The consumption and production activities that take place in a country, that seeks efficiency and proper allocation of resources that will benefit the public as a whole, is commonly known as the Economy. In addition to consumption and production, the economy also includes and is responsible for the trading business- imports and exports, foreign exchange, Market stability, Labour market, Money Market, and other services within and outside the country. It can be said that economy is a term, which is synonymous with Economic System.
Adam Smith gave all the basic economic laws and ideals; modern economics is based on. In his famous book, “The Wealth of Nations”, he defined economics. Therefore, the definition of economics by Adam Smith is that it is the science of wealth that aims at studying the process of consumption, production, and building-up of Wealth.
Let us look at the types of economies, in addition to the types of economic examples.
Types of Economies
This economic system is segregated into two types, based on its openness. An open economy is an economy that involves itself with other foreign nations. Therefore, open economy example includes India, the USA, etc. Close economy is that economy that considers itself to be self-sufficient and does not get involved with foreign nations. There is no closed economy; therefore, there is no closed economy example.
It must be noted that the economic system also includes the question of whether the distribution of resources, in addition to the services and goods, is done properly. To make this distribution easier, the government takes up four types of economic systems. These include-
- Socialist system: These systems have a centralised system, where the wealth and the economy are strictly maintained by the state. A Socialist economy example is North Korea.
- Capitalist System: This system includes government interference with restrictions. This system incorporates the principle and ideals of the Free Market within it. The supply and demand in the economy are regulated by the Market forces. The capitalist economy example is the UK.
- Traditional system: This system relies on the cultural and traditional values of the respective state. These systems are likely to be found in rural areas or countries that are developing based on farming and agriculture.
- Mixed System: This system of economy is the blend of both Socialist and capitalist systems. A mixed economy example is India.
Keynesian Theory
Keynesian theory is one most sought out and famous economic theories in the consumption function. This theory was given by John Keynes. In the “General Theory”- published in the year 1936- Keynes laid the foundation of modern macroeconomics. His theory of the economy deals with the aggregate demand of the economy; in addition to its impact on the output and the inflation level in the economy. He gave the theory or thesis of income and employment, business cycle, and Money theory.
According to Keynes, the income level determines the consumption of each societal member. Keynes emphasized on the overall size of the income as a indicator of consumption. The theory of consumption is commonly known as absolute income theory. His theory explains the deviation in an individual’s consumption due to a change in his level of income.
About the consumption behaviour, Keynes makes two comments:
- Keynes suggests that the expenditure on consumption depends primarily on the absolute income of the current period, which means, consumption is a positive function concerning the absolute level of current income. The more the income, the more is the consumption expenditure.
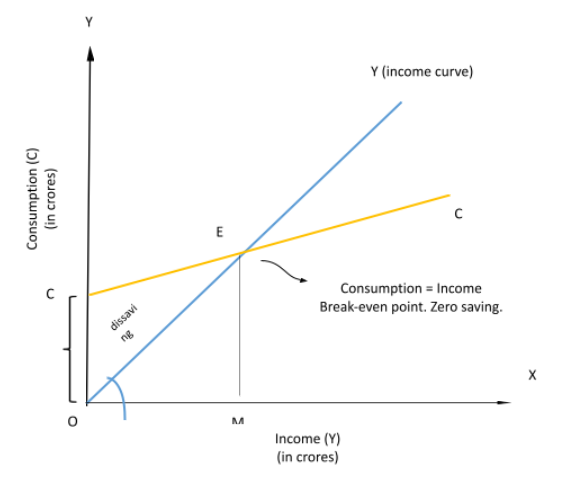
- Keynes points out that the expenditure on consumption does not have a proportional relationship with the income. With an increment in income, the consumption also increases but the proportion is different. The proportion to income is called Average tendency to consume. Keynes argues that the average tendency to consume falls as income increases. The Keynes consumption function can be expressed as follows-
C = m + n Y;
In the above equation,
- C = consumption expenditure
- Y = National income (excluding the taxes)
- ‘m’ and ‘n’ are constants.
Keynesian theory can be showed through the following figure, which includes the income and consumption curve-
Conclusion
The consumption and production activities that take place in a country, that seeks efficiency and proper allocation of resources that will benefit the public as a whole, is commonly known as the Economy. The definition of economics by Adam Smith is that it is the science of wealth that aims at studying the process of consumption, production, and building-up of Wealth. Keynesian theory is one most sought out and famous economic theories in the consumption function. This theory was given by John Keynes. He gave the thesis of income and employment, business cycle, and Money theory.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




