A right circular workpiece would be a three-dimensional physical block of two equal bases connected by a complete circular surface, each of which has a round disk shape. The vector of the appropriate cylinder would be a line that runs through the middle or connects the locations of two circular foundations. The height “h” represents the gap between two-cylinder foundations, known as a perpendicular line. The radius of such a right rectangular channel, denoted by “r”, would be the distance between the base and the outer limit of one of the other two bases. As a result, contour lines and a rectangle combine to produce a right circular cylinder.
Right Circular Cylinder Definition
We can make the correct round cylinder by stacking a few circular pieces of paper together. It is a rotational symmetry cylinder, even though it’s kept perpendicular to the circular basis. A rotational symmetry cylinder is a three-dimensional geometry having circular extremities. The circular foundations are aligned to one another and have the same diameter. The endpoints on the circle base are at a specified interval from the cylinder’s shaft, which is a straight line. The most frequent geometric form is the circular cross-section cylinder. A cylinder can be called a right-angled cylinder when the segment connecting the centres of the rounds is horizontal toward the surfaces of the foundations. For example, a beverage container, a gas cylinder, etc.
Another sort of cylinder would be the oblique cylinder, which has no equal bases and looks like a diagonal building.
Parts of Right Circular Cylinder:
The circular base at the top
The lateral face is curved.
Circular face at the bottom
Right Circular Cylinder Properties
The properties of the right circular cylinder, like those of every other three-dimensional form, are as follows:
This object has two rounded edges, one particular form, and two rotating faces.
Cylindrical components are always compatible with one another.
The size of the cylinder is determined by the radius of the base and the thickness of the cylinder.
With the grounds perfectly above each other, the shaft makes a straight angle with them.
The foundation and top of the cylinder are similar to one another.
Right Circular Cylinder Formula
The following are some properties of right circular cylinder formulas:
A right circular cylinder’s foundation refers to each of the cylinder’s spherical ends.
The vector of the proper rectangular channel is a vertical line that connects the centres of different geometric bottoms and is parallel to the foundation of the right cylinder.
The radius of the circular bottom is known as the radius. The tube’s elevation is defined as the measure of the movement of the piston. The elevation of the appropriate circular pipe is the angular displacement in between circular foundations.
The lateral aspect is the curved region between two levels of a straight, circular tube that connects them.
The right circular cylinder’s physical properties are measured in physical metres for both effects of surface sections (m2, cm2, in2, or ft2).
A right-angle cylinder’s outer layer is considered an area occupied by the cylinder’s perimeter. A right circular hemisphere has two kinds of external areas:
A cylindrical-shaped engine nacelle contact surface region, also known as the lateral contact area of such a right cylinder. It would be the region between matching round bottoms of the straight, circular tube encompassed by the curving cylinder surface.
A right circular cylinder’s volume fraction, an area filled by the complete cylinder. Two circles plus a lower surface make up this section of the cylinder. As a result, while calculating the overall permeability of the straight, circular tube, one must add the regions of two circles and the different shapes at the end.
Here are the formulas of a Right Circular Cylinder:
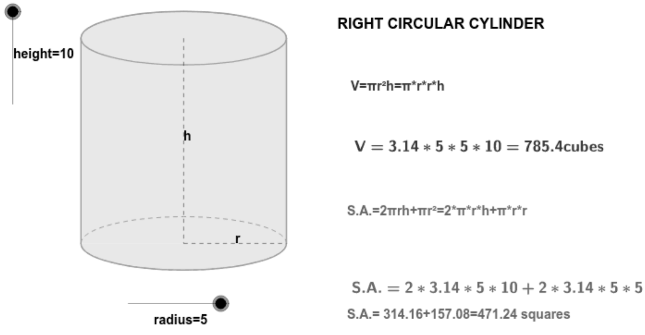
Volume
The combination of either of the regions of the upper and lower circular pattern and the cylinder’s elevation gives the capacity of the right rectangular channel. Cubic units are used to measure the quantity of the right rectangular channel. The quantity of a straight, circular cylinder gets calculated using the formula.
Right Circular Cylinder Volume(V) = Location of the Circular Foundation the Right Cylinder’s Elevation
Formula for Volume, Curved Surface Area and Total Surface Area
Volume: The volume of the cylinder can be measured using the formula πr2h, where r = d/2.
Curved surface area: The curved surface area of a hemisphere(CSA) = ½ (curved surface area of a sphere) = ½ (4 π r2) = 2 π r2 , where “r” is the radius of the hemisphere.
Total surface area: Total surface area of cylinder =2πr(r+h) sq. units.
Conclusion
A cylinder would be a prism-shaped material with round foundations. A cylinder can be called a right-angled cylinder when the segment connecting the centres of the rounds is horizontal toward the surfaces of the foundations. A cylinder would be a prism-shaped material with round bottoms. A complete three-dimensional figure would be a circular cross-section cylinder. It could be a cylinder, including a complete circular area on both extremities and two parallel supports. Surface energy and capacity are the two important features of the correct cylinder. Essentially, the proper cylinder can be used to get the formulae for the greater surface area of the cylinders. In three dimensions, an oblique tube is one in which the foundations of the cylinders are not perpendicular to one another.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






