Correlation Coefficient Formula:
- The correlation coefficient is a statistical measure of the strength of the relationship between the relative moments of two variables. The values range between -1.0 and 1.0. A calculated number greater than 1.0 or less than -1.0 means that there was an error in the correlation measurement.
- Correlation coefficients are used to measure how strong a relationship is between two variables. There are several types of correlation coefficient, but the most popular is Pearson’s. Pearson’s correlation (also called Pearson’s R) is a correlation coefficient commonly used in linear regression.
- A correlation coefficient zero means that for every positive increase in one variable, there is a positive increase of a fixed proportion in the other.
- A correlation coefficient of -1 means that for every positive increase in one variable, there is a negative decrease of a fixed proportion in the other.
- Zero means that for every increase, there isn’t a positive or negative increase. The two just aren’t related. The absolute value of the correlation coefficient gives us the relationship strength. The larger the number, the stronger the relationship.
- The coefficient of correlation is a pure number without the effect of any units on it. It also does not get affected when we add the same number to all the values of one variable.
- We are correlating for measuring the association, we simply mean that when we are correlating the two variables, then there might be the possibility that the third variable may be influencing them. The strength of the relationship varies in degree based on the value of the correlation coefficient.
Formula for Correlation Coefficient
Population correlation coefficient
ρxy =Ϭxy/Ϭx Ϭy
where, Ϭx, Ϭy = population standard Deviation
Ϭxy = population covariance.
Sample correlation coefficient between x and y
γxy =Sxy/ Sx Sy
where, Sx Sy = sample standard Deviation
Sxy = sample covariance
How to find correlation coefficient:
Correlation is used almost everywhere in statistics. It is expressed in the form of a number that is known as the correlation coefficient. There are mainly two types of correlation.
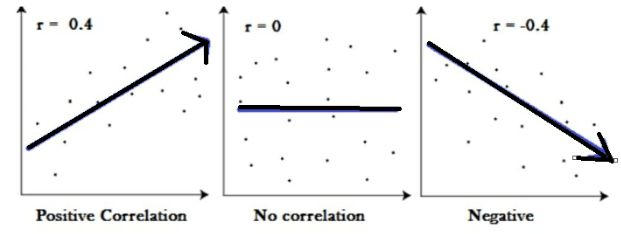
- Positive Correlation
- Negative Correlation
Correlation Coefficient Properties:
The correlation coefficient is all about establishing relationships between two variables. Some properties of correlation coefficient are as follows.
- Correlation coefficient remains in the same measurement as in which the two variables are.
- The sign of the correlation coefficient has to always be the same as the variance.
- The numerical value of correlation coefficient will be between -1 to +1 It is known as the real number value.
- The negative value of the coefficient suggests that the correlation is strong and negative and if r goes approaching -1 then it means that the relationship is going towards the negative side. When ‘r’ approaches the side of +1 then it means the relationship is strong and positive. By this we can say that if +1 is the result of the correlation then the relationship is in a positive state.
- The weak correlation is signed when the coefficient of correlation approaches zero when ‘r’ is near about zero then we can deduce that the relationship is weak.
- Correlation coefficient can be very dicey because we cannot say whether the participants are truthful or not. The coefficient of correlation is not affected when we interchange the two variables. The correlation coefficient is not affected when we interchange the two variables.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




