When air that is at a specific dry bulb and dew point (DP) temperature is cooled below the dew point temperature, a cooling and dehumidification process is obtained.
As soon as the air gets into contact with the cooling coil, which is kept at a temperature that is lower than the air’s dew point temperature, the air’s DB temperature begins to decrease. The process of cooling continues, and at some point it approaches the value of the temperature at which the dew point of the air is reached. Because of this, dew will form on the surface of the coil, and the moisture content of the air will decrease, which will cause the humidity level to decrease as well.
At this time, the water vapour that is already present in the air will begin to transform into the dew particles. Therefore, when air is cooled below the temperature at which it would start to condense, there occurs both cooling and dehumidification of the air.
Application of Cooling and Dehumidification
The process of cooling and dehumidification is the air conditioning application that sees the most widespread use. The cooling coil in central air conditioning systems is cooled by either the refrigerant or the chilled water.
The air in the room is cooled and its humidity is removed whenever it travels over this coil. The cooling and dehumidification process is often obtained by passing the air over the coil through which the cool refrigerant, chilled water, or cooled gas is passed. This causes the air to flow through the coil at a lower temperature. During the process of cooling and dehumidifying the air, the temperature of the dry bulb, the wet bulb, and the dew point all fall to lower values.
In a similar fashion, both the sensible heat and the latent heat of the air will lose some of their intensity, which will ultimately result in a lower overall enthalpy for the air. On the psychrometric chart, the process of cooling and dehumidification is depicted as a straight angular line. The value of the DB temperature is used as the starting point for the line, which then continues downward and to the left.
The Process of Dehumidification
A dehumidifier is a piece of air conditioning equipment that lowers and keeps the level of humidity in the air at a consistent level.
This is done for a variety of purposes, the most common of which are to improve health and thermal comfort, get rid of musty odours, and stop the growth of mildew by collecting water from the air. It is applicable in a variety of settings, including households, businesses, and even factories.
In commercial structures such as indoor ice rinks and swimming pools, as well as industrial factories and storage warehouses, large dehumidifiers are utilised. Standard air conditioning systems dehumidify the air while also cooling it.
This is accomplished by operating the cooling coils at temperatures lower than the dewpoint and then draining away the water that condenses on them. The method of dehumidification, in which heat is produced instead of water, is analogous to the opposite of adding water to the space using an evaporative cooler. Because of this, a dehumidifier installed in a room will constantly warm the space and lower the relative humidity indirectly. Additionally, it will reduce the humidity more directly by condensing and removing water from the air.
Relative Humidity During Sensible Cooling
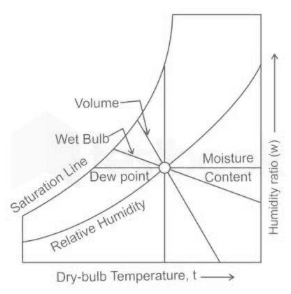
The psychrometric chart has lines that are vertical, which represent the dry bulb temperatures, lines that are diagonal, which indicate the wet bulb temperatures, and lines that are curved, which show the relative humidity.
The actual temperature of the gas or gas combination is referred to as the dry bulb temperature. The temperature read off of an accurate thermometer that has a wick that has been dipped in distilled water is referred to as the wet bulb temperature.
The dew point temperature is the temperature at which liquid droplets begin to form when moist air is constantly cooled below a certain threshold. Along the saturation line, the relative humidity is always one hundred percent. If the relative humidity cannot shift in response to changes in temperature, then the specific humidity of the environment cannot be held constant. If the air is saturated, then its relative humidity is at 100 percent, which indicates that it is unable to absorb any more moisture. As a result, if the air is forced to pass over water, it will not absorb any of the water’s moisture, and as a result, the air’s temperature will not change. When air is said to be saturated, the temperature of the dry bulb, the temperature of the wet bulb, and the dew point temperature are all the same. When there is sensible heating, the relative humidity of the air lowers, and when in a sensible cooling process the relative humidity of the air increases.
Conclusion
Dehumidifiers function by removing moisture from the air that is circulated through the device. Condensate dehumidifiers and desiccant dehumidifiers are the two most popular varieties of dehumidifiers, however there are many additional dehumidifier designs that are currently being developed. Condensate dehumidifiers employ a refrigeration cycle to collect water known as condensate,
which is typically regarded as greywater but may at times be reused for industrial purposes. Condensate is collected by the unit after it has been exposed to low temperatures. Condensate can be turned into drinkable water by using a reverse osmosis filter, which is offered by some manufacturers.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




