The total amount of power produced by an internal combustion engine’s cylinders during one full cycle due to combustion of fuel . It is the sum of an engine’s braking power and the power generated by friction within the engine.
IP=BP+FP
IP=Indicated power
BP= Brake power
FP= friction power
In a nutshell, it refers to the maximum power that can be extracted from the expanding gases produced by the combustion of fuel within the cylinder. This power is calculated without taking into account losses that occur as a result of friction, mechanical stress, or heat and enthalpy.
This means that this is the theoretical maximum and actual power developed within the cylinder, but it does not reach the crankshaft in its entirety.
Measuring Indicated Power
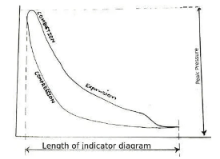
Utilizing either the indicator diagram or the power card diagram of an engine will allow you to accurately measure the indicated power of the engine. To evaluate the performance of an engine’s individual cylinder units, an indicator diagram must first be constructed.
Under different operating conditions, the power that is indicated for an engine can shift. Therefore, the indicator diagram for a particular cylinder or engine is taken at a specific frequency or RPM. The mechanical representation of this is then able to be as follows:
I.P= (100 k pm L A N)
_____________ KW
60
k equals the number of cylinders in the engine,
Mean effective pressure, expressed in bars as Pm
A equals the surface area of the piston measured in metres squared.
N equals the rotational speed, also known as the RPM speed, of the engine. (N=N for a two-stroke engine and N=N/2 for a four-stroke engine).
L = The distance travelled in metres per stroke,
Difference Between the Brake Power and the Indicated Power
The power that is indicated is the power that is developed in a cylinder by an engine, as was described above. It is equal to the sum of the power that is produced at the crankshaft as well as the power that is lost due to friction and heat.
A portion of this power is expended in order to overcome the friction that is caused by the many moving parts, and some of it is lost in the form of heat by the cylinder walls and the exhaust. The efficiency of the fuel-air mixture that was burned in that particular cylinder is used to calculate the indicated power.
On the other hand, the brake power refers to the power that is actually available at the crankshaft for the application.
When calculating the torque and angular velocity of the rotating output shaft at the manufacturing facility, large brake dynamo-meters or any other type of brake mechanism may be used.
These braking dynamometers are also separated into two primary types, known as absorption dynamometers and transmission dynamometers, according to the way in which they work.
Now, because the actual brake power is almost never the same as the indicated brake power. Mathematically speaking, you are able to say this because it is the result of taking the indicated power and subtracting the friction power. The mechanical representation of this is then able to be as follows:
Brake power = 2πNT/60 Watts
Where,
N = the speed of the engine in revolutions per minute
T equals the turning moment, which can also be calculated by multiplying W by L. Where W is the load on the brakes measured in newtons and L is the length of the arms measured in metres.
How the Measurement of Indicated Power Is Done on Marine Diesel Engines
In order to determine the indicated power output of a marine diesel engine for a unit, we must first obtain the indicator diagram for the unit. The next step is to compute the area of the curve diagram that has been provided.
An indicator instrument is a specialised piece of equipment that is used on ships for the purpose of recording an indicator diagram. Which consists of a miniature piston that is contained within a cylinder and is forced to move against the resistance of a calibrated spring.
The instrument can be used to draw all of the major types of indicator diagrams that are employed in the process of analysing and correcting engine parameters.
The total power generated by the engine can then be calculated using this information, as well as the compression pressure, peak pressure, and overall efficiency of the engine. In a similar manner, any deviation in the diagram helps us know of any irregularity in the fuel injection process and the conditions of the running gears.
In order to measure, the indicator instrument is positioned so that its drum is in phase with the movement of the piston. This is done by placing the instrument on the indicator cock. Concerning the movement of the piston, the P-V diagram, also known as the Indicator Diagram, depicts the fluctuation of the cylinder’s pressure.
The area of the diagram is determined by first measuring it with a planimeter or platometer, which is followed by the multiplication of the cylinder constant and the speed of the engine.
Conclusion
The total amount of power produced by an internal combustion engine’s cylinders during one full cycle is subtracted from the total amount of power indicated by the engine. It is the total of an engine’s braking power and the power generated by friction within the engine.In a nutshell, it refers to the maximum power that can be extracted from the expanding gases produced by the combustion of fuel within the cylinder.Utilizing either the indicator diagram or the power card diagram of an engine will allow you to accurately measure the indicated power of the engine. To evaluate the performance of an engine’s individual cylinder units, an indicator diagram must first be constructed.When calculating the torque and angular velocity of the rotating output shaft at the manufacturing facility, large brake dynamo-meters or any other type of brake mechanism may be used.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out