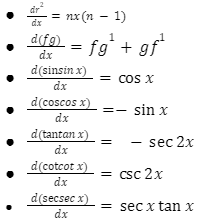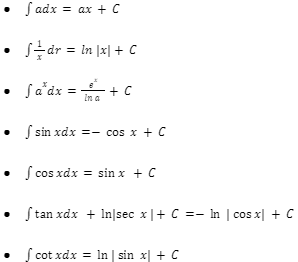Calculus is a branch of mathematics that deals with continuous change and is one of the most significant branches of mathematics. Calculus is built around two major concepts: derivatives and integrals.
The derivative of a function is used to calculate its rate of change, while the integral is used to calculate the area under the curve. The integral collects the discrete values of a function over a range of values, but the derivative gives the explanation of the function at a given point.
Calculus is also known as infinite calculus or “the calculus of infinitesimals. “Infinitesimal numbers are numbers with a value that is close to zero but not precisely zero.
Calculus definition
Calculus is a mathematical concept that is commonly utilized in mathematical models to get optimal solutions and so aids in comprehending the changes in the values of a function.
Calculus classification
Calculus is divided into two sections:
Differential Calculus
Integral Calculus
1. Differential Calculus
The method of differentiation is used in differential calculus to calculate the derivative of a function. The rate of change of a function near a certain value is given by the derivative of the function at that value. The slope of a tangent to a function’s graph is measured using a derivative.
The maxima and minima values of a function are calculated using derivatives to determine the best solution. Differential aids in the investigation of a quotient’s limit, dealing with variables such as x and y, functions f(x), and changes in the variables x and y. Differentials are denoted by the letters dy and dx. Differentiation is the method used to find the derivatives dy/dx or f'(x). represents the derivative of a function, y, with respect to variable x.
Here are some calculus formulas for finding a function’s derivative. Here are some calculus formulas for finding a function’s derivative.
2. Integral Calculus
The anti-derivatives of a function are found using integral calculus. The integrals of the function are sometimes known as anti-derivatives. Integrating a function is the process of determining its anti-derivative.
The study of integrals and their properties is known as integral calculus. It can be used to calculate f from f’ (from its derivative). If a function, such as f, can be differentiated in any interval, then f’ can be defined in that interval. for any function, and determining the area under a curve.
Integral calculus has two types:
Definite Integrals: The integrals have definite values.
Indefinite Integrals : The value of the integral is indefinite with an arbitrary constant, C
Here are a few formulas for calculating the integral of a function.
Calculus’s Applications
Studying a system in order to identify the best answer for predicting the future of any given function condition.
Calculus concepts are important in everyday life, whether it’s for solving the area of intricate shapes, assessing survey data, automobile safety, For instance, consider company planning, credit card payment data, or determining the changing conditions of a system that affect us.
Calculus is used by economists, biologists, architects, medical specialists, and statisticians. To estimate the size and geometry of construction structures, architects and engineers, for example, use different calculus theories.
Calculus is used to mimic a variety of things, including birth and death rates, radioactive decay, reaction rates, heat and light, motion, and electricity.
Conclusion
In this article we conclude that, Calculus concepts are important in everyday life, whether it’s for solving the area of intricate shapes, assessing survey data, automobile safety, company planning, credit card payment records, or determining the changing conditions of a system that influence us, for example. Calculus is used by economics, engineers, designers, medical specialists, and statisticians. To estimate the size and geometry of construction structures, architects and engineers, for example, use different calculus theories.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out