Which Is the Non- Benzenoid Aromatic Compound?
A.Benzene
B.Pyridine
C.Toluene
D.Phenol
Answer:- (B) Pyridine
Explanation- Unsaturated hydrocarbons with a ring structure displaying particular features, such as an extraordinary degree of stability, are aromatic compounds. The majority of aromatic chemicals have benzene rings or structures similar to them. Aromatic substances can also show aromatic qualities. Resonance structures, which may contain either single or double bonds, are frequently used to depict these molecules.
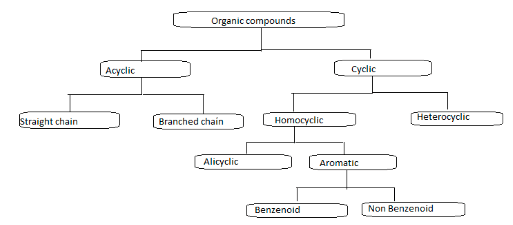
Several general requirements must be satisfied for a molecule to be considered aromatic.
To be considered aromatic, a molecule must have a planar cyclic structure.
Aromatic rings are required only to include atoms capable of sp2 hybridization and can create a delocalized system of pi molecular orbitals.
The Huckel rule mandates that aromatic compounds adhere to it, which stipulates that the number of pi electrons in a delocalized system must be equal to 4n + 2, where n is an integer. This rule must be adhered to by aromatic compounds.
For a chemical to be classified as an aromatic compound, it must adhere to the guidelines outlined above. When we examine flow charts, aromatic chemicals are often classified as either benzenoid or non-benzenoid compounds. [citation needed]
As we have previously learned, Benzenoid and non-benzenoid aromatic compounds are the two primary classifications of aromatic compounds.
Benzenoid compounds are aromatic compounds with at least one benzene ring present in their chemical structure. These molecules are classified as benzenoid compounds.
It is possible to identify it based on the presence of one or more fused or isolated benzene rings within the molecule’s structure.
Benzenoid compounds are subdivided into monocyclic, bicyclic, and tricyclic categories according to the number of benzene rings connected within their structures.
Non-benzenoid compounds are aromatic compounds with conjugated systems with planar cyclic structures that lack benzene rings. Heterocycles, including nitrogen, oxygen, and other elements, can also be aromatic and have a non-benzenoid structure.
When comparing the chemicals phenol, pyridine, benzene, and toluene, the one with a non-benzenoid structure is pyridine.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






