Answer:
Create a molecular orbital diagram (MOT) by connecting the atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals. The MOT diagram is filled with the total electrons associated with the molecules.
The molecular orbital arrangement must be written to answer this query. To determine the bond order using the molecular orbital arrangement, follow these steps:
Bond order =1 / 2[ Bonding – antibonding ]
Let’s start with the oxygen molecule’s MOT. The 16 electrons are found in the oxygen molecule O2. The results of the MOT are as follows:
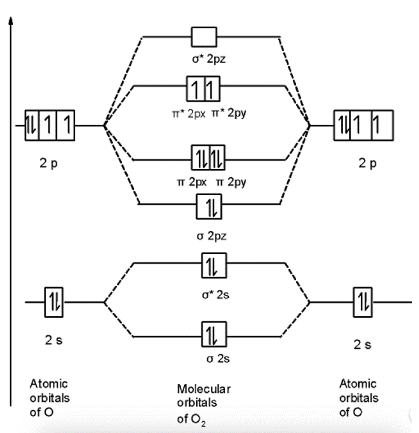
To begin, we can write the molecule’s molecular orbital arrangement. A total of 16 electrons make up an O2 molecule. The molecule O2 has the following molecular orbital configuration:
σ1 s²,*1 s²,σ² s²,*2 s²,σ²pz²,2px²π=2py²π,2px¹*=2py¹*
There are 10 bonding and 6 nonbonding electrons in the orbitals according to the molecular orbital configuration.
According to the molecular orbital configuration, there are 10 bonding and 6 nonbonding electrons in the orbitals.
Therefore, Bond order =1 / 2[ Bonding-antibonding ]
=1 / 2[10-6]=1 / 2(4)= 2
As a result, the bond order of =1 / 2[10-6]=1 / 2(4)=2 is 2.
Similarly for others,
For O2+molecule, an electron is removed from * 2py orbital.
Bond order = 10 – 5 / 2 = 2.5
For O2+ molecule, an electron is added toπ *π2px¹
orbital.
∴ Bond order =10-7 / 2=1.5
For O22- molecule, two electrons are added to π2px¹
and *2py1 orbitals.
∴ Bond order =10-8 / 2=1
So, the order is:
O22-< O2– < O2< O2+ .
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out



