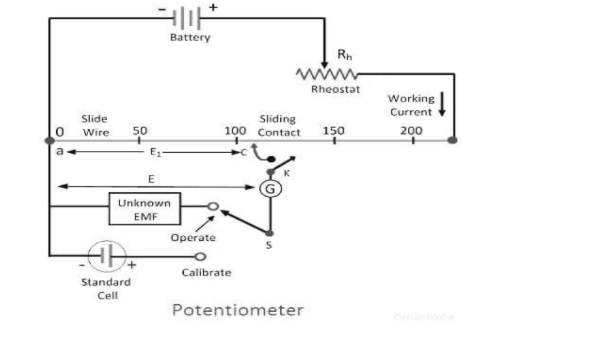
Potentiometer
A passive electronic component is known as a potentiometer. Across the whole length of the resistor in a potentiometer, the total input voltage is applied. The voltage drop between the sliding and fixed contact is the output voltage. The potentiometer is used for measuring displacement in any direction and is also used in electronic devices like sound systems for increasing or decreasing the volume.
Voltmeter
A voltmeter is based on the deflection method, voltmeter approximately measures the unknown emf. There is infinite resistance present in an ideal voltmeter, the reading of the voltmeter becomes more accurate as the resistance of the voltmeter increases. The resistance of the converted voltmeter is Rv = R + G. The voltmeters are designed in such a way that some can be used in Alternating Current (AC), some in Direct current (DC), and also in Radio Frequency (RD) but specialized voltmeters are used in this.
A diagram showing the flow of voltage
Potentiometer and Voltmeter: Detailing
For calculating the emf of a cell and for getting the accurate measurement of a potential difference the potentiometer is used. The potentiometer also acts as an ideal voltmeter; the internal resistance of a cell is also determined by the ideal voltmeter. The potentiometer has one variable terminal and two fixed terminals i.e. a potentiometer is made up of a total of three terminals. Both the ends of the resistive element that is known as the track is connected by the two fixed terminals of the potentiometer, and with the sliding wiper, the third terminal is connected. When the wiper moves over the resistive path, the resistance of the potentiometer gets changed. The resistance of the potentiometer varies when the wiper moves along the resistive element. The flow of electric current is controlled by decreasing or increasing the resistance of the potentiometer. When the resistance of the potentiometer is increased, a small amount of current is allowed to flow and a large amount of current is blocked. Whereas, when the resistance of the potentiometer is decreased, a small amount of electric current is blocked from flowing and a large amount of current is allowed to flow. Both the potentiometer and voltmeter are voltage measuring devices. Because of the high internal resistance of the voltmeter, the meter draws or extracts a small amount of current. The digital voltmeter and analogue voltmeter are the two types of voltmeter. On the internal resistance, the working principle of the voltmeter depends. The voltmeter is always connected parallel with the circuit. From the current that flows through the circuit and the product of the resistance, the value of the unknown voltage is known in an analogue voltmeter.
Potentiometer and Voltmeter: Differences
| Sl. No. | Potentiometer | Voltmeter |
| 1 | The potentiometer has high sensitivity | The voltmeter has low sensitivity |
| 2 | The resistance of the potentiometer becomes infinite while measuring the unknown potential difference | The resistance of the voltmeter becomes high but finite while measuring the unknown potential difference |
| 3 | The potentiometer accurately measures the unknown emf | Voltmeter approximately measures the unknown emf |
| 4 | From the emf source potentiometer does not draw any current | From the emf source voltmeter does draw current |
| 5 | A potentiometer is used for measuring various applications, some of them are – calibration of ammeter and voltmeter, comparison of EMFs, measurement of initial resistance of a cell, measurement of thermal emfs | Only emf and an unknown potential difference are measured by using a voltmeter |
| 6 | A potentiometer is based on the zero deflection method | A voltmeter is based on the deflection method |
| 7 | No current is drawn from the source, in a balanced position | While taking the reading, the current flows from the source |
| 8 | The potential difference or the emf measured by the potentiometer is equivalent or similar to the actual value | The potential difference measured by the voltmeter is always different from the actual value |
| 9 | The device of the potentiometer works on the principle of the Wheatstone bridge | The device of the voltmeter is generally based on the magnetic effect of current |
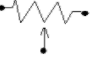
| 10 | The symbol of a potentiometer is | Symbol of a voltmeter is |
Conclusion
It is to conclude that the resistance of the potentiometer becomes infinite while measuring the unknown potential difference. The resistance of the voltmeter becomes high but finite while measuring the unknown potential difference.
The symbol of a potentiometer is
The symbol of a voltmeter is
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out