability of lone pairs of electrons on the nitrogen. Aromatic amines are colourless liquids or solids with an unpleasant odour. The melting and boiling points of aromatic amines are greater when compared to aliphatic amines of the same molecular weight. The Diazonium Salts formed from aromatic amines are an important chemical of the dye industry. They are used in foods as well. They are also used in pesticides due to its cancer causing properties. It can also be used as an acid-base indicator.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





