An important aspect of Chemistry is Phosphorus, a non-metal.
There are various allotropic forms of Phosphorus that exist in nature. The most important forms of phosphorus are categorised as black Phosphorus, red Phosphorus, and White Phosphorus. In this particular topic, we will learn about the Allotropic forms of phosphorus forms along with their nature and properties.
What is phosphorus?
Phosphorus was discovered by Alchemist Hennig Brand of Hamburg in 1669. The name phosphorus originated from the Greek word ‘Phos’ meaning light and ‘Phoros’ meaning bearer, creating the term ‘bringing light’. This is because the white phosphorus oxidizes in the air and glows in the dark. Atoms are made up of three kinds of smaller particles, known as protons, neutrons, and electrons.
The basic properties of phosphorus are as follows:-
- It has Atomic Number 15
- It has an Atomic mass of 30.9738 g.mol -1
- It has oxidation state ± 3, 4, 5
- It Density is 1.82 g/ml at 20°C
- Its electronic configuration is [Ne] 3s23p3
Uses of Phosphorus
White phosphorus is used in flares and incendiary materials, Red phosphorus is used in the material stuck on the side of matchboxes, used to light up. Phosphorus compounds are also used in the making of fertilizers. Ammonium phosphate is made from phosphate ores. The ores are first changed in phosphoric acids before being converted to ammonium phosphate.
Phosphorus is used in the production of steel. Phosphates are also used as an ingredient in some detergents. Phosphates are majorly used for the making of fine chinaware and special glasses.
It also has biological importance to all living things. It makes the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA and RNA. It is also important for energy transfer in cells as part of ATP and is also found in other biologically essential molecules.
Allotropic forms of phosphorus
Phosphorus is one of the multivalent non-metals belonging to the nitrogen group. It exists in nature in various allotropic forms and is an important element for the life of living organisms.
The allotropes of Phosphorus are:-
- White Phosphorus
- Black Phosphorus
- Red Phosphorus

White phosphorus is the form of phosphorus that exists in the P4 state. It is a white, colourless, or yellow waxy solid having a garlic-like smell. It does not exist in nature but is prepared from phosphate rocks. It reacts quickly with oxygen and easily catches fire at 100 to 15o above room temperature.
In the atomic structure, all 4 phosphorus atoms are linked with a covalent bond in the form of a ring. In the ring form, the subtended angle is 60 degrees, which causes an angular strain in the molecule. The alternative name of White phosphorus is Tetra phosphorus or Yellow phosphorus.
When the white Phosphorus dissolves in NaOH in an inert environment in presence of PH3, the reaction that takes place is as follows
P4 + 3NaOH + 3H2O → PH3 + 3NaH2PO2
Properties of White phosphorus are:-
- It is translucent waxy white solid
- It has a high pungent, garlic-like smell
- It is corrosive in nature
- It is highly toxic in nature
- It is a polar compound so it is not soluble in nature
- It possesses chemiluminescent properties due to which it glows in the dark
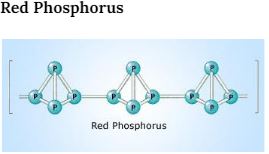
The nature of Red phosphorus is polymeric. In the structure of red phosphorus, P4 tetrahedral molecules are inter-linked in a straight chain way. The structure of red phosphorus is very close to the molecule of P4. Each phosphorus atom in the P4 molecule is attached by a covalent bond to 3 other phosphorus atoms in the tetrahedral structure. When one of these covalent bonds is disintegrated, these tetrahedral structures can forward to bond with adjustment phosphorus atoms, making a polymer-like structure.
Properties of Red Phosphorus
- Red phosphorus is dark red in colour and has an iron-grey lustre
- It has no smell. So, it is an odourless element.
- It is present in an amorphous state
- It is not a toxic element
- Melting point is 860K
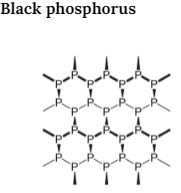
Black phosphorus exists in two forms i.e. α-black and β-black. An α-black form of Black phosphorus is formed When red phosphorus is heated at 803K in a sealed tube. It can be elevated in the air and has opaque monoclinic or rhombohedral crystals. It does not oxidize in the air. β-Black form of Black phosphorus is formed when a white form is heated under high pressure at 473 K. It does not burn in the air up to 673K.
Properties of Black phosphorus
- It is black in colour and poses a black metallic lustre.
- The melting point is about 860 K.
- It is present in both amorphous and crystalline forms.
- Black phosphorus has a specific gravity of 2.69.
Conclusion
Reference to the above notes, it is clear that phosphorus is one of the important topics of physical chemistry. It exists in three forms: White, Black, and Red. It has versatile applications and uses in our day-to-day life. Here we also studied the various molecular structure, chemical reactions, and balance equations of this topic.
This section consists of the theory part and the difficulty level of the questions are low. Allotropic forms of phosphorus are one of the important topics. According to the new paper pattern, it is expected that 2-3 questions will be from this chapter. So, read all the notes thoroughly in order to secure full marks on this topic.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





