Answer: The mass of one mole of a compound and the number of grams per mole of a compound is defined by its molar mass. To put it another way, the molar mass is the total mass in grams of all the atoms that make up a mole of a specific molecule. The molar mass is a mass property of a substance, not a molecular property. The molecular mass is usually expressed in grams per mole.
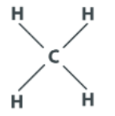
Methane has the chemical formula CH4 indicating that between the C and H atoms, there are a total of four bonds. Its structure is:
The steps to be followed to find Methane’s molar mass are:
- Methane’s molecular formula is CH4 according to which we can find the number of atoms in a molecule.
- Next, using the mass of carbon, and hydrogen given in the Periodic Table, calculate the atomic mass of each element.
- Then, multiply the subscript representing the number of atoms by the atomic mass of hydrogen.
- Add the atomic masses of all the atoms in the molecule to get the molar mass.
Thus, when the atomic masses of carbon and hydrogen are rounded to four significant figures, the molar mass will be:
CH4=( Atomic mass of C)+4( Atomic mass of H)
CH4=(12.01)+4(1.008)
CH4=16.042g/mol .
Some applications of methane are:
- Methane is utilized as a fuel in autos, furnaces, and water heaters since it is an energy powerhouse.
- Used to generate energy, which is a common application.
- As a rocket fuel when processed into a liquid state.
- As an antifreeze element in industry.
- As a fertilizer.
- Methane is present in several sanitization products.
- In the testing of gas appliances, methane is employed.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out