Important Facts About Some Metals
The surroundings around us are made up of different elements, compounds, or mixtures. Elements are substances whose molecules are made up of identical atoms. Scientists classified elements further into three types:
- Metals
- Non-Metals
- Metalloids
In this article, we will learn about some important and interesting facts about metals and their physical and chemical properties, along with their types and uses.
What are Metals?
Metals are naturally occurring substances found beneath the Earth’s surface. They are lustrous and good heat conductors. A metal is a material found naturally under the surface of the Earth. They are classified into different forms and types. They are hard and wire and can be formed into sheets. Metals lose valence electrons to form positively charged ions or cations. Gold, silver, iron, copper, aluminium, magnesium, calcium, sodium, and platinum are a few examples of metals.
Physical Properties of Metals
Hardness
Metal is hard. It is not the case with potassium and sodium. They both are delicate and can be easily cut with the help of a knife or blade.
Sonority
Metals tend to produce sounds when they get striked. They are sonorous.
Malleability
The property of metals can be battered into thin sheets. This is termed or referred to as malleability.
Ductility
Metal has a ductile property. A wire is formed when it is pulled via a hole.
Density
Metals are rich in high density. However, lithium, Potassium and Sodium have a lower density compared to water. Hence, they are considered as an exception.
Physical State
Under ordinary temperatures, metals tend to remain solid. But, it is not the same with gallium and mercury. They are in a liquid state in the room or at normal temperature.
Conductors of Electricity
A metal is a good conductor of electricity. However, in this case, Lead is an exception. It is neither a good conductor of electricity nor heat.
Lustre
Newly cut or cleaned metals mirror rich light without sparkling and the metals look radiant.
Conduction of Heat
A metal is a good conductor of heat. Aluminium, Copper and silver are bad conductors of heat.
Melting point and Boiling point
Metals have a high melting point and boiling point except for metals like sodium, potassium, mercury, and gallium.
Chemical Properties of Metals
- Electronic configuration
The electronic configuration is the basis of the chemical behaviour of elements. For example, most metals have up to three electrons on their furthest shell.
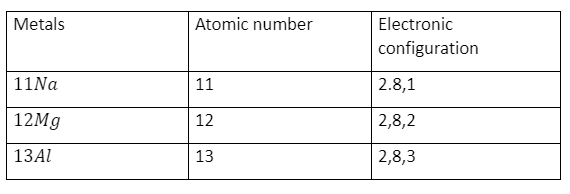
Formation of ions
Metals have a tendency to lose their valence electrons to form positively charged ions, that is, cations.
Na →Na+ + e-
(2,8,1) (2,8)
Sodium Sodium ion
Mg → Mg+++ 2e-
(2,8,2) (2,8)
Magnesium Magnesium ion
Al→ Al+++ + 3e-
(2,8,3) (2,8)
Aluminium Aluminium ion
Reaction with oxygen
Metals combine with oxygen to combine oxides.
Metals + Oxygen ———-> Metal Oxide
The metal oxides are basic in nature. Metal oxides react with an acid to form salt and water.
Metals oxide + Acid ———–> Salt + Water
Reaction with acid
Most of the metals react with dilute acids to form metal salts while hydrogen gas is released.
Metal + dilute Acid ————–> Salt + Hydrogen gas
Reaction with water
Most metals have no observable and rapid reaction with cold water. However, some metals, such as sodium and potassium, react with cold water to produce hydroxides and hydrogen gas. Similar reactions require steam in the case of magnesium metals.
Types of Metals
- Precious metals: Precious metals include gold, silver, platinum, and diamond and are traded worldwide. They are used to make everything from ornaments to electronic devices.
- Uncommon earth metals: These aren’t particularly interesting, but their extraction is confusing and difficult. The periodic table includes scandium, yttrium, lanthanum, and the 14 components (lanthanides) that follow lanthanum.
- Alloys are created by combining at least two metallic components to create new substances with unique chemical and physical properties.
Uses of Metals
- Because of their conductivity and low resistance, metals make electric wires. Copper and aluminium are two examples of such metals.
- A few metals are used as household utensils or manufacturing plant hardware for legitimate hotness transfer. Iron, aluminium, and Copper are examples of such metals.
- One vital and hazardous metal found in our clinical pack is mercury which is utilised in thermometers.
- Zinc is used to protect the iron from rusting, which is extremely common in iron because it rusts in the presence of oxygen and dampness. The Galvanization cycle refers to the process of applying the Zinc layer.
- Vehicle batteries are made of Lead which is a metal.
- A few rare accessible metals, for example, gold and silver, are used to make adornments; occasionally, extremely thin sheets of gold and silver are used to keep on top of desserts.
- Chromium and nickel are utilised in treated steel.
- Chromium and nickel are likewise utilised in the process known as Electroplating.
- Zirconium is used in the manufacture of indestructible preparations.
Since metals are bendable, aluminium is extremely well known for shaping exceptionally thin sheets. It is used for bundling.
Conclusion:
Metals are formed naturally beneath the Earth’s surface. They are lustrous and have excellent heat and electricity conductors. Metals are lustrous. They have a high degree of malleability and ductility. Metals have numerous applications and are used all over the world.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




