The periodic table was introduced in the late 18th century by renowned chemist and inventor, Dmitri Mendeleev. He is regarded as the father of the periodic table. Initially, the periodic table was created without any classification or groups. It had elements displayed from left to right in an increasing number of their atomic weight. The modern periodic table based on this observation was divided into multiple groups and classified according to their atomic number.
Periodicity in properties of elements
Periodicity is defined by similar properties of elements in order of increasing atomic number. The different groups available on the periodic table are created based on periodicity. This helps scientists in understanding the different types of elements and the similarity in their nature. This also creates gaps in the table that can be filled with new elements whenever discovered as per the atomic properties. The properties of elements are determined by factors like how easily an electron can be separated from an atom, the bonding power of any given element, the measurement of atomic radius in an element and the attraction of an atom towards an electron from a different element. The different forms of energy in elements are classified as moving from left to right in increasing order of strength towards that energy. At the same time, the energy flow decreases when measured from top to bottom.
Lanthanoids and Actinoids
Apart from the periods and groups defined in the periodic table, there are two separate classes of elements available in a different table as they have similar properties however, are exceptions to the flow of atomic number. Lanthanoids do not form bonds easily and are non-radioactive. Actinides are radioactive with an affinity for bonds.
The Classification of elements in the periodic table
The different groups of elements are mentioned below:
- Alkali Metals
- Alkaline Earth Metals
- Boron Family
- Carbon Family
- Pnicogens
- Chalcogens
- Halogens
- Zero group
Elements are classified into different groups based on their atomic number or in other words, by the number of electrons in their atomic structure. This is the basis of if an element is a metal or something else.
A brief understanding of the periodic table elements
The modern periodic table was the first insight received into the compound capabilities of elements and periodic table elements have helped in the broader understanding of chemistry thanks to this arrangement. The diagram below will help us in understanding it better.
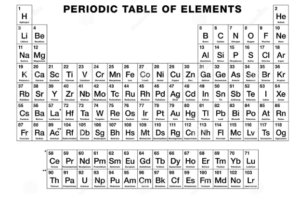
- Alkali metals – This group of elements display the properties of metals, with the distinction of being extremely soluble. It has a neutralising effect when mixed with acids and has caustic, corrosive characteristics.
- Alkaline earth metals – All elements displaying the normal metallic properties are alkaline earth metals. They are good conductors of electricity and can hold their density in extreme conditions.
- Boron Family – These are metalloids. These elements display properties of trace minerals and can help with regenerative assistance in the human body.
- Carbon Family – These elements can hold up to four electrons which makes them great in forming covalent bonds. This property is known as being tetravalent.
- Pnicogens – This is a family of rare elements that is harmful to the human body if consumed directly. This is made up of elements like nitrogen, arsenic, bismuth and phosphorus.
- Chalcogens – Oxygen and similar elements form up this group. They contain both metallic and non-metallic properties.
- Halogens – This group of reactive non metals heat up to provide a source of light.
- Zero group – These are inert gases like helium and argon and are extremely non-reactive and rare in nature.
The classification of elements and periodicity in properties of the modern periodic table differ in variations of usage. There is a scope for definition as transitive and non-transitive elements. Also, differentiated on the basis of their natural state of gas, liquid or solid at room temperature and can also be given meaning in terms of their physical characteristics. How each element looks in its raw form is its own compositional classification. Also, as discussed earlier, the lanthanoids and actinoids are completely different in their classification and don’t fit the normal groups.
Conclusion
There is scope for the discovery of more elements in the future due to the invention of particle accelerators and fission experiments. Scientists have been creating “man-made” elements since the early nineties. Thanks to the property of the periodic table to be able to include more elements as they are found, the scientific world can look forward to an improved and tremendously exciting modern periodic table in the times to come.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




